James Webb Space Telescope – A Bigger and Better
... the Universe billions of years ago. With a big enough telescope, it is theoretically possible to map how stars and galaxies came into being and subsequently evolved nearly all the way back to the ‘Big Bang’, some 13.6 billion years ago. ...
... the Universe billions of years ago. With a big enough telescope, it is theoretically possible to map how stars and galaxies came into being and subsequently evolved nearly all the way back to the ‘Big Bang’, some 13.6 billion years ago. ...
Planets of Our, and Other, Solar Systems
... 1. Mg 26 is uniformly distributed throughout the solar system and throughout studied meteorites. 2. CAI’s (calcium rich inclusions) within meteorites have a very narrow (~1600K) temperature range within which they solidify, and this corresponds to a very narrow time range when they could incorporate ...
... 1. Mg 26 is uniformly distributed throughout the solar system and throughout studied meteorites. 2. CAI’s (calcium rich inclusions) within meteorites have a very narrow (~1600K) temperature range within which they solidify, and this corresponds to a very narrow time range when they could incorporate ...
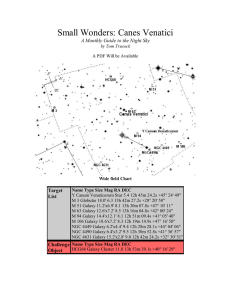
Small Wonders: Canes Venatici
... transparent night with my old 10" scope where the arms were easily visible. A 15" or 18" scope will show spiral structure under nearly any conditions, and I was recently blessed with a look at it through a 25" at a dark sky site. In the 25" telescope, the arms took on a very well defined look and we ...
... transparent night with my old 10" scope where the arms were easily visible. A 15" or 18" scope will show spiral structure under nearly any conditions, and I was recently blessed with a look at it through a 25" at a dark sky site. In the 25" telescope, the arms took on a very well defined look and we ...
Galaxy Structure
... approximately 100 kpc and may account for as much as (3–6) × 1012M⊙ (Fich and Tremaine 1991). It exceeds by far the mass contained in the spiral disk and bulge region. ...
... approximately 100 kpc and may account for as much as (3–6) × 1012M⊙ (Fich and Tremaine 1991). It exceeds by far the mass contained in the spiral disk and bulge region. ...
The Magellan 20 Telescope Science Goals
... in the plane of the sky. A 3D tomographic reconstruction of the mass distribution and kinematics of the IGM becomes possible, mapping tenuous structures with densities down to the mean density of the universe. A combination with a traditional galaxy redshift survey of the same volume sampled by the ...
... in the plane of the sky. A 3D tomographic reconstruction of the mass distribution and kinematics of the IGM becomes possible, mapping tenuous structures with densities down to the mean density of the universe. A combination with a traditional galaxy redshift survey of the same volume sampled by the ...
19. Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed Our goals for learning
... • Although all the Milky Way’s interstellar gas has roughly the same composition — about 70% hydrogen, 28% helium, and 2% heavy elements (by mass) — gas in different stages of the stargas-star cycle produces different kinds of radiation. Molecules in molecular clouds and hydrogen atoms in atomic gas ...
... • Although all the Milky Way’s interstellar gas has roughly the same composition — about 70% hydrogen, 28% helium, and 2% heavy elements (by mass) — gas in different stages of the stargas-star cycle produces different kinds of radiation. Molecules in molecular clouds and hydrogen atoms in atomic gas ...
Cosmology and Particle Physics
... All observers see themselves as stationary; the other objects in space appear to be moving away from them. Hubble was directly responsible for discovering that the universe was much larger than had previously been imagined and that it had this amazing characteristic of rapid expansion. Universal exp ...
... All observers see themselves as stationary; the other objects in space appear to be moving away from them. Hubble was directly responsible for discovering that the universe was much larger than had previously been imagined and that it had this amazing characteristic of rapid expansion. Universal exp ...
ies la arboleda – centro tic - plurilingüe
... (A)- The universe was contained in a single point in space. All of the matter and energy of space was then contained at this point. What existed prior to this event is completely unknown. About 13.73 billion years (13.730.000.000 years) ago a tremendous explosion started the expansion of the univers ...
... (A)- The universe was contained in a single point in space. All of the matter and energy of space was then contained at this point. What existed prior to this event is completely unknown. About 13.73 billion years (13.730.000.000 years) ago a tremendous explosion started the expansion of the univers ...
