Astronomy Report Southern Cross Authors Maria Constanza Pavez
... This circumpolar constellation (always situated above the horizon) of the South Hemisphere, is located between the Centauri and the Fly constellations, just above the Polar Antarctic Circle and it is crossed by the Milky Way. The Crux is visible the whole year between 25 N and 90 S degrees of latitu ...
... This circumpolar constellation (always situated above the horizon) of the South Hemisphere, is located between the Centauri and the Fly constellations, just above the Polar Antarctic Circle and it is crossed by the Milky Way. The Crux is visible the whole year between 25 N and 90 S degrees of latitu ...
sections 16-18 instructor notes
... iii. by examining orbits of high velocity stars. Such stars are nearby halo stars that have high apparent velocities relative to the Sun because most of their orbital motion is in the direction of the Galactic centre. The results depend upon the assumption that all such stars are bound to the Galax ...
... iii. by examining orbits of high velocity stars. Such stars are nearby halo stars that have high apparent velocities relative to the Sun because most of their orbital motion is in the direction of the Galactic centre. The results depend upon the assumption that all such stars are bound to the Galax ...
Project Medley Topics
... do these newly discovered planets compare to those in our solar system? Is there a reason that we detect the planets that we’re finding? Why not more Earth-like planets? Assignment 11 Define a Planet Make your own working definition for a planet, star, moon, asteroid and comet. Then, decide which c ...
... do these newly discovered planets compare to those in our solar system? Is there a reason that we detect the planets that we’re finding? Why not more Earth-like planets? Assignment 11 Define a Planet Make your own working definition for a planet, star, moon, asteroid and comet. Then, decide which c ...
NEO lecture 02 - Observations of NEOs
... The camera at ESA’s telescope on Tenerife is cooled by liquid nitrogen to temperatures such that the dark current and its noise contribution can be neglected. The readout is slow enough so that also its noise contribution can be neglected. The camera is operated with a bias of DNbias ~ 8000. For a ...
... The camera at ESA’s telescope on Tenerife is cooled by liquid nitrogen to temperatures such that the dark current and its noise contribution can be neglected. The readout is slow enough so that also its noise contribution can be neglected. The camera is operated with a bias of DNbias ~ 8000. For a ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... Figure 4. (a) If the angular velocity Ω was constant, then a given region of the galaxy would retain the same shape and only change in orientation. In this case, there would be no change in the distance between the Sun and any star. Hence there would be no Doppler shift. However, there would be prop ...
... Figure 4. (a) If the angular velocity Ω was constant, then a given region of the galaxy would retain the same shape and only change in orientation. In this case, there would be no change in the distance between the Sun and any star. Hence there would be no Doppler shift. However, there would be prop ...
The Distances to the Stars
... One of the most fundamental - and difficult - goals of astronomy is to measure the size of the Universe. At the end of the semester you will approach this goal and measure the distances to remote galaxies. However, the journey begins here with the measurement of the distances between the Sun and the ...
... One of the most fundamental - and difficult - goals of astronomy is to measure the size of the Universe. At the end of the semester you will approach this goal and measure the distances to remote galaxies. However, the journey begins here with the measurement of the distances between the Sun and the ...
Slide 1
... MF at high masses agrees with index (-1.3) predicted by Padoan & Nordlund theory (for simulation power spectrum slope) until ~ 0.5ff. But much flatter at later times (~ -0.7 to -0.5) due to core coalescence. Get clear turnover at low masses (not observed). ...
... MF at high masses agrees with index (-1.3) predicted by Padoan & Nordlund theory (for simulation power spectrum slope) until ~ 0.5ff. But much flatter at later times (~ -0.7 to -0.5) due to core coalescence. Get clear turnover at low masses (not observed). ...
Giant Planets at Small Orbital Distances
... tends to zero and its e ective temperature tends to Teq. The present Jupiter is depicted by a diamond in the lower right-hand corner of Figure 2. Its evolutionary track closely follows the convective Hayashi track. For a given mass and composition, every fully convective model lies on the same curve ...
... tends to zero and its e ective temperature tends to Teq. The present Jupiter is depicted by a diamond in the lower right-hand corner of Figure 2. Its evolutionary track closely follows the convective Hayashi track. For a given mass and composition, every fully convective model lies on the same curve ...
The Early Evolution of Protostars
... becomes tenuous The luminosity is not an indicator of stellar mass until nuclear burning dominates (Lacc ~ M*dMacc/dt) Stellar ages from tracks may be way off (Baraffe et al. 2009) The initial conditions for planet formation may be determined by time since last episode of disk instability ...
... becomes tenuous The luminosity is not an indicator of stellar mass until nuclear burning dominates (Lacc ~ M*dMacc/dt) Stellar ages from tracks may be way off (Baraffe et al. 2009) The initial conditions for planet formation may be determined by time since last episode of disk instability ...
Lecture 2: ppt, 5 MB
... Supernovae: Massive stars end in glorious explosions. Hubble found three mysterious rings of material encircling a doomed star that exploded as a supernova in 1987. During the years since the eruption, Hubble spied brightened spots on the ...
... Supernovae: Massive stars end in glorious explosions. Hubble found three mysterious rings of material encircling a doomed star that exploded as a supernova in 1987. During the years since the eruption, Hubble spied brightened spots on the ...
CHP 11
... 1. Protostars are difficult to observe because a. the protostar stage is very short. b. they are surrounded by cocoons of gas and dust. c. they radiate mainly in the infrared. d. all of the above e. they are all so far away that the light hasn't reached us yet. 2. The nuclear reactions in a star's c ...
