Na+ - cloudfront.net
... one neuron to the next? What feature of the NS allows your body to rapidly respond to the environment? What 3 neurons are involved in the process from #7 above? What is an action potential? What is the name of the chemical that is released from synaptic terminals of neurons? ...
... one neuron to the next? What feature of the NS allows your body to rapidly respond to the environment? What 3 neurons are involved in the process from #7 above? What is an action potential? What is the name of the chemical that is released from synaptic terminals of neurons? ...
Glial cell - TheTruthAboutStuff.com
... Astrocytes signal each other using calcium. The gap junctions (also known as electrical synapses) between astrocytes allow the messenger molecule 1P3 to diffuse from one astrocyte to another. 1P3 activates calcium channels on cellular organelles, releasing calcium into the cytoplasm. This calcium ma ...
... Astrocytes signal each other using calcium. The gap junctions (also known as electrical synapses) between astrocytes allow the messenger molecule 1P3 to diffuse from one astrocyte to another. 1P3 activates calcium channels on cellular organelles, releasing calcium into the cytoplasm. This calcium ma ...
glossary of terms
... Kinesphere (reach space): “the sphere around the body whose periphery can be reached by easily extended limbs without stepping away from that place which is the point of support when standing on on ...
... Kinesphere (reach space): “the sphere around the body whose periphery can be reached by easily extended limbs without stepping away from that place which is the point of support when standing on on ...
Review Historical aspects of the anatomy of the reticular formation
... olivary bodies and the midbrain, which Bechterew named the central tegmental tract. This author also identified nuclei in the pontine reticular formation, including the nucleus of Roller. Fibres from the lateral and posterior grey columns terminate in these nuclei. According to Bechterew, the most i ...
... olivary bodies and the midbrain, which Bechterew named the central tegmental tract. This author also identified nuclei in the pontine reticular formation, including the nucleus of Roller. Fibres from the lateral and posterior grey columns terminate in these nuclei. According to Bechterew, the most i ...
Spinal nerves
... Blood Supply to Brain • Arterial blood supply is branches from circle of Willis on base of brain • Vessels on surface of brain----penetrate tissue • Uses 20% of our bodies oxygen & glucose needs – blood flow to an area increases with activity in that area – deprivation of O2 for 4 min does permanen ...
... Blood Supply to Brain • Arterial blood supply is branches from circle of Willis on base of brain • Vessels on surface of brain----penetrate tissue • Uses 20% of our bodies oxygen & glucose needs – blood flow to an area increases with activity in that area – deprivation of O2 for 4 min does permanen ...
The Science of Psychology
... Structures that control emotion, learning, memory, motivation Parts of cortex controlling senses and movement Parts of cortex responsible for higher forms of thought Differences between left side and right side of the brain How hormones interact with nervous system and affect behavior ...
... Structures that control emotion, learning, memory, motivation Parts of cortex controlling senses and movement Parts of cortex responsible for higher forms of thought Differences between left side and right side of the brain How hormones interact with nervous system and affect behavior ...
Ch. 2 ppt
... Structures that control emotion, learning, memory, motivation Parts of cortex controlling senses and movement Parts of cortex responsible for higher forms of thought Differences between left side and right side of the brain How hormones interact with nervous system and affect behavior ...
... Structures that control emotion, learning, memory, motivation Parts of cortex controlling senses and movement Parts of cortex responsible for higher forms of thought Differences between left side and right side of the brain How hormones interact with nervous system and affect behavior ...
Nervous Tissue - MrsSconyersAnatomy
... What causes a graded potential? Describe what happens to cause an action potential. What happens during depolarization? What does ...
... What causes a graded potential? Describe what happens to cause an action potential. What happens during depolarization? What does ...
wave life sciences closes $18 million series a financing to advance
... drug product during its synthesis, affording precisely tailored drug molecules designed to possess optimized pharmacokinetic and therapeutic properties. WaVe’s technology, when applied to antisense, directs cellular machinery to disable mRNA through cleavage at defined, predetermined sites, which en ...
... drug product during its synthesis, affording precisely tailored drug molecules designed to possess optimized pharmacokinetic and therapeutic properties. WaVe’s technology, when applied to antisense, directs cellular machinery to disable mRNA through cleavage at defined, predetermined sites, which en ...
Time representation in reinforcement learning models of
... The role of the basal ganglia and dopamine in interval timing has been studied most extensively in the context of two procedures: the peak procedure (Catania, 1970; Roberts, 1981) and the bisection procedure (Church & Deluty, 1977). The peak procedure consists of two trial types: On fixed-interval t ...
... The role of the basal ganglia and dopamine in interval timing has been studied most extensively in the context of two procedures: the peak procedure (Catania, 1970; Roberts, 1981) and the bisection procedure (Church & Deluty, 1977). The peak procedure consists of two trial types: On fixed-interval t ...
Mechanisms of Sleep Control - UCLA Integrative Center for
... Clinical observations and lesion studies led to the concept of a waking center in the posterior hypothalamus. Lesions and chemical inactivation of this area produced hypersomnia (von-Economo, 1918; Ranson, 1939; Nauta, 1946; Lin et al., 1989). Unit recording studies have found cells in this region t ...
... Clinical observations and lesion studies led to the concept of a waking center in the posterior hypothalamus. Lesions and chemical inactivation of this area produced hypersomnia (von-Economo, 1918; Ranson, 1939; Nauta, 1946; Lin et al., 1989). Unit recording studies have found cells in this region t ...
