Ecology – Honors Biology
... Population: group of individuals belonging to same species living in the same area: (Species) Group of organisms that can breed together. ...
... Population: group of individuals belonging to same species living in the same area: (Species) Group of organisms that can breed together. ...
AG-WL-03.453-05.2_ Wildlife and Human Conflict
... Diversity measures combine information on the number of species and abundance A decrease in diversity may indicate some species have been displaced or eliminated Does not reflect replacement of one species with another ...
... Diversity measures combine information on the number of species and abundance A decrease in diversity may indicate some species have been displaced or eliminated Does not reflect replacement of one species with another ...
Chapter 14 Interaction in Ecosystems Study Guide
... 12. Some birds are known as honey guides because they may be followed by humans to wild beehives. When the humans take honey from the hives, the birds are able to feast on the honey and bees, too. This type of relationship is best described as __________________________________________. 13. Starfish ...
... 12. Some birds are known as honey guides because they may be followed by humans to wild beehives. When the humans take honey from the hives, the birds are able to feast on the honey and bees, too. This type of relationship is best described as __________________________________________. 13. Starfish ...
Invasive
... • Late 1930’s introduced by accident in Alabama in shiploads of lumber and cargo. • Interspecific competition reduced native ant species by 90%! • Fire ants are very aggressive and through direct combat reduced native species. • Since there are no natural predators, they produced more colonies than ...
... • Late 1930’s introduced by accident in Alabama in shiploads of lumber and cargo. • Interspecific competition reduced native ant species by 90%! • Fire ants are very aggressive and through direct combat reduced native species. • Since there are no natural predators, they produced more colonies than ...
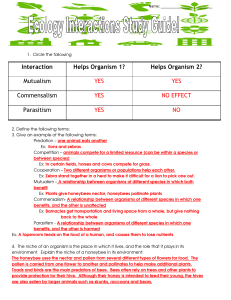
Interaction Helps Organism 1? Helps Organism 2? Mutualism YES
... Ex: Plants give honeybees nectar, honeybees pollinate plants Commensalism- A relationship between organisms of different species in which one benefits, and the other is unaffected Ex: Barnacles get transportation and living space from a whale, but give nothing back to the whale Parasitism - A relati ...
... Ex: Plants give honeybees nectar, honeybees pollinate plants Commensalism- A relationship between organisms of different species in which one benefits, and the other is unaffected Ex: Barnacles get transportation and living space from a whale, but give nothing back to the whale Parasitism - A relati ...
Starter - MNWIKIESS
... Some of the species on the list… The Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis) Critically Endangered. Its population has declined by an estimated 97.6% since 1960, with numbers bottoming out at 2,410 in 1995, mainly as a result of poaching. Since then, numbers have doubled to 4,880 by the end of 2010. Cu ...
... Some of the species on the list… The Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis) Critically Endangered. Its population has declined by an estimated 97.6% since 1960, with numbers bottoming out at 2,410 in 1995, mainly as a result of poaching. Since then, numbers have doubled to 4,880 by the end of 2010. Cu ...
Slide 1
... Question 8 - Ecosystems 8. Describe the 4 types of symbiotic relationships. Remember to write full ...
... Question 8 - Ecosystems 8. Describe the 4 types of symbiotic relationships. Remember to write full ...
How Introduced Species Affect Ecosystems
... Native species are plants and animals that naturally inhabit an area. Introduced species are species that have been introduced into an ecosystem by humans, either intentionally or accidentally. Introduced species usually beneficial or harmless, then can at times dramatically change and ecosystem. Th ...
... Native species are plants and animals that naturally inhabit an area. Introduced species are species that have been introduced into an ecosystem by humans, either intentionally or accidentally. Introduced species usually beneficial or harmless, then can at times dramatically change and ecosystem. Th ...
Unit 7 Review - 2 - Iowa State University
... d. Daily temperature extremes 11. The cyclic growth exhibited by populations of showshoe hares in the North America taiga most likely results from… a. Predation by lynx b. Fluctuations in the hare’s food c. Hunting by humans d. A and B 12. The niche of an animal is… a. The number of individuals of t ...
... d. Daily temperature extremes 11. The cyclic growth exhibited by populations of showshoe hares in the North America taiga most likely results from… a. Predation by lynx b. Fluctuations in the hare’s food c. Hunting by humans d. A and B 12. The niche of an animal is… a. The number of individuals of t ...
The Future of Alien Invasive Species: Changing Social Views Jeffrey
... • Biodiversity loss: extinction and vulnerability to predation/pests; habitat change and degradation; homogenisation of ecosystems • Socio-economic: in many countries, human dietary needs are met by introduced species (barley, wheat, potatoes…). But pests, disease and loss of species mean a high cos ...
... • Biodiversity loss: extinction and vulnerability to predation/pests; habitat change and degradation; homogenisation of ecosystems • Socio-economic: in many countries, human dietary needs are met by introduced species (barley, wheat, potatoes…). But pests, disease and loss of species mean a high cos ...
