Complete Nervous System Worksheet
... -presynaptic means anything before the synapse and postsynaptic means anything after the synapse. Therefore the cell transmitting the nerve impulse is called the presynaptic cell and the cell receiving the information is called the postsynaptic cell. -nerve impulses reaching the presynaptic ending c ...
... -presynaptic means anything before the synapse and postsynaptic means anything after the synapse. Therefore the cell transmitting the nerve impulse is called the presynaptic cell and the cell receiving the information is called the postsynaptic cell. -nerve impulses reaching the presynaptic ending c ...
Internal Regulation I
... somatic motor: motivating appropriate behaviors by the somatic motor system ...
... somatic motor: motivating appropriate behaviors by the somatic motor system ...
PAPER Glucosensing neurons do more than just sense glucose
... brain areas such as the hypothalamus, glucosensing neurons also contain receptors for insulin, leptin, monoamines and other transmitters and peptides involved in energy homeostasis.8 – 12 Thus, many or all glucosensing neurons respond to both short- and long-term signals relating to both the physica ...
... brain areas such as the hypothalamus, glucosensing neurons also contain receptors for insulin, leptin, monoamines and other transmitters and peptides involved in energy homeostasis.8 – 12 Thus, many or all glucosensing neurons respond to both short- and long-term signals relating to both the physica ...
Psych 9A. Lec. 08 PP Slides: Midterm Review
... Nicotine molecules mimic the neurotransmitters to which postsynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the brain are sensitive and, in this manner, activate the receptors and enhance this system’s effects. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? (a) Nicotine is an agonist. (b) Nicotine crosses the b ...
... Nicotine molecules mimic the neurotransmitters to which postsynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the brain are sensitive and, in this manner, activate the receptors and enhance this system’s effects. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? (a) Nicotine is an agonist. (b) Nicotine crosses the b ...
Gee JNeuro 2012 - Stanford University
... Dopamine D2 receptors (D2Rs) play a major role in the function of the prefrontal cortex (PFC), and may contribute to prefrontal dysfunction in conditions such as schizophrenia. Here we report that in mouse PFC, D2Rs are selectively expressed by a subtype of layer V pyramidal neurons that have thick ...
... Dopamine D2 receptors (D2Rs) play a major role in the function of the prefrontal cortex (PFC), and may contribute to prefrontal dysfunction in conditions such as schizophrenia. Here we report that in mouse PFC, D2Rs are selectively expressed by a subtype of layer V pyramidal neurons that have thick ...
Chapter 15 the autonomic nervous system -
... where each system works to produce the best outcome for the situation, both systems have inhibitory and excitatory components ...
... where each system works to produce the best outcome for the situation, both systems have inhibitory and excitatory components ...
Chapter 12 - Nervous Tissue
... open: ___ moves out of the axon causing the membrane voltage to become more negative again 5. Original resting Na+ and K+ ion concentrations are restored by the sodium/potassium _______ (moves ___ in and ___ out) ...
... open: ___ moves out of the axon causing the membrane voltage to become more negative again 5. Original resting Na+ and K+ ion concentrations are restored by the sodium/potassium _______ (moves ___ in and ___ out) ...
The Nervous System
... • Integration: Interneurons - integrate (analyze and interpret) sensory input. • Motor Output: Motor Neurons – communicate with effector cells. Produce reflexes (automatic responses to stimuli) in the simplest circuits. ...
... • Integration: Interneurons - integrate (analyze and interpret) sensory input. • Motor Output: Motor Neurons – communicate with effector cells. Produce reflexes (automatic responses to stimuli) in the simplest circuits. ...
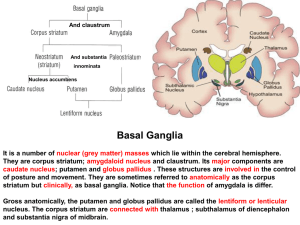
21. Basal ganglion
... It contains several groups of neurons. One of them is the nucleus basalis that project to the cerebral cortex and utilize acetylcholine as their neurotransmitter. These neurons undergo degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. ...
... It contains several groups of neurons. One of them is the nucleus basalis that project to the cerebral cortex and utilize acetylcholine as their neurotransmitter. These neurons undergo degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. ...