Open access - Bioinformation
... Since ER plays a critical role in breast cancer [13, 14], several therapies have been developed over the past few decades among which endocrine therapy is the foremost treatment for ERPositive breast cancer patients [15]. The therapy includes (AIs) aromatase inhibitors, (SERMs) selective estrogen re ...
... Since ER plays a critical role in breast cancer [13, 14], several therapies have been developed over the past few decades among which endocrine therapy is the foremost treatment for ERPositive breast cancer patients [15]. The therapy includes (AIs) aromatase inhibitors, (SERMs) selective estrogen re ...
university of central florida - Christopher W. Blackwell, Ph.D., ARNP
... Risks include long-standing hypertension and small strokes often without significant loss of muscle strength. Symptom onset may be sudden or subtle depending upon the location, size, and frequency of the infarct and a stepwise deterioration of cognitive function occurs with plateaus and occasion ...
... Risks include long-standing hypertension and small strokes often without significant loss of muscle strength. Symptom onset may be sudden or subtle depending upon the location, size, and frequency of the infarct and a stepwise deterioration of cognitive function occurs with plateaus and occasion ...
Project synopsis on
... noninvasive, with the electrodes placed along the scalp, although invasive electrodes are sometimes used in specific applications. EEG measures voltage fluctuations resulting from ionic current within the neurons of the brain. In clinical contexts, EEG refers to the recording of the brain's spontane ...
... noninvasive, with the electrodes placed along the scalp, although invasive electrodes are sometimes used in specific applications. EEG measures voltage fluctuations resulting from ionic current within the neurons of the brain. In clinical contexts, EEG refers to the recording of the brain's spontane ...
Nervous System (Human): Introduction
... Neurons These basic units of the nervous system intercommunicate electrochemically via synapses (junctions) between their projecting axons and dendrites – processes whose number and pattern divide neurons into three types: unipolar, bipolar, and multipolar. From unipolar or bipolar receptor neurons, ...
... Neurons These basic units of the nervous system intercommunicate electrochemically via synapses (junctions) between their projecting axons and dendrites – processes whose number and pattern divide neurons into three types: unipolar, bipolar, and multipolar. From unipolar or bipolar receptor neurons, ...
Slide ()
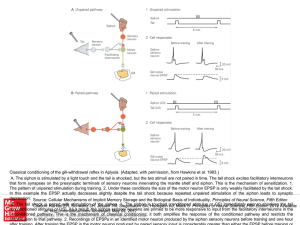
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
Cuneiform Neurons Activated during
... data from AS-carbachol cats with those from animals in quiet wakef ulness. In the present report, we examined, as before, two control cats in which the same procedures were followed, except that 0.1 l of saline was injected instead of carbachol. Four additional control animals, which were awake, we ...
... data from AS-carbachol cats with those from animals in quiet wakef ulness. In the present report, we examined, as before, two control cats in which the same procedures were followed, except that 0.1 l of saline was injected instead of carbachol. Four additional control animals, which were awake, we ...
3._Biological_Basis_of_Behavior_objectives
... 1. Be able to state the definition of biological psychology. 2. Identify various technology used to register brain activity and/or take images of the brain. 3. Define the nervous system. 4. Name and describe the functions of the neuronal parts that allow them to communicate. 5. Describe the main fun ...
... 1. Be able to state the definition of biological psychology. 2. Identify various technology used to register brain activity and/or take images of the brain. 3. Define the nervous system. 4. Name and describe the functions of the neuronal parts that allow them to communicate. 5. Describe the main fun ...
Growth and Development
... As they grow, neurons become arranged by function. Some move into the CEREBRAL CORTEX Others move to subcortical levels, which regulate fundamental activities such as breathing and heart rate (and are below the cerebral cortex). Networks of neurons become more complex over the first few years of lif ...
... As they grow, neurons become arranged by function. Some move into the CEREBRAL CORTEX Others move to subcortical levels, which regulate fundamental activities such as breathing and heart rate (and are below the cerebral cortex). Networks of neurons become more complex over the first few years of lif ...
THE SCIENCE OF LOVE: IS THERE SUCH A THING?
... poorly regulated in sSERT people (rendering them more stress-prone). ...
... poorly regulated in sSERT people (rendering them more stress-prone). ...
Splice variant - Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental
... In brief, superficial slices (0.4 mm thick) were manually cut from both cerebral hemispheres of 3-month-old Sprague-Dawley rats (weight about 300 g; Orion Ltd, Espoo, Finland) and immediately transferred to 4 mL of medium (composition in mM): NaCl 127, KCl 5, CaCl2 2.5, NaH2PO4 1.3, MgSO4 1.2, HEPES ...
... In brief, superficial slices (0.4 mm thick) were manually cut from both cerebral hemispheres of 3-month-old Sprague-Dawley rats (weight about 300 g; Orion Ltd, Espoo, Finland) and immediately transferred to 4 mL of medium (composition in mM): NaCl 127, KCl 5, CaCl2 2.5, NaH2PO4 1.3, MgSO4 1.2, HEPES ...
chapter 9 the chemical senses, neural coding, and central nervous
... specifically activated by a class of molecule (e.g., salt, acid, or sugar). Some receptor cells have more of a given type of ion chanel than do others. For example, one cell may have a high proportion of ion channels that are sensitive to salt, and another a high proportion of ion channels sensitive ...
... specifically activated by a class of molecule (e.g., salt, acid, or sugar). Some receptor cells have more of a given type of ion chanel than do others. For example, one cell may have a high proportion of ion channels that are sensitive to salt, and another a high proportion of ion channels sensitive ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.