01 - cloudfront.net
... above the main sequence on the H-R diagram. 20. bright main-sequence stars that are more massive than the sun and become larger than regular giant stars 21. A 22. C 23. A 24. D 25. A 26. A supernova is a star that has such a tremendous explosion that it blows itself apart. Unlike a nova, a white dwa ...
... above the main sequence on the H-R diagram. 20. bright main-sequence stars that are more massive than the sun and become larger than regular giant stars 21. A 22. C 23. A 24. D 25. A 26. A supernova is a star that has such a tremendous explosion that it blows itself apart. Unlike a nova, a white dwa ...
Stars and Sun
... Small and medium stars use up the gases in the core and become a giant star Large, cool stars, red in color Sun will become a giant in 5 billion years • Will cover orbit of Mercury, Venus and Earth • Will be a giant for a billion years ...
... Small and medium stars use up the gases in the core and become a giant star Large, cool stars, red in color Sun will become a giant in 5 billion years • Will cover orbit of Mercury, Venus and Earth • Will be a giant for a billion years ...
H-R Diagram Notes
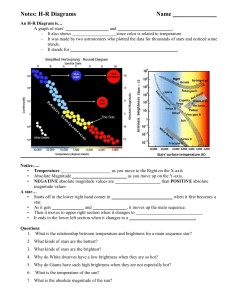
... • Temperature ______________________ as you move to the Right on the X-axis • Absolute Magnitude ________________________ as you move up on the Y-axis. • NEGATIVE absolute magnitude values are ____________________ than POSITIVE absolute magnitude values A star… • Starts off in the lower right hand c ...
... • Temperature ______________________ as you move to the Right on the X-axis • Absolute Magnitude ________________________ as you move up on the Y-axis. • NEGATIVE absolute magnitude values are ____________________ than POSITIVE absolute magnitude values A star… • Starts off in the lower right hand c ...
Hunting for Extrasolar Planets: Methods and Results
... A photometric method: Transits. This is the most active area of planet searching today because 1. It does not require a large telescope! 2. Chances of finding a planet-star system nearly edge-on is small, so need lots of observations; 3. Big payoff: you can learn about a stars diameter and mass, an ...
... A photometric method: Transits. This is the most active area of planet searching today because 1. It does not require a large telescope! 2. Chances of finding a planet-star system nearly edge-on is small, so need lots of observations; 3. Big payoff: you can learn about a stars diameter and mass, an ...
Extraterrestrial Life: Homework #5 Due, in class, Thursday April 10th
... Due, in class, Thursday April 10th 1) Briefly explain the radial velocity (or Doppler) method for detecting extrasolar planets. Why does this technique work best for finding massive planets, and those in short period orbits around their host stars? The method is described in lecture #19. It works be ...
... Due, in class, Thursday April 10th 1) Briefly explain the radial velocity (or Doppler) method for detecting extrasolar planets. Why does this technique work best for finding massive planets, and those in short period orbits around their host stars? The method is described in lecture #19. It works be ...
DOC
... 1. I can describe the differences between the relative sizes of various bodies in space (planetary systems, stars, star clusters, galaxies). 2. I can recall that the universe is made up of interacting bodies (planets, stars, etc.) that behave in a predictable way. 3. I can recall that our sola ...
... 1. I can describe the differences between the relative sizes of various bodies in space (planetary systems, stars, star clusters, galaxies). 2. I can recall that the universe is made up of interacting bodies (planets, stars, etc.) that behave in a predictable way. 3. I can recall that our sola ...
Stars: Other Suns
... • Measure directly only with binary systems of stars (lots!) • Revolve around center of mass • Apply Kepler’s 3rd law to get sum of masses from orbital period, separation (need distance!) ...
... • Measure directly only with binary systems of stars (lots!) • Revolve around center of mass • Apply Kepler’s 3rd law to get sum of masses from orbital period, separation (need distance!) ...
Light and Telescopes
... accuracy) observations of stellar and planetary positions over a period of 20 years • His research costed 5-10% of Danish GNP • shows that comets and novas are extralunar contrary to Aristotle • Shows that stars can change (Supernova of 1572) • Proves that comets are superlunar ...
... accuracy) observations of stellar and planetary positions over a period of 20 years • His research costed 5-10% of Danish GNP • shows that comets and novas are extralunar contrary to Aristotle • Shows that stars can change (Supernova of 1572) • Proves that comets are superlunar ...
Topic 2 Booster PP - AstronomyGCSE.co.uk
... Slightly smaller than Earth, dense CO2 atmosphere makes it very hot Mars Thin atmosphere mostly CO2, surface features, evidence of erosion Jupiter Biggest, mostly hydrogen, giant red spot, 4 Galilean moons Saturn Mostly hydrogen, ring system Uranus Mostly hydrogen, some methane makes it blue, discov ...