The Cosmic Perspective Other Planetary Systems: The New Science
... • We cannot measure an exact mass for a planet without knowing the tilt of its orbit, because Doppler shift tells us only the velocity toward or away from us. • Doppler data give us lower limits on masses. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • We cannot measure an exact mass for a planet without knowing the tilt of its orbit, because Doppler shift tells us only the velocity toward or away from us. • Doppler data give us lower limits on masses. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
spectral lines as distant measurement tools
... Figure 2: The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram (HRD) plotting intrinsic stellar brightness (vertical) against spectral type (horizontal). The horizontal axis follows Annie Cannon’s Harvard classification which you just rediscovered. Stars to the right have red appearance, to the left they are blue. The ...
... Figure 2: The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram (HRD) plotting intrinsic stellar brightness (vertical) against spectral type (horizontal). The horizontal axis follows Annie Cannon’s Harvard classification which you just rediscovered. Stars to the right have red appearance, to the left they are blue. The ...
Orbital and Physical Characteristics of Extrasolar Planets Systems
... • The distribution of exoplanet masses increases for decreasing planet masses (Figure 5). It is ascertained relatively large number of planets with very low masses (M sin i≤0,2Mj ) (Figure 6). The same conclusion has been made also by the authors of [6–10]; • The previous analyses established that t ...
... • The distribution of exoplanet masses increases for decreasing planet masses (Figure 5). It is ascertained relatively large number of planets with very low masses (M sin i≤0,2Mj ) (Figure 6). The same conclusion has been made also by the authors of [6–10]; • The previous analyses established that t ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... astronomical unit = the mean distance of the Earth from Sun = 150 million kms.), with masses 1.1 M0 and 0.9 M 0 . The third component, Proxima Centauri orbits around the center of mass (of A and B) at a distance of about 10,000 AU with a mass of ...
... astronomical unit = the mean distance of the Earth from Sun = 150 million kms.), with masses 1.1 M0 and 0.9 M 0 . The third component, Proxima Centauri orbits around the center of mass (of A and B) at a distance of about 10,000 AU with a mass of ...
Temperate Earth-sized planets transiting a nearby ultracool
... Research Excellence, Support and Training (CREST) are operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Bangalore. M.G., E.J. and V.V.G. are FRS–FNRS research associates. L.D. and C.O. are FRS–FNRS PhD students. We thank V. Mégevand, the ASTELCO telescope team, S. Sohy, V. Chantry, and A. Fumel for ...
... Research Excellence, Support and Training (CREST) are operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Bangalore. M.G., E.J. and V.V.G. are FRS–FNRS research associates. L.D. and C.O. are FRS–FNRS PhD students. We thank V. Mégevand, the ASTELCO telescope team, S. Sohy, V. Chantry, and A. Fumel for ...
Unit 1
... – Stars spend most of their lives on the main sequence – Lifetime depends on the star’s mass and luminosity • More luminous stars burn their energy more rapidly than less luminous stars. • High-mass stars are more luminous than low-mass stars • High mass stars are therefore shorter-lived! ...
... – Stars spend most of their lives on the main sequence – Lifetime depends on the star’s mass and luminosity • More luminous stars burn their energy more rapidly than less luminous stars. • High-mass stars are more luminous than low-mass stars • High mass stars are therefore shorter-lived! ...
presentation (PPT format)
... galaxy, the average motion and how the galaxy brightness will appear distributed: this is called fundamental plane Measuring 2 quantities we can get the actual size of the galaxy and by the apparent size get the distance ...
... galaxy, the average motion and how the galaxy brightness will appear distributed: this is called fundamental plane Measuring 2 quantities we can get the actual size of the galaxy and by the apparent size get the distance ...
Institute for Astrophysical Research Seminar Series
... From Foreground Trash to Bountiful Treasure: Galactic Stratigraphy, Magnetic Activity and the Kinematics of M dwarfs in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey ...
... From Foreground Trash to Bountiful Treasure: Galactic Stratigraphy, Magnetic Activity and the Kinematics of M dwarfs in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey ...
PDF format
... • We cannot measure an exact mass for a planet without knowing the tilt of its orbit, because Doppler shift tells us only the velocity toward or away from us. • Doppler data give us lower limits on masses. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • We cannot measure an exact mass for a planet without knowing the tilt of its orbit, because Doppler shift tells us only the velocity toward or away from us. • Doppler data give us lower limits on masses. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
The Galactic Halo The Galactic Disk Height and Thickness of MW
... young stars, but old stars are also present. rich in dust and gas. star formation is ongoing. stars moving in circular orbits around the Galactic center. ...
... young stars, but old stars are also present. rich in dust and gas. star formation is ongoing. stars moving in circular orbits around the Galactic center. ...