Ch548thed
... Example of disturbance leading to change primary succession - soil never formed before secondary succession - existing community was disturbed and returned to original state. ...
... Example of disturbance leading to change primary succession - soil never formed before secondary succession - existing community was disturbed and returned to original state. ...
14.4 Interactions within Communities
... a given ecosystem. • Some organisms within communities cannot exist independently of one another and work together for survival. ...
... a given ecosystem. • Some organisms within communities cannot exist independently of one another and work together for survival. ...
invasive species
... Plants, animals, and microbes not native to a region which, when introduced either accidentally or intentionally, out-compete native species for available resources, reproduce prolifically, and dominate regions and ecosystems. Because they often arrive in new areas unaccompanied by their native pre ...
... Plants, animals, and microbes not native to a region which, when introduced either accidentally or intentionally, out-compete native species for available resources, reproduce prolifically, and dominate regions and ecosystems. Because they often arrive in new areas unaccompanied by their native pre ...
Community Interactions
... • Individualistic view (Gleason) • Interactive view (Clements) • Whittaker’s test • Plant communities are loose associations without discrete boundaries ...
... • Individualistic view (Gleason) • Interactive view (Clements) • Whittaker’s test • Plant communities are loose associations without discrete boundaries ...
File - Big Green Planet
... Competitive Exclusion Principle: A theory first proposed by Joseph Grinnell and later formulated by Georgy Gause based on laboratory experiments. It states that two species cannot occupy a single niche at the same time without one of the species eventually crowding out the other. It is not seen very ...
... Competitive Exclusion Principle: A theory first proposed by Joseph Grinnell and later formulated by Georgy Gause based on laboratory experiments. It states that two species cannot occupy a single niche at the same time without one of the species eventually crowding out the other. It is not seen very ...
How Changes Occur Naturally in Ecosystems
... • “Pioneer species” can survive harsh conditions. • Provide food, water, nutrients ...
... • “Pioneer species” can survive harsh conditions. • Provide food, water, nutrients ...
Lesson 6.2
... feed on sea urchins, which feed on kelp. Without the sea otter, the sea urchins would over populate. If there are too many sea urchins, there would eventually be no more kelp forest! ...
... feed on sea urchins, which feed on kelp. Without the sea otter, the sea urchins would over populate. If there are too many sea urchins, there would eventually be no more kelp forest! ...
How Introduced Species Affect Ecosystems
... • However, some take over the habitat of the native species. These are called invasive species. ...
... • However, some take over the habitat of the native species. These are called invasive species. ...
Keystone species powerpoint
... Some populations of organisms can be removed or lessened with little effect. Why do you think it could have little effect with certain organisms? Some populations of organisms are vital to ecosystems. The event of removing them or lessening them would cause a negative effect. It might stop there or ...
... Some populations of organisms can be removed or lessened with little effect. Why do you think it could have little effect with certain organisms? Some populations of organisms are vital to ecosystems. The event of removing them or lessening them would cause a negative effect. It might stop there or ...
Darwinian speciation in Amazon butterflies James Mallet Predictions
... Instead, some lineages diversify rapidly, others slowly. This suggests a lineage's ability to colonize new ecological niches is more important in diversification than climatic forcing of the whole biota. I show how favourable local fluctuations in warning colour and mimicry evolution can be amplifie ...
... Instead, some lineages diversify rapidly, others slowly. This suggests a lineage's ability to colonize new ecological niches is more important in diversification than climatic forcing of the whole biota. I show how favourable local fluctuations in warning colour and mimicry evolution can be amplifie ...
The Blue Mussel Project - University of Puget Sound
... Reproductive Isolation is key, but what about hybrids? Morphological Species Concept Species differ consistently in form Concept that is most used In practice – Species are: a) groups of individuals or populations that are reproductively isolated from each other or b) groups that for the most part r ...
... Reproductive Isolation is key, but what about hybrids? Morphological Species Concept Species differ consistently in form Concept that is most used In practice – Species are: a) groups of individuals or populations that are reproductively isolated from each other or b) groups that for the most part r ...
Bifrenaria

Bifrenaria, abbreviated Bif. in horticultural trade, is a genus of plant in family Orchidaceae. It contains 20 species found in Panama, Trinidad and South America. There are no known uses for them, but their abundant, and at first glance artificial, flowers, make them favorites of orchid growers.The genus can be split in two clearly distinct groups: one of highly robust plants with large flowers, that encompass the first species to be classified under the genus Bifrenaria; other of more delicate plants with smaller flowers occasionally classified as Stenocoryne or Adipe. There are two additional species that are normally classified as Bifrenaria, but which molecular analysis indicate to belong to different orchid groups entirely. One is Bifrenaria grandis which is endemic to Bolívia and which is now placed in Lacaena, and Bifrenaria steyermarkii, an inhabitant of the northern Amazon Forest, which does not have an alternative classification.