SENSORY NERVOUS SYSTEM
... into this category. In general, the stimuli that activate tonic receptors are parameters that must be monitored continuously by the body. It is important that these receptors do not adapt to a stimulus and continue to generate action potentials to relay this information to the CNS. ...
... into this category. In general, the stimuli that activate tonic receptors are parameters that must be monitored continuously by the body. It is important that these receptors do not adapt to a stimulus and continue to generate action potentials to relay this information to the CNS. ...
Drivers and modulators from push-pull and balanced synaptic input
... constant, and !(x) is a step function that takes the value 1 if x>0 and zero otherwise. Equation 1 gives the firing rate in terms of an input current, or equivalently the effective steady-state potential it produces. This formula is valid in the absence of ‘‘noise’’, which means non-variable synapti ...
... constant, and !(x) is a step function that takes the value 1 if x>0 and zero otherwise. Equation 1 gives the firing rate in terms of an input current, or equivalently the effective steady-state potential it produces. This formula is valid in the absence of ‘‘noise’’, which means non-variable synapti ...
The Binding Problem
... is both divergent and convergent. Neurons in a given cortical area send divergent outputs to other areas, enabling the cells in these areas to receive convergent input from many sources. This type of organization provides neuronal populations at the highest levels of the hierarchy with broad access ...
... is both divergent and convergent. Neurons in a given cortical area send divergent outputs to other areas, enabling the cells in these areas to receive convergent input from many sources. This type of organization provides neuronal populations at the highest levels of the hierarchy with broad access ...
Ativity 13 - PCC - Portland Community College
... cortex of the brain and terminates within the medulla (another part of the brain) or within the spinal cord. • Damage to upper motor neurons can result in spasticity and exaggerated reflexes (because of the loss of inhibition) “Spastic Paralysis” ...
... cortex of the brain and terminates within the medulla (another part of the brain) or within the spinal cord. • Damage to upper motor neurons can result in spasticity and exaggerated reflexes (because of the loss of inhibition) “Spastic Paralysis” ...
Where is the proprioception first processed? Thalamus vs. Cerebellum
... • Many of them are sensitive to the direction of movement. ...
... • Many of them are sensitive to the direction of movement. ...
Neurotransmitters
... circuit • Signal stimulates neurons arranged in parallel arrays that eventually converge on a single output cell • Impulses reach output cell at different times, causing a burst of impulses called an after-discharge • Example: May be involved in exacting mental processes such as mathematical calcula ...
... circuit • Signal stimulates neurons arranged in parallel arrays that eventually converge on a single output cell • Impulses reach output cell at different times, causing a burst of impulses called an after-discharge • Example: May be involved in exacting mental processes such as mathematical calcula ...
Molekuláris bionika és Infobionika Szakok tananyagának
... ARE THE TRIGGERS RECEPTOR. HEAT AND PAIN RECEPTORS IN THE SKIN AFFERENT PATH. THIN, MYELINATED AND UNMYELEINATED AXONS OF PSEUDOUNIPOLAR CELLS OF SPINAL GANGLIA ...
... ARE THE TRIGGERS RECEPTOR. HEAT AND PAIN RECEPTORS IN THE SKIN AFFERENT PATH. THIN, MYELINATED AND UNMYELEINATED AXONS OF PSEUDOUNIPOLAR CELLS OF SPINAL GANGLIA ...
THE ELECTRICAL BRAIN
... which must cross the synaptic gap to deliver their message. The entire process takes about half a millisecond. That may seem fast, but for many physiological processes — such as the flight reflex of the blowfish, during which it instantaneously flips its tail to escape predators — it would be too sl ...
... which must cross the synaptic gap to deliver their message. The entire process takes about half a millisecond. That may seem fast, but for many physiological processes — such as the flight reflex of the blowfish, during which it instantaneously flips its tail to escape predators — it would be too sl ...
Neuromuscular spindle The central nervous system continuously
... region, and (2) the nuclear chain fiber, so-called because its central portion contains a chain-like array of nuclei. The distal portion of both nuclear bag and nuclear chain fibers consists of striated muscle with contractile properties. The neuromuscular spindle is innervated by two types of affer ...