Slayt 1
... • İt is related in equilibrium of the body in various places • Equilibrium disturbances are; – Loss in synergic movements is called ataxic movement – Tremor and hipotonic states are due to its pathology – Nistagmus is remated to it and means horizontal or vertical involuntary ...
... • İt is related in equilibrium of the body in various places • Equilibrium disturbances are; – Loss in synergic movements is called ataxic movement – Tremor and hipotonic states are due to its pathology – Nistagmus is remated to it and means horizontal or vertical involuntary ...
Presentation Package - faculty.coe.unt.edu
... • Neurons communicate with one another by releasing neurotransmitters across synapses. • Synapses involve a presynaptic axon terminal, a postsynaptic receptor, neurotransmitters, and the space between them. • Neurotransmitters bind to the receptors and cause depolarization (excitation) or hyperpolar ...
... • Neurons communicate with one another by releasing neurotransmitters across synapses. • Synapses involve a presynaptic axon terminal, a postsynaptic receptor, neurotransmitters, and the space between them. • Neurotransmitters bind to the receptors and cause depolarization (excitation) or hyperpolar ...
Growth arrest specific gene 7 is associated with schizophrenia and
... Gas7△CC had no effect on the ability of neurons to initiate excessive neurites (Figs. 1d, g and 2a, b), suggesting that the F-BAR domain is necessary for normal function of Gas7 and the ability of the F-BAR domain to induce filopodia requires the existence of both the FCH and CC domains. According t ...
... Gas7△CC had no effect on the ability of neurons to initiate excessive neurites (Figs. 1d, g and 2a, b), suggesting that the F-BAR domain is necessary for normal function of Gas7 and the ability of the F-BAR domain to induce filopodia requires the existence of both the FCH and CC domains. According t ...
the Unit 2 study guide in RTF format (which you may re
... 2. What is the role of a myelin sheath? What can occur if myelin sheaths are damaged? 3. When a neuron is at its resting potential, what does this mean? How is this related to negative and positive ions? 4. What is the absolute refractory period? 5. What is the all-or-none law? 6. What are receptor ...
... 2. What is the role of a myelin sheath? What can occur if myelin sheaths are damaged? 3. When a neuron is at its resting potential, what does this mean? How is this related to negative and positive ions? 4. What is the absolute refractory period? 5. What is the all-or-none law? 6. What are receptor ...
Chapter 2: The Biological Basis of Behavior
... The "all-or-none law" refers to the fact that ______. a. all the neurons in a single nerve fire simultaneously or not at all b. all the neurons in a particular area of the brain fire simultaneously or not at all c. a neuron fires at full strength or not at all d. all the dendrites on a neuron must r ...
... The "all-or-none law" refers to the fact that ______. a. all the neurons in a single nerve fire simultaneously or not at all b. all the neurons in a particular area of the brain fire simultaneously or not at all c. a neuron fires at full strength or not at all d. all the dendrites on a neuron must r ...
house symposium 2015 - Instituto do Cérebro
... Animals respond differently to stress. While some individuals are able to overcome the stressor (resilience), others may develop depression or post- traumatic stress disorder. Several lines of evidence suggest a link between behavioral phenotype and long-term plasticity in the classic brain reward c ...
... Animals respond differently to stress. While some individuals are able to overcome the stressor (resilience), others may develop depression or post- traumatic stress disorder. Several lines of evidence suggest a link between behavioral phenotype and long-term plasticity in the classic brain reward c ...
the Unit 2 study guide in PDF format.
... 2. What is the role of a myelin sheath? What can occur if myelin sheaths are damaged? 3. When a neuron is at its resting potential, what does this mean? How is this related to negative and positive ions? 4. What is the absolute refractory period? 5. What is the all-or-none law? 6. What are receptor ...
... 2. What is the role of a myelin sheath? What can occur if myelin sheaths are damaged? 3. When a neuron is at its resting potential, what does this mean? How is this related to negative and positive ions? 4. What is the absolute refractory period? 5. What is the all-or-none law? 6. What are receptor ...
Minireview: Role of Glia in Neuroendocrine Function
... Integration of hormonal signaling by glial cells occurs in at least two fundamental ways: 1) the hormone acts directly on the glia, which in turn signals to the neuron to modulate its function (5, 6). Signaling to the neuron may involve secretion of a growth factor, neurohormone, or transmitter-like ...
