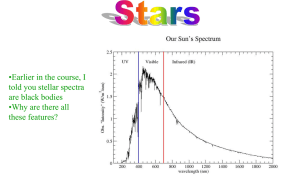
Star Location, Constellations and Intro to Solar System 1
... What to Remember - EW • What time during the day a star rises, is overhead, and sets changes with the seasons • look up on Star Chart (right ascension is the East-West location) • Changes 2 hours/month • Only on the Equator can all stars be viewed from a single location Hawaii or northern Chile a ...
... What to Remember - EW • What time during the day a star rises, is overhead, and sets changes with the seasons • look up on Star Chart (right ascension is the East-West location) • Changes 2 hours/month • Only on the Equator can all stars be viewed from a single location Hawaii or northern Chile a ...
Milky Way
... •When a low mass object orbits a high mass object, there is a simple relationship between the distance and the velocity: ...
... •When a low mass object orbits a high mass object, there is a simple relationship between the distance and the velocity: ...
Relative Speed of the Planets: UAC 2008
... "If the Moon be with Saturn or Mars, without the assistance of some good aspect from Jupiter and Venus; and if Saturn be slow in motion, or is going Retrograde, it’s so much the worse, and it’s one argument the sick will dye at that time; if other testimonies concurre, it’s more certaine." ...
... "If the Moon be with Saturn or Mars, without the assistance of some good aspect from Jupiter and Venus; and if Saturn be slow in motion, or is going Retrograde, it’s so much the worse, and it’s one argument the sick will dye at that time; if other testimonies concurre, it’s more certaine." ...
uv surface environment of earth-like planets orbiting
... We reduce the stellar flux of all other host stars by the same factor as a first order approximation of how much stellar flux would be received at a corresponding epoch for the other host stars. This procedure is not meant to capture the nuances of stellar evolution. Rather, it is intended to compare a ...
... We reduce the stellar flux of all other host stars by the same factor as a first order approximation of how much stellar flux would be received at a corresponding epoch for the other host stars. This procedure is not meant to capture the nuances of stellar evolution. Rather, it is intended to compare a ...
Exploring the cosmos
... Earth. He named it ‘helium’ after the Greek word for Sun, helios. This element was only found on Earth decades later. ...
... Earth. He named it ‘helium’ after the Greek word for Sun, helios. This element was only found on Earth decades later. ...
MASSIVE CLOSE BINARIES
... that Case B is the more frequent class of interacting binaries. Compared to Case B, it is trivial to understand that Case A components have smaller final masses whereas it is obvious that Case C (and non-interacting) binaries are similar to single stars. Equation 1 decides upon the mass loss during ...
... that Case B is the more frequent class of interacting binaries. Compared to Case B, it is trivial to understand that Case A components have smaller final masses whereas it is obvious that Case C (and non-interacting) binaries are similar to single stars. Equation 1 decides upon the mass loss during ...
6.1 Introduction
... in the gas from which stars have recently formed, such as the Orion nebula. Possibly these most metal-poor stars have been enriched by only one previous generation of stars which themselves presumably formed out of pristine gas. Thus, the chemical composition of the most metal-poor stars known is on ...
... in the gas from which stars have recently formed, such as the Orion nebula. Possibly these most metal-poor stars have been enriched by only one previous generation of stars which themselves presumably formed out of pristine gas. Thus, the chemical composition of the most metal-poor stars known is on ...
view of the Great Nebula. - Cool Cosmos
... combined with the large numbers of stars in the Milky Way, lead to the conclusion that planet formation is probably a common phenomenon. ...
... combined with the large numbers of stars in the Milky Way, lead to the conclusion that planet formation is probably a common phenomenon. ...
Slide 1
... • The primary scientific goal is to attain a signal to noise (SNR) ratio of 105:1 by combining a series of images of a target star over an extended integration time. – This is the SNR required to definitively observe an exo-planet transit in front of its parent star. – The target star will be betwee ...
... • The primary scientific goal is to attain a signal to noise (SNR) ratio of 105:1 by combining a series of images of a target star over an extended integration time. – This is the SNR required to definitively observe an exo-planet transit in front of its parent star. – The target star will be betwee ...
Oct 06, 2001
... C. It is moving away from the Earth. D. It will live longer than a B spectral class main sequence star. E. It is the same size as a red giant star of the same temperature. 28. There are reported to be about 6,000 stars visible to the naked eye. How many of those stars would you expect to be part of ...
... C. It is moving away from the Earth. D. It will live longer than a B spectral class main sequence star. E. It is the same size as a red giant star of the same temperature. 28. There are reported to be about 6,000 stars visible to the naked eye. How many of those stars would you expect to be part of ...
Entropy
... Classification of stars is based on the so-called HR diagram. Usually, the HR diagram is plotted either in the coordinates of color index (B–V) versus absolute stellar magnitude MV or in the coordinates of effective temperature Teff versus luminosity L. Stars tend to fall only into certain regions o ...
