File
... Native: I was here first! 1. Native: those that normally live and thrive in a particular community. 2. Nonnative (Invasive) species: those that migrate, deliberately or accidentally introduced into a community. ...
... Native: I was here first! 1. Native: those that normally live and thrive in a particular community. 2. Nonnative (Invasive) species: those that migrate, deliberately or accidentally introduced into a community. ...
Lecture Nine: Community Interactions
... The various species in an ecosystem do not live in a vaccuum! They have evolved over the millennia in response to pressures from both the environment and from other species with which they live and interact. SYMBIOSIS - "living together" This term refers to the members of two different species (i.e. ...
... The various species in an ecosystem do not live in a vaccuum! They have evolved over the millennia in response to pressures from both the environment and from other species with which they live and interact. SYMBIOSIS - "living together" This term refers to the members of two different species (i.e. ...
Invasive Species
... Kudzu grows almost too well. During warm summer months, kudzu can grow 1-2 feet each day! A kudzu plant, in optimal growing conditions, can grow 60+ feet per year. Kudzu rapidly spread and covered trees, power poles, buildings, etc., destroying plants, causing electrical outages, and becoming an eno ...
... Kudzu grows almost too well. During warm summer months, kudzu can grow 1-2 feet each day! A kudzu plant, in optimal growing conditions, can grow 60+ feet per year. Kudzu rapidly spread and covered trees, power poles, buildings, etc., destroying plants, causing electrical outages, and becoming an eno ...
Endangered, Extinct, Endemic & Exotic Species
... because it relied on the dodo to spread its seeds. When the dodo ate the fruit from the tree, it couldn't digest it and would poop it out. This is how the seeds were spread. No dodo droppings - no Calvaria tree. ...
... because it relied on the dodo to spread its seeds. When the dodo ate the fruit from the tree, it couldn't digest it and would poop it out. This is how the seeds were spread. No dodo droppings - no Calvaria tree. ...
Answers - SolPass
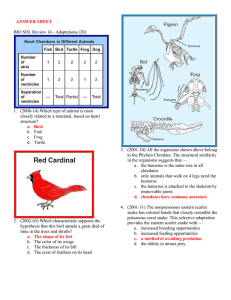
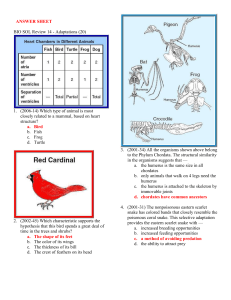
... Three of the birds spend most of their time on the ground, while one bird rarely walks on the ground. Which foot belongs to the bird that is best adapted for grasping branches? a. A b. B c. C d. D 6. (2001-14) Two plant species found in a dry region of the western United States exhibit vastly differ ...
... Three of the birds spend most of their time on the ground, while one bird rarely walks on the ground. Which foot belongs to the bird that is best adapted for grasping branches? a. A b. B c. C d. D 6. (2001-14) Two plant species found in a dry region of the western United States exhibit vastly differ ...
BIO SOL Review 14
... Three of the birds spend most of their time on the ground, while one bird rarely walks on the ground. Which foot belongs to the bird that is best adapted for grasping branches? a. A b. B c. C d. D 6. (2001-14) Two plant species found in a dry region of the western United States exhibit vastly differ ...
... Three of the birds spend most of their time on the ground, while one bird rarely walks on the ground. Which foot belongs to the bird that is best adapted for grasping branches? a. A b. B c. C d. D 6. (2001-14) Two plant species found in a dry region of the western United States exhibit vastly differ ...
Chapter 48 - Community Ecology
... ½ pt – Although originally considered an example of Batesian, this example is probably better explained as an example of Müllerian as both species are toxic to some degree. ½ pt – web citation 4. Explain the Competitive Exclusion Principle and how it relates to the concept of the ecological niche. 1 ...
... ½ pt – Although originally considered an example of Batesian, this example is probably better explained as an example of Müllerian as both species are toxic to some degree. ½ pt – web citation 4. Explain the Competitive Exclusion Principle and how it relates to the concept of the ecological niche. 1 ...