... Integration of hormonal signaling by glial cells occurs in at least two fundamental ways: 1) the hormone acts directly on the glia, which in turn signals to the neuron to modulate its function (5, 6). Signaling to the neuron may involve secretion of a growth factor, neurohormone, or transmitter-like ...
Neurobiology of ADHD Gail Tripp , Review
... Imaging studies have delineated gross anatomical changes in brain dimensions associated with ADHD, and a number of excellent reviews exist (Bush et al., 2005; Durston, 2003; Kieling et al., 2008; Swanson et al., 2007). The most consistent finding is an overall reduction in total brain size that persi ...
... Imaging studies have delineated gross anatomical changes in brain dimensions associated with ADHD, and a number of excellent reviews exist (Bush et al., 2005; Durston, 2003; Kieling et al., 2008; Swanson et al., 2007). The most consistent finding is an overall reduction in total brain size that persi ...
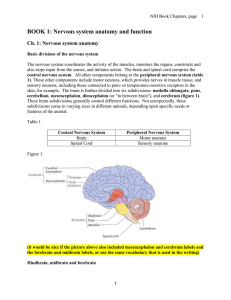
BOOK 1: Nervous system anatomy and function
... membrane potential positive (the upswing or rising phase of the action potential). A little later in time, actually one or two milliseconds later, the neuronal membrane prevents Na+ from coming in, but allows another positively charged ion, K+ (the ion for potassium), to leave the neuron. As K+ leav ...
... membrane potential positive (the upswing or rising phase of the action potential). A little later in time, actually one or two milliseconds later, the neuronal membrane prevents Na+ from coming in, but allows another positively charged ion, K+ (the ion for potassium), to leave the neuron. As K+ leav ...
Late-Onset Triple A Syndrome: A Risk of Overlooked or
... The association among familial glucocorticoid deficiency due to ACTH insensitivity, achalasia of the cardia, alacrima and autonomic dysfunction was firstly described in 1978 by Allgrove et al. [1] in two pairs of siblings (aged 4–6 years). This rare condition is also called triple A syndrome (adrena ...
... The association among familial glucocorticoid deficiency due to ACTH insensitivity, achalasia of the cardia, alacrima and autonomic dysfunction was firstly described in 1978 by Allgrove et al. [1] in two pairs of siblings (aged 4–6 years). This rare condition is also called triple A syndrome (adrena ...
48x36 Poster Template
... and neuron cell death. By observing cilia in mice with degenerative diseases, we can better understand the role of cilia in brain function and survival of neurons. ...
... and neuron cell death. By observing cilia in mice with degenerative diseases, we can better understand the role of cilia in brain function and survival of neurons. ...
Jim Williams Positives of Aging As we age, we experience a
... people. The brains of some older adults remodel themselves to use the hemispheres together, which is more powerful and efficient. This remodeling appears to lend more creativity to the aging brain. This creativity frequently manifests in older adults finding satisfaction in various artistic endeavor ...
... people. The brains of some older adults remodel themselves to use the hemispheres together, which is more powerful and efficient. This remodeling appears to lend more creativity to the aging brain. This creativity frequently manifests in older adults finding satisfaction in various artistic endeavor ...
quantitative proteomics of mitochondrial proteins in a mouse model
... proteins. Hsp60 transiently binds certain newly synthesized and stress-denatured proteins and mediates their folding or refolding into the functional 3-dimensional conformation. The genes encoding the mitochondrial Hsp60 chaperone or its homologs are essential in bacteria, yeast, fruit fly [10-12] a ...
... proteins. Hsp60 transiently binds certain newly synthesized and stress-denatured proteins and mediates their folding or refolding into the functional 3-dimensional conformation. The genes encoding the mitochondrial Hsp60 chaperone or its homologs are essential in bacteria, yeast, fruit fly [10-12] a ...
Responding to the environment humans
... Nerve impulses are electrical messages that travel along the nerves at about 100m/s (roughly 360km/h). The myelin sheath that consists of fat helps to insulate the electrical impulse to avoid the leaking of information. Nodes of Ranvier act as booster sites to speed up the transmission. ...
... Nerve impulses are electrical messages that travel along the nerves at about 100m/s (roughly 360km/h). The myelin sheath that consists of fat helps to insulate the electrical impulse to avoid the leaking of information. Nodes of Ranvier act as booster sites to speed up the transmission. ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.