... 1. Protostars are difficult to observe because a. the protostar stage is very short. b. they are surrounded by cocoons of gas and dust. c. they radiate mainly in the infrared. d. all of the above e. they are all so far away that the light hasn't reached us yet. 2. The nuclear reactions in a star's c ...
Lab Writeup
... (b) Put the Moon in the field of the telescope, and estimate the fraction of the width of the field occupied by the Moon. Discuss the value with your lab partners, and come up with a seems to be a best value. Let R be the fraction of the field of view occupied by the Moon, expressed as a number betw ...
... (b) Put the Moon in the field of the telescope, and estimate the fraction of the width of the field occupied by the Moon. Discuss the value with your lab partners, and come up with a seems to be a best value. Let R be the fraction of the field of view occupied by the Moon, expressed as a number betw ...
Observing Stellar Evolution
... generations of stars generated the elements that make up our planet and the chemical elements required for life. It is not an understatement to say that we exist because stars exist. The Observing Stellar Evolution Observing Program will be of interest to beginning observers as well as more experien ...
... generations of stars generated the elements that make up our planet and the chemical elements required for life. It is not an understatement to say that we exist because stars exist. The Observing Stellar Evolution Observing Program will be of interest to beginning observers as well as more experien ...
Shortв•`lived radioactivity in the early solar system: The Superв•`AGB
... Soni (2006) pollution of 26Al due to the winds of lowmass AGB stars (initial masses lower than approximately 1.5 Mx) and Wolf-Rayet stars (initial masses higher than approximately 60 Mx) would have left no signature in the O isotopic composition. These two stellar sources do not produce 60Fe and to ...
... Soni (2006) pollution of 26Al due to the winds of lowmass AGB stars (initial masses lower than approximately 1.5 Mx) and Wolf-Rayet stars (initial masses higher than approximately 60 Mx) would have left no signature in the O isotopic composition. These two stellar sources do not produce 60Fe and to ...
instructor notes stellar evolution, star clusters
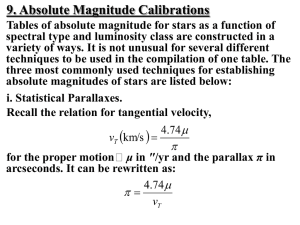
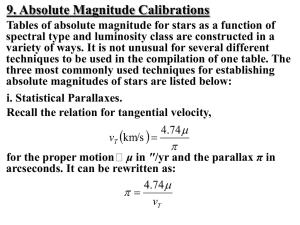
... stars is by means of the Wilson-Bappu effect, namely that the width of the central emission component of the Ca II K line in G and K-type stars is directly related to the absolute magnitude of the star — the broader the emission line width, denoted W2, the more luminous the star. The original calibr ...
... stars is by means of the Wilson-Bappu effect, namely that the width of the central emission component of the Ca II K line in G and K-type stars is directly related to the absolute magnitude of the star — the broader the emission line width, denoted W2, the more luminous the star. The original calibr ...
So, what`s the problem for high
... emission was made by physicists who built IR detectors and put them on telescopes. The first important far-ir source was the Galactic Center, discovered by a one-inch telescope on a high altitude balloon. It’s luminosity comes largely from formation of high-mass stars. The Infrared Astronomy Satelli ...
... emission was made by physicists who built IR detectors and put them on telescopes. The first important far-ir source was the Galactic Center, discovered by a one-inch telescope on a high altitude balloon. It’s luminosity comes largely from formation of high-mass stars. The Infrared Astronomy Satelli ...
supernova remnants: a link between massive stars and the
... that when the NS forms, the new star overshoots its equilibrium configuration giving a large compression to the neutron core (the core collapses in about 1 sec). This produces a rebound that sends a strong supersonic shock wave in about 0.01 sec that travels through the infalling matter. In a short ...
... that when the NS forms, the new star overshoots its equilibrium configuration giving a large compression to the neutron core (the core collapses in about 1 sec). This produces a rebound that sends a strong supersonic shock wave in about 0.01 sec that travels through the infalling matter. In a short ...
Hubble - STScI
... myriad of stars in our Milky Way Galaxy, he launched a revolution that changed our view of an Earth-centered universe. The launch of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope aboard the space shuttle Discovery 15 years ago initiated another revolution in astronomy. For the first time, a large telescope that see ...
... myriad of stars in our Milky Way Galaxy, he launched a revolution that changed our view of an Earth-centered universe. The launch of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope aboard the space shuttle Discovery 15 years ago initiated another revolution in astronomy. For the first time, a large telescope that see ...
Magnitudes and Colours of Stars - Lincoln
... 3. When both mv and the distance are known, the absolute visual magnitude Mv is calculated. ...
... 3. When both mv and the distance are known, the absolute visual magnitude Mv is calculated. ...
SEEING STARS! SEEING STARS!
... Print a copy of the Plough/Big Dipper Map (see end of activity sheet), and stick the map onto the piece of black cardboard. Poke a hole through where the stars appear on the paper (to transfer the map to the black card). Using the chart above measure a length of straw for each of the stars. Stick th ...
... Print a copy of the Plough/Big Dipper Map (see end of activity sheet), and stick the map onto the piece of black cardboard. Poke a hole through where the stars appear on the paper (to transfer the map to the black card). Using the chart above measure a length of straw for each of the stars. Stick th ...