... region, and (2) the nuclear chain fiber, so-called because its central portion contains a chain-like array of nuclei. The distal portion of both nuclear bag and nuclear chain fibers consists of striated muscle with contractile properties. The neuromuscular spindle is innervated by two types of affer ...
A"computational"approach"towards"the"ontogeny"of" mirror"neurons
... 1, , 2, and 5. 1,' refers to the amount of stimulation caused by other sources than neurons within the network and can be either on or off. The input signal further consists of the activation bias 2,' and Gaussian noise determined by 5. Each time step # represents 1 ms of activity. The parameters (, ...
... 1, , 2, and 5. 1,' refers to the amount of stimulation caused by other sources than neurons within the network and can be either on or off. The input signal further consists of the activation bias 2,' and Gaussian noise determined by 5. Each time step # represents 1 ms of activity. The parameters (, ...
Human Cortex: Reflections of Mirror Neurons
... that strongly during movement execution and observation (Figure 2A) and did not exhibit visual or motor (within modality) adaptation in our study [12]. Secondly, given that subjects executed movements with their right hand, it is surprising that cross-modal adaptation was found only in the ipsilater ...
... that strongly during movement execution and observation (Figure 2A) and did not exhibit visual or motor (within modality) adaptation in our study [12]. Secondly, given that subjects executed movements with their right hand, it is surprising that cross-modal adaptation was found only in the ipsilater ...
2/pg
... • Signal between neurons: the synapse – synapse is point of contact (tiny gap) between cells – specialized to promote and regulate transmission of signal from one cell to another – chemical signal is passed: neurotransmitter – neuron-muscle synapse = neuromuscular junction ...
... • Signal between neurons: the synapse – synapse is point of contact (tiny gap) between cells – specialized to promote and regulate transmission of signal from one cell to another – chemical signal is passed: neurotransmitter – neuron-muscle synapse = neuromuscular junction ...
optimization of neuronal cultures derived from human induced
... Supplement (Invitrogen), 500 µM glutamine (Invitrogen), and 6.25 µM glutamate (Sigma). When neurons were cocultured with glia, medium consisted of Advanced DMEM/F12 plus 1% fetal calf serum. Cultures were analyzed between 2 and 7 weeks in vitro on the MANTRA system or on a fluorescence microscope im ...
... Supplement (Invitrogen), 500 µM glutamine (Invitrogen), and 6.25 µM glutamate (Sigma). When neurons were cocultured with glia, medium consisted of Advanced DMEM/F12 plus 1% fetal calf serum. Cultures were analyzed between 2 and 7 weeks in vitro on the MANTRA system or on a fluorescence microscope im ...
The Nervous System
... why action potentials can only move forward from the point of stimulation. Increased permeability of the sodium channel occurs when there is a deficit of calcium ions. when there is a deficit of calcium ions (Ca+2) in the interstitial fluid the sodium channels are activated (opened) by very little i ...
... why action potentials can only move forward from the point of stimulation. Increased permeability of the sodium channel occurs when there is a deficit of calcium ions. when there is a deficit of calcium ions (Ca+2) in the interstitial fluid the sodium channels are activated (opened) by very little i ...
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal
... • Describe the two major groups of receptors and their subtypes (and their usual ligands.) • Distinguish between receptor stimulation and cell stimulation. ...
... • Describe the two major groups of receptors and their subtypes (and their usual ligands.) • Distinguish between receptor stimulation and cell stimulation. ...
Final Motor System2010-10-01 06:264.1 MB
... It works together with premotor cortex. Involved in organizing or planning and prgramming motor sequences, while M1 executes movements. Lesions: do not cause paralysis but produces awkwardness in performing complex activity and difficulty with bimanual coordinated activity. ...
... It works together with premotor cortex. Involved in organizing or planning and prgramming motor sequences, while M1 executes movements. Lesions: do not cause paralysis but produces awkwardness in performing complex activity and difficulty with bimanual coordinated activity. ...
Slide 1
... emitted pulse consists of four harmonics (H1–H4), the strongest of which is H2 at about 60 kHz. Each harmonic has an initial part of constant frequency (CF) and a later part of changing frequency (frequency modulation, FM). The echoes are returned after a travel time that causes a delay relative to ...