... Slightly smaller than Earth, dense CO2 atmosphere makes it very hot Mars Thin atmosphere mostly CO2, surface features, evidence of erosion Jupiter Biggest, mostly hydrogen, giant red spot, 4 Galilean moons Saturn Mostly hydrogen, ring system Uranus Mostly hydrogen, some methane makes it blue, discov ...
Frank Drake
... chance of major gamma ray bombardment. Too far out, and not enough supernovae occur to supply the elements needed for life. ...
... chance of major gamma ray bombardment. Too far out, and not enough supernovae occur to supply the elements needed for life. ...
Are Earth-like exoplanets common?
... number of lensing events at any given time of some baseline magnitude. ...
... number of lensing events at any given time of some baseline magnitude. ...
Before Reading
... • Do you think it is possible to count all the stars in the sky? Why or why not? ...
... • Do you think it is possible to count all the stars in the sky? Why or why not? ...
lec06_07oct2011
... * Capable of detecting (with some probability) multiple planets in a single lightcurve. In summary, the microlensing can be used to study the statistical abundance of exoplanets in our Galaxy with properties similar to the planets in our own Solar System. ...
... * Capable of detecting (with some probability) multiple planets in a single lightcurve. In summary, the microlensing can be used to study the statistical abundance of exoplanets in our Galaxy with properties similar to the planets in our own Solar System. ...
Why Is the Sun a Star
... atoms and radiating some energy, but not in the fantastic amounts like true stars. These stars are known as brown dwarfs since they emit some light but are not as bright as the smallest true stars. They are dimly glowing like a cooling campfire ember. When you look out into the night sky across vast ...
... atoms and radiating some energy, but not in the fantastic amounts like true stars. These stars are known as brown dwarfs since they emit some light but are not as bright as the smallest true stars. They are dimly glowing like a cooling campfire ember. When you look out into the night sky across vast ...
Stellar evolution, I
... the main sequence and into the region of the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram occupied by white dwarf stars. The densest stars (white dwarfs) pulsate the fastest, with time scales of minutes, while the least dense stars in the instability strip (K giants) pulsate most slowly, with time scales up to 100 d ...
... the main sequence and into the region of the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram occupied by white dwarf stars. The densest stars (white dwarfs) pulsate the fastest, with time scales of minutes, while the least dense stars in the instability strip (K giants) pulsate most slowly, with time scales up to 100 d ...
Exoplanets for Amateur Astronomers
... COROT has 4 CCD detectors. These detectors are arranged in a square pattern with two each dedicated to the planetary detection and asteroseismology. The field of view for planetary detection is 3.5°. It will observe perpendicular to its orbital plane, meaning there will be no Earth occultations, all ...
... COROT has 4 CCD detectors. These detectors are arranged in a square pattern with two each dedicated to the planetary detection and asteroseismology. The field of view for planetary detection is 3.5°. It will observe perpendicular to its orbital plane, meaning there will be no Earth occultations, all ...
chapter 18
... helium nuclei to form carbon nuclei. c) hydrogen nuclei to form helium nuclei. d) carbon nuclei to form magnesium nuclei. ...
... helium nuclei to form carbon nuclei. c) hydrogen nuclei to form helium nuclei. d) carbon nuclei to form magnesium nuclei. ...
E1 a-d
... Stars have ____________________ sizes, colors, and patterns. The ___________ of a star tells us the star’s temperature. ____________ can be red, yellow, or blue. Red Dwarf stars are smaller than other stars and have the ____________ temperature. ______ stars burn their fuel very slowly and ...
... Stars have ____________________ sizes, colors, and patterns. The ___________ of a star tells us the star’s temperature. ____________ can be red, yellow, or blue. Red Dwarf stars are smaller than other stars and have the ____________ temperature. ______ stars burn their fuel very slowly and ...
Document
... 2. In order from largest to smallest in size, write the name of each object in the chart below. WRITE IN PENCIL! 3. Write the letter of the definition that you believe goes with each term in the definition column. 4. Correct your answers in class. ERASE AND FIX! 5. Write out the name and correct def ...
... 2. In order from largest to smallest in size, write the name of each object in the chart below. WRITE IN PENCIL! 3. Write the letter of the definition that you believe goes with each term in the definition column. 4. Correct your answers in class. ERASE AND FIX! 5. Write out the name and correct def ...
After Dark in Allenspark
... Because 1 billion mph/1 thousand mph = 1 million = mass of Ed/mass of planet). So, to find the planet, you look at the light from the star. When the star moves toward us, the light from the star is shifted slightly to the blue, and when it moves away, the light's shifted slightly to the red. Looking ...
... Because 1 billion mph/1 thousand mph = 1 million = mass of Ed/mass of planet). So, to find the planet, you look at the light from the star. When the star moves toward us, the light from the star is shifted slightly to the blue, and when it moves away, the light's shifted slightly to the red. Looking ...