Machine Learning
... • Popular and successful algorithms • Matlab • Data sets of text, speech, pictures, user actions, neural data… ...
... • Popular and successful algorithms • Matlab • Data sets of text, speech, pictures, user actions, neural data… ...
hw1_sol
... • Be sure to organize the pages in order and staple them all together, otherwise you will lose one point • Fill out the following section. You will lose an additional point if you fail to provide these details Your Last Name_____________________________ Your First Name__________________________ ...
... • Be sure to organize the pages in order and staple them all together, otherwise you will lose one point • Fill out the following section. You will lose an additional point if you fail to provide these details Your Last Name_____________________________ Your First Name__________________________ ...
Math 1312 Test Review --
... b) A company is to select three different representatives to send to three different conventions during the year. Forty-two people volunteer to attend. How many different groups of three can be selected ? ...
... b) A company is to select three different representatives to send to three different conventions during the year. Forty-two people volunteer to attend. How many different groups of three can be selected ? ...
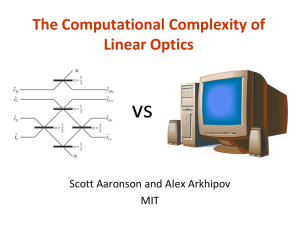
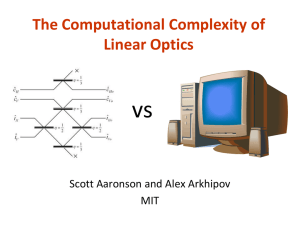
Another version - Scott Aaronson
... Building a QC able to factor large numbers is damn hard! After 16 years, no fundamental obstacle has been found (or even seriously proposed), but who knows? Can’t we “meet the physicists halfway,” and show computational hardness for quantum systems closer to what they actually work with now? ...
... Building a QC able to factor large numbers is damn hard! After 16 years, no fundamental obstacle has been found (or even seriously proposed), but who knows? Can’t we “meet the physicists halfway,” and show computational hardness for quantum systems closer to what they actually work with now? ...
The Learnability of Quantum States
... sampling algorithm, and let r be its randomness. Use approximate counting to ...
... sampling algorithm, and let r be its randomness. Use approximate counting to ...
Solution - University of Arizona Math
... standard normal pdf. Let Z = Y − X + 4. (a) Find the mean and variance of Z. Solution: E[Z] = E[Y ] − E[X] + 4 = 4. var(Z) = var(Y ) + var(−X) = var(Y ) + var(X) = 1 + 1 = 2. (b) Find the probability density function (pdf) of Z. Hint: this can be done with very little computation. Solution: It is ea ...
... standard normal pdf. Let Z = Y − X + 4. (a) Find the mean and variance of Z. Solution: E[Z] = E[Y ] − E[X] + 4 = 4. var(Z) = var(Y ) + var(−X) = var(Y ) + var(X) = 1 + 1 = 2. (b) Find the probability density function (pdf) of Z. Hint: this can be done with very little computation. Solution: It is ea ...
Stochastic processes
... yields the sample function m ( t, s ) where the number of active calls is measured for every second over one 15 minute interval. Say this measurement is taken every day starting at 10AM. An ensemble average can be obtained from all measurements for t = 2min after 10AM. Or a time average can be obtai ...
... yields the sample function m ( t, s ) where the number of active calls is measured for every second over one 15 minute interval. Say this measurement is taken every day starting at 10AM. An ensemble average can be obtained from all measurements for t = 2min after 10AM. Or a time average can be obtai ...
Hardware random number generator

In computing, a hardware random number generator (TRNG, True Random Number Generator) is an apparatus that generates random numbers from a physical process, rather than a computer program. Such devices are often based on microscopic phenomena that generate low-level, statistically random ""noise"" signals, such as thermal noise, the photoelectric effect, and other quantum phenomena. These processes are, in theory, completely unpredictable, and the theory's assertions of unpredictability are subject to experimental test. A hardware random number generator typically consists of a transducer to convert some aspect of the physical phenomena to an electrical signal, an amplifier and other electronic circuitry to increase the amplitude of the random fluctuations to a measurable level, and some type of analog to digital converter to convert the output into a digital number, often a simple binary digit 0 or 1. By repeatedly sampling the randomly varying signal, a series of random numbers is obtained. The main application for electronic hardware random number generators is in cryptography, where they are used to generate random cryptographic keys to transmit data securely. They are widely used in Internet encryption protocols such as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL).Random number generators can also be built from ""random"" macroscopic processes, using devices such as coin flipping, dice, roulette wheels and lottery machines. The presence of unpredictability in these phenomena can be justified by the theory of unstable dynamical systems and chaos theory. Even though macroscopic processes are deterministic under Newtonian mechanics, the output of a well-designed device like a roulette wheel cannot be predicted in practice, because it depends on the sensitive, micro-details of the initial conditions of each use. Although dice have been mostly used in gambling, and in more recent times as ""randomizing"" elements in games (e.g. role playing games), the Victorian scientist Francis Galton described a way to use dice to explicitly generate random numbers for scientific purposes in 1890.Hardware random number generators generally produce a limited number of random bits per second. In order to increase the data rate, they are often used to generate the ""seed"" for a faster Cryptographically secure pseudorandom number generator, which then generates the pseudorandom output sequence.