... emitted pulse consists of four harmonics (H1–H4), the strongest of which is H2 at about 60 kHz. Each harmonic has an initial part of constant frequency (CF) and a later part of changing frequency (frequency modulation, FM). The echoes are returned after a travel time that causes a delay relative to ...
Garza-Juliann-Project(1)
... Peripheral Nervous System Nervous tissue is made up of 2 principal ...
... Peripheral Nervous System Nervous tissue is made up of 2 principal ...
Chapter 11-自律神經及體運動神經系統檔案
... Figure 11.7 Neurotransmitters and receptors in the autonomic nervous system. (a) Neurotransmitters and receptors for the three distinct anatomical pathways of the sympathetic nervous system. In all cases, the preganglionic neuron releases acetylcholine (Ach), which then binds to nicotinic cholinergi ...
... Figure 11.7 Neurotransmitters and receptors in the autonomic nervous system. (a) Neurotransmitters and receptors for the three distinct anatomical pathways of the sympathetic nervous system. In all cases, the preganglionic neuron releases acetylcholine (Ach), which then binds to nicotinic cholinergi ...
Organization of Somatic Nervous system, Spinal nerve and Reflex arc
... Simplified reflex arc stimulus sensory neurone receptor spinal relay cord of neurone central nervous system motor neurone ...
... Simplified reflex arc stimulus sensory neurone receptor spinal relay cord of neurone central nervous system motor neurone ...
Chapter 11-自律神經及體運動神經系統檔案
... Myasthenia gravis 重症肌無力 is a disease affecting transmission at neuromuscular junction Because the muscles most frequently affected are those of the head, difficulties in speaking (dysarthria) 發音困難 and in swallowing (dysphagia) 吞嚥困難 are common symptoms; dropping of the eyelids (ptosis) 眼瞼下垂 is al ...
... Myasthenia gravis 重症肌無力 is a disease affecting transmission at neuromuscular junction Because the muscles most frequently affected are those of the head, difficulties in speaking (dysarthria) 發音困難 and in swallowing (dysphagia) 吞嚥困難 are common symptoms; dropping of the eyelids (ptosis) 眼瞼下垂 is al ...
PDF file
... The following technical characteristics required by developmental learning make such work challenging: (1) Integrate both bottom-up and top-down attention; (2) Integrate attentionbased recognition and object-based spacial attention interactively; (3) Enable supervised and unsupervised learning in an ...
... The following technical characteristics required by developmental learning make such work challenging: (1) Integrate both bottom-up and top-down attention; (2) Integrate attentionbased recognition and object-based spacial attention interactively; (3) Enable supervised and unsupervised learning in an ...
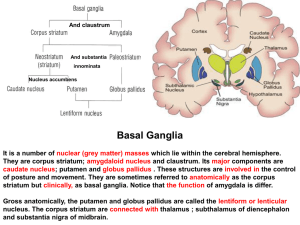
21. Basal ganglion
... unwanted; involuntary movements.The following signs is present: 1- Choreiform movements first appear as involuntary movements of the extremities and twitching of the face (facial grimacing). Later, more muscle groups are involved so the patient becomes immobile and unable to speak or swallow. 2- Pro ...
... unwanted; involuntary movements.The following signs is present: 1- Choreiform movements first appear as involuntary movements of the extremities and twitching of the face (facial grimacing). Later, more muscle groups are involved so the patient becomes immobile and unable to speak or swallow. 2- Pro ...
Central Nervous System I. Brain - Function A. Hindbrain 1. Medulla
... Second-order neurons – have their origin in the gray matter of the spinal cord. These neurons cross to the opposite side of the spinal cord and sent their axons into the white of the spinal cord to pass upward to the thalamus. These are the interneurons or association neurons. Third –order neurons – ...
... Second-order neurons – have their origin in the gray matter of the spinal cord. These neurons cross to the opposite side of the spinal cord and sent their axons into the white of the spinal cord to pass upward to the thalamus. These are the interneurons or association neurons. Third –order neurons – ...
Caridoid escape reaction

The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfish, allows crustaceans to escape predators through rapid abdominal flexions that produce powerful swimming strokes — thrusting the crustacean backwards through the water and away from danger. The type of response depends on the part of the crustacean stimulated, but this behavior is complex and is regulated both spatially and temporally through the interactions of several neurons.