Presentations on Monday before the field
... between areas of wintering and nesting and to increase a sistematic knowledge on birds of lake maggiore area. The station is part of a vast network of capture and ringing centers covering migration routes from northern europe to the trans-saharan africa region’s. The center of Fondotoce will operate ...
... between areas of wintering and nesting and to increase a sistematic knowledge on birds of lake maggiore area. The station is part of a vast network of capture and ringing centers covering migration routes from northern europe to the trans-saharan africa region’s. The center of Fondotoce will operate ...
Systems
... What is ecology? (oikos = house or place to life; logos = study of Ecology is the study of the way living things interact with each other and their physical surroundings. It looks at the ways an organism is molded by its surroundings, how they make use of these surroundings, and how the area is alt ...
... What is ecology? (oikos = house or place to life; logos = study of Ecology is the study of the way living things interact with each other and their physical surroundings. It looks at the ways an organism is molded by its surroundings, how they make use of these surroundings, and how the area is alt ...
5.4 wkst
... underlined word or words to make the statement true. Write your changes on the line. 1. Secondary succession begins with bare rock. 2. The first species to colonize newly exposed land are called primary species. 3. Over the course of ecological succession, species diversity increases over time. 4. W ...
... underlined word or words to make the statement true. Write your changes on the line. 1. Secondary succession begins with bare rock. 2. The first species to colonize newly exposed land are called primary species. 3. Over the course of ecological succession, species diversity increases over time. 4. W ...
My Community, Our Earth
... placed on the Endangered Species list and the protection afforded the animals the opportunity to rebound. The population made a strong comeback, Implications & Conclusions and in 1977 the American Alligator was reclassi Due to its role as a keystone species, the fied as a Threatened species. There ...
... placed on the Endangered Species list and the protection afforded the animals the opportunity to rebound. The population made a strong comeback, Implications & Conclusions and in 1977 the American Alligator was reclassi Due to its role as a keystone species, the fied as a Threatened species. There ...
Worksheet Chapter 5.2
... underlined word or words to make the statement true. Write your changes on the line. 1. Organisms with wide tolerance ranges, able to use a wide array of habitats or resources, are called specialists. 2. Zebra mussels have demonstrated competitive exclusion by outcompeting all the native mussels in ...
... underlined word or words to make the statement true. Write your changes on the line. 1. Organisms with wide tolerance ranges, able to use a wide array of habitats or resources, are called specialists. 2. Zebra mussels have demonstrated competitive exclusion by outcompeting all the native mussels in ...
1 - Quia
... Nutrient cycling Protection of coastlines Protection of aquatic food sources Zoos and aquariums Indicator species for water, air and soil quality 2. Explain the ecological justification for preserving endangered species. Provide three examples of endangered species preservation with an ecological ju ...
... Nutrient cycling Protection of coastlines Protection of aquatic food sources Zoos and aquariums Indicator species for water, air and soil quality 2. Explain the ecological justification for preserving endangered species. Provide three examples of endangered species preservation with an ecological ju ...
4.2.2-.4 Causes of Extinction
... Rates of Extinction: = number of species becoming extinct per unit time. Rates of extinction are very difficult to estimate, because we don't even know within an order of magnitude how many species there are. Fossil records can reveal the average "lifetimes" of species, or how long different cl ...
... Rates of Extinction: = number of species becoming extinct per unit time. Rates of extinction are very difficult to estimate, because we don't even know within an order of magnitude how many species there are. Fossil records can reveal the average "lifetimes" of species, or how long different cl ...
Ecological Succession - The Consulting Students
... simple species. This, over time, changes to communities with a large number of more complex species. There are the following three stages in ecological succession: 1. Pioneer species stage The bare ground conditions favour pioneer plant species. These species grow best where there is little competit ...
... simple species. This, over time, changes to communities with a large number of more complex species. There are the following three stages in ecological succession: 1. Pioneer species stage The bare ground conditions favour pioneer plant species. These species grow best where there is little competit ...
primary productivity - Broadneck High School
... Fishing down the marine food web. After the large fish at the top of the food web are fished out, fisheries go after smaller fish and invertebrates at lower levels in the food web while their trawling destroys animals and plants on the sea floor. Time increases toward the right along the blue arrow ...