... Classification of stars is based on the so-called HR diagram. Usually, the HR diagram is plotted either in the coordinates of color index (B–V) versus absolute stellar magnitude MV or in the coordinates of effective temperature Teff versus luminosity L. Stars tend to fall only into certain regions o ...
The Evening Sky Map
... Conjunction – An alignment of two celestial bodies such that they present the least angular separation as viewed from Earth. Constellation – A defined area of the sky containing a star pattern. Diffuse Nebula – A cloud of gas illuminated by nearby stars. Double Star – Two stars that appear close to ...
... Conjunction – An alignment of two celestial bodies such that they present the least angular separation as viewed from Earth. Constellation – A defined area of the sky containing a star pattern. Diffuse Nebula – A cloud of gas illuminated by nearby stars. Double Star – Two stars that appear close to ...
Chapter 17 Star Stuff
... make iron, and end in supernova explosions • Low-mass stars with <2MSun have long lives, never become hot enough to fuse carbon nuclei, and end as white dwarfs • Intermediate mass stars can make elements heavier than carbon but end as white dwarfs ...
... make iron, and end in supernova explosions • Low-mass stars with <2MSun have long lives, never become hot enough to fuse carbon nuclei, and end as white dwarfs • Intermediate mass stars can make elements heavier than carbon but end as white dwarfs ...
Activity and rotation of Kepler-17
... planet eclipses its host star, it might cross in front of one of these spots creating a “bump” in the transit light curve. By modelling these spot signatures, it is possible to determine the physical properties of the spots such as size, temperature, and location. In turn, the monitoring of the spot ...
... planet eclipses its host star, it might cross in front of one of these spots creating a “bump” in the transit light curve. By modelling these spot signatures, it is possible to determine the physical properties of the spots such as size, temperature, and location. In turn, the monitoring of the spot ...
PDF - Amazing Space, STScI
... bulge of our Milky Way galaxy. Looking at a narrow slice of sky, the telescope nabbed 16 potential alien worlds orbiting a variety of stars. Astronomers have estimated that about 5 percent of stars in the galaxy may have Jupiter-sized, star-hugging planets. So this discovery means there are probably ...
... bulge of our Milky Way galaxy. Looking at a narrow slice of sky, the telescope nabbed 16 potential alien worlds orbiting a variety of stars. Astronomers have estimated that about 5 percent of stars in the galaxy may have Jupiter-sized, star-hugging planets. So this discovery means there are probably ...
Hubble Space Telescope`s
... bulge of our Milky Way galaxy. Looking at a narrow slice of sky, the telescope nabbed 16 potential alien worlds orbiting a variety of stars. Astronomers have estimated that about 5 percent of stars in the galaxy may have Jupiter-sized, star-hugging planets. So this discovery means there are probably ...
... bulge of our Milky Way galaxy. Looking at a narrow slice of sky, the telescope nabbed 16 potential alien worlds orbiting a variety of stars. Astronomers have estimated that about 5 percent of stars in the galaxy may have Jupiter-sized, star-hugging planets. So this discovery means there are probably ...
Cepheid Calibration
... Henrietta Leavitt: Timeless Contributions Sometimes a great advance in science is achieved through selfless work performed by a modest person not striving for recognition on the stage of history. Such was the contribution of Henrietta Leavitt, one of many female “computers” working at the Harvard C ...
... Henrietta Leavitt: Timeless Contributions Sometimes a great advance in science is achieved through selfless work performed by a modest person not striving for recognition on the stage of history. Such was the contribution of Henrietta Leavitt, one of many female “computers” working at the Harvard C ...
Abstracts - Physics of Evolved Stars 2015
... solar masses per year. Evolutionary models suggest that this phase does not last much longer than 10^5 years, implying that these stars are not likely to have lost more than one solar mass before entering the high mass-loss phase. To evolve into a post-AGB star, with a white dwarf cooling at the cen ...
... solar masses per year. Evolutionary models suggest that this phase does not last much longer than 10^5 years, implying that these stars are not likely to have lost more than one solar mass before entering the high mass-loss phase. To evolve into a post-AGB star, with a white dwarf cooling at the cen ...
Neutron Stars
... Periods shorter than this do not exist (such as in the previous calculation) because the object would have to rotate so fast it would overcome gravity and fly apart. ...
... Periods shorter than this do not exist (such as in the previous calculation) because the object would have to rotate so fast it would overcome gravity and fly apart. ...
Milky Way inner halo reveals its age | COSMOS magazine
... halo of the Milky Way are 11.4 billion years old, which is within the range of previous estimates of 10 to 14 billion years. The oldest reliably aged cluster of stars in the outer halo region to date is 13.5 billion years old. White dwarf stars form when normal stars like the sun have burnt up all t ...
... halo of the Milky Way are 11.4 billion years old, which is within the range of previous estimates of 10 to 14 billion years. The oldest reliably aged cluster of stars in the outer halo region to date is 13.5 billion years old. White dwarf stars form when normal stars like the sun have burnt up all t ...