Chapter 13 Power Point Lecture
... • We cannot measure an exact mass for a planet without knowing the tilt of its orbit, because Doppler shift tells us only the velocity toward or away from us. • Doppler data give us lower limits on masses. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • We cannot measure an exact mass for a planet without knowing the tilt of its orbit, because Doppler shift tells us only the velocity toward or away from us. • Doppler data give us lower limits on masses. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Astro 27 Solar System Formation and ExoPlanets Slide Show
... 1. Mg 26 is uniformly distributed throughout the solar system and throughout studied meteorites. 2. CAI’s (calcium rich inclusions) within meteorites have a very narrow (~1600K) temperature range within which they solidify, and this corresponds to a very narrow time range when they could incorporate ...
... 1. Mg 26 is uniformly distributed throughout the solar system and throughout studied meteorites. 2. CAI’s (calcium rich inclusions) within meteorites have a very narrow (~1600K) temperature range within which they solidify, and this corresponds to a very narrow time range when they could incorporate ...
Lecture8_v2 - Lick Observatory
... there and produce a single whirl, in which, colliding with one another and revolving in all manner of ways, they begin to separate like to like. ...
... there and produce a single whirl, in which, colliding with one another and revolving in all manner of ways, they begin to separate like to like. ...
Transit surveys for Earths in the habitable zones of white dwarfs
... added noise (LSST Science Book 2009). I find LSST can detect >9 CHZ planets if η⊕ >5×10−3, where detection requires that at least three epochs fall within transit with two points each detected at >7σ. The LSST survey will be biased toward detecting shorter period (∝ P −4/3 ) and large-size planets t ...
... added noise (LSST Science Book 2009). I find LSST can detect >9 CHZ planets if η⊕ >5×10−3, where detection requires that at least three epochs fall within transit with two points each detected at >7σ. The LSST survey will be biased toward detecting shorter period (∝ P −4/3 ) and large-size planets t ...
New Worlds Ahead: The Discovery of Exoplanets
... also easier to find around low-mass stars than heavier stars. Furthermore, a planet must at least complete one full orbit in order to have its parameters constrained (although more orbits are usually needed to obtain good constraints). Hence when more data are collected with time, planets on larger ...
... also easier to find around low-mass stars than heavier stars. Furthermore, a planet must at least complete one full orbit in order to have its parameters constrained (although more orbits are usually needed to obtain good constraints). Hence when more data are collected with time, planets on larger ...
Space Interferometry Mission

The Space Interferometry Mission, or SIM, also known as SIM Lite (formerly known as SIM PlanetQuest), was a planned space telescope developed by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), in conjunction with contractor Northrop Grumman. One of the main goals of the mission was the hunt for Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of nearby stars other than the Sun. SIM was postponed several times and finally cancelled in 2010.In addition to hunting for extrasolar planets, SIM would have helped astronomers construct a map of the Milky Way galaxy. Other important tasks would have included collecting data to help pinpoint stellar masses for specific types of stars, assisting in the determination of the spatial distribution of dark matter in the Milky Way and in the Local Group of galaxies and using the gravitational microlensing effect to measure the mass of stars.The spacecraft would have used optical interferometry to accomplish these and other scientific goals. This technique collects light with multiple mirrors (in SIM's case, two) which is combined to make an interference pattern which can be very precisely measured.The initial contracts for SIM Lite were awarded in 1998, totaling US$200 million. Work on the SIM project required scientists and engineers to move through eight specific new technology milestones, and by November 2006, all eight had been completed.SIM Lite was originally scheduled for a 2005 launch, aboard an Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV). As a result of continued budget cuts, the launch date has been pushed back at least five times. NASA has set a preliminary launch date for 2015 and U.S. federal budget documents confirm that a launch date is expected ""no earlier"" than 2015. The budget cuts to SIM Lite are expected to continue through FY 2010. As of February 2007, many of the engineers working on the SIM program had moved on to other areas and projects, and NASA directed the project to allocate its resources toward engineering risk reduction. However, the preliminary budget for NASA for 2008 included zero dollars for SIM.In December 2007, the Congress restored funding for fiscal year 2008 as part of an omnibus appropriations bill which the President later signed. At the same time the Congress directed NASA to move the mission forward to the development phase. In 2009 the project continued its risk reduction work while waiting for the findings and recommendations of the Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey, Astro2010, performed by the National Academy of Sciences, which would determine the project's future.On 13 August 2010, the Astro2010 Decadal Report was released and did not recommend that NASA continue the development of the SIM Lite Astrometric Observatory. This prompted NASA Astronomy and Physics Director, Jon Morse, to issue a letter on 24 September 2010 to the SIM Lite project manager, informing him that NASA was discontinuing its sponsorship of the SIM Lite mission and directing the project to discontinue Phase B activities immediately or as soon as practical. Accordingly, all SIM Lite activities were closed down by the end of calendar year 2010.