... Fishing down the marine food web. After the large fish at the top of the food web are fished out, fisheries go after smaller fish and invertebrates at lower levels in the food web while their trawling destroys animals and plants on the sea floor. Time increases toward the right along the blue arrow ...
Animal Populations
... ButterfliesThey have brief life cycles and are affected by climate change and pesticides. Birds plan their breeding season around when the caterpillers are most abundant TroutHealthy stream=abundant trout They need clean water, a specific temperature, protection, unsilted gravel to spawn and an abun ...
... ButterfliesThey have brief life cycles and are affected by climate change and pesticides. Birds plan their breeding season around when the caterpillers are most abundant TroutHealthy stream=abundant trout They need clean water, a specific temperature, protection, unsilted gravel to spawn and an abun ...
Ecosystems
... • Competition: two or more organisms attempt to use the same resource E.g. – two plants on forest floor compete for sunlight • Parasitism: the relationship between the parasite and its host E.g. – Ticks on a Hedgehog • Mutualism: relationship between two species in which both benefit E.g. – Ants and ...
... • Competition: two or more organisms attempt to use the same resource E.g. – two plants on forest floor compete for sunlight • Parasitism: the relationship between the parasite and its host E.g. – Ticks on a Hedgehog • Mutualism: relationship between two species in which both benefit E.g. – Ants and ...
Factors affecting the variety of species in an ecosystem
... To succeed in a community, organisms must be suited to their environment - this often involves adaptation - can be structural or behavioural ...
... To succeed in a community, organisms must be suited to their environment - this often involves adaptation - can be structural or behavioural ...
Chapter 4: The Forces of Evolution and the Formation of Species
... selection under similar environments rather than shared ancestry. • Cladistics: method of classification using ancestral and derived traits to distinguish patterns of evolution within lineages. ...
... selection under similar environments rather than shared ancestry. • Cladistics: method of classification using ancestral and derived traits to distinguish patterns of evolution within lineages. ...
Evolution of new species requires few genetic changes
... mutes genetic variants unimportant to speciation—allowing them to identify key genetic areas affected by natural selection. The butterfly species, they discovered, differed in only 12 small regions of their genomes, while remaining mostly identical throughout the rest. Eight of these coded for wing ...
... mutes genetic variants unimportant to speciation—allowing them to identify key genetic areas affected by natural selection. The butterfly species, they discovered, differed in only 12 small regions of their genomes, while remaining mostly identical throughout the rest. Eight of these coded for wing ...
Communities - Choteau Schools
... • Occurs in stages. – Each stage has conditions suitable for some organisms but not for others. ...
... • Occurs in stages. – Each stage has conditions suitable for some organisms but not for others. ...
Marine Communities
... Random Distribution: Position of one organism in no way influences positions of others in the same community. Very rare. Abyssal Plains. ...
... Random Distribution: Position of one organism in no way influences positions of others in the same community. Very rare. Abyssal Plains. ...
Slide 1
... fits into an ecosystem • Restate competitive exclusion principle: similar species CANNOT coexist if they have the exact same niche ...
... fits into an ecosystem • Restate competitive exclusion principle: similar species CANNOT coexist if they have the exact same niche ...
Bifrenaria

Bifrenaria, abbreviated Bif. in horticultural trade, is a genus of plant in family Orchidaceae. It contains 20 species found in Panama, Trinidad and South America. There are no known uses for them, but their abundant, and at first glance artificial, flowers, make them favorites of orchid growers.The genus can be split in two clearly distinct groups: one of highly robust plants with large flowers, that encompass the first species to be classified under the genus Bifrenaria; other of more delicate plants with smaller flowers occasionally classified as Stenocoryne or Adipe. There are two additional species that are normally classified as Bifrenaria, but which molecular analysis indicate to belong to different orchid groups entirely. One is Bifrenaria grandis which is endemic to Bolívia and which is now placed in Lacaena, and Bifrenaria steyermarkii, an inhabitant of the northern Amazon Forest, which does not have an alternative classification.