Bland-Altman Analysis
... has been accepted as the standard statistical approach to assess the agreement between two methods of clinical measurement (Altman and Bland, 1983; Bland and Altman, 1986; Mantha et al, 2000). In this approach, for each patient, the new method (mini-Wright) measurement is subtracted from the standar ...
... has been accepted as the standard statistical approach to assess the agreement between two methods of clinical measurement (Altman and Bland, 1983; Bland and Altman, 1986; Mantha et al, 2000). In this approach, for each patient, the new method (mini-Wright) measurement is subtracted from the standar ...
Chapter 3 Solutions
... 3.45. (a) About 0.6% of healthy young adults have osteoporosis (the cumulative probability below a standard score of —2.5 is 0.0062). (b) About 31% of this population of older women has osteoporosis the BMD level that is 2 5 standard deviations below the young adult mean would standardize to —0 5 fo ...
... 3.45. (a) About 0.6% of healthy young adults have osteoporosis (the cumulative probability below a standard score of —2.5 is 0.0062). (b) About 31% of this population of older women has osteoporosis the BMD level that is 2 5 standard deviations below the young adult mean would standardize to —0 5 fo ...
Tejas Engineers Academy
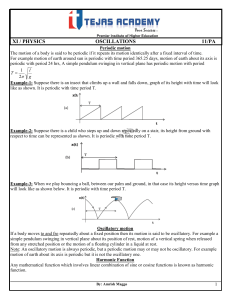
... 22. The motion of a particle executing SHM is described by the displacement function: x(t) = A cos(ωt + φ) If the initial (t=0) position of the particle is 1 cm and its initial velocity is ω cm/s, what are its amplitude and initial phase angle? The angular frequency of the particle is π s-1. If inst ...
... 22. The motion of a particle executing SHM is described by the displacement function: x(t) = A cos(ωt + φ) If the initial (t=0) position of the particle is 1 cm and its initial velocity is ω cm/s, what are its amplitude and initial phase angle? The angular frequency of the particle is π s-1. If inst ...
Semi-markov decision problems and performance sensitivity analysis
... in PA. These concepts provide an intuitive explanation for both PA and MDPs (in view of discrete sensitivity) and their relations [6], [7]. The performance potential at state can be approximated by the mean of the sum of the performance functransitions on a sample path starting from tions at the fir ...
... in PA. These concepts provide an intuitive explanation for both PA and MDPs (in view of discrete sensitivity) and their relations [6], [7]. The performance potential at state can be approximated by the mean of the sum of the performance functransitions on a sample path starting from tions at the fir ...
Measures of Central Tendency and Variability
... The median of a set of scores is the “middle” score, when the scores are arranged from lowest to highest. When there is an odd number of scores, there is one score that falls right in the middle, and it is the median. When there is an even number of scores, there are two middle scores, in which case ...
... The median of a set of scores is the “middle” score, when the scores are arranged from lowest to highest. When there is an odd number of scores, there is one score that falls right in the middle, and it is the median. When there is an even number of scores, there are two middle scores, in which case ...
Measures of Variability
... The difference between the highest and lowest values in the middle 50% of a dataset Less biased by outliers than the Range Based on sample with upper and lower 25% of the data “trimmed” However this kind of trimming essentially ignores half of your data – better to trim top and bottom 1 or 5% ...
... The difference between the highest and lowest values in the middle 50% of a dataset Less biased by outliers than the Range Based on sample with upper and lower 25% of the data “trimmed” However this kind of trimming essentially ignores half of your data – better to trim top and bottom 1 or 5% ...
mean
... The median (M) is the midpoint of the distribution, the number such that half the observations are smaller and other the half are larger. To find the median of a distribution: 1.Arrange all observations in order of size, from smallest to largest. 2.If the number of observations is odd the median i ...
... The median (M) is the midpoint of the distribution, the number such that half the observations are smaller and other the half are larger. To find the median of a distribution: 1.Arrange all observations in order of size, from smallest to largest. 2.If the number of observations is odd the median i ...
Econometrics_Lesson_..
... compute the variance of each and see if your intuition was correct. The variance of PDF 2 is approximately 0.875 while the variance of PDF 1 is approximately 0.055. Sometimes we are interested in the square root of the variance. The square root of the variance is called the standard deviation of the ...
... compute the variance of each and see if your intuition was correct. The variance of PDF 2 is approximately 0.875 while the variance of PDF 1 is approximately 0.055. Sometimes we are interested in the square root of the variance. The square root of the variance is called the standard deviation of the ...
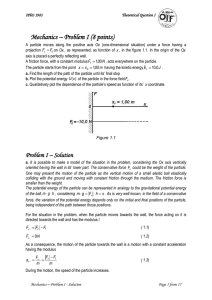
Solution
... One may present the motion of the particle as the vertical motion of a small elastic ball elastically colliding with the ground and moving with constant friction through the medium. The friction force is smaller than the weight. The potential energy of the particle can be represented in analogy to t ...
... One may present the motion of the particle as the vertical motion of a small elastic ball elastically colliding with the ground and moving with constant friction through the medium. The friction force is smaller than the weight. The potential energy of the particle can be represented in analogy to t ...