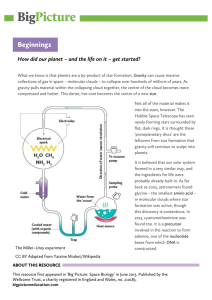
04_Home_Science3 (04_Home_Science3)
... What determines pitch? A. solids B. liquids C. amplitude D. the rate of vibration 15. Jane hears a fire truck siren that does not change in pitch or loudness. The fire truck is A. leaving the station. B. parked at the station. C. passing by the station. D. coming toward the station. 16. Accurate wea ...
... What determines pitch? A. solids B. liquids C. amplitude D. the rate of vibration 15. Jane hears a fire truck siren that does not change in pitch or loudness. The fire truck is A. leaving the station. B. parked at the station. C. passing by the station. D. coming toward the station. 16. Accurate wea ...
STAR SYTEMS AND GALAXIES
... • In a binary system usually one star is much brighter than the other. • We can detect binary systems easily if one star blocks another, called an eclipsing binary. • We have found planets moving around stars in other systems. We can only detect very large planets because the planets must have enoug ...
... • In a binary system usually one star is much brighter than the other. • We can detect binary systems easily if one star blocks another, called an eclipsing binary. • We have found planets moving around stars in other systems. We can only detect very large planets because the planets must have enoug ...
Astronomy 2
... uses data from lots of stars, so there are lots of dots. The position of each dot on the diagram corresponds to the star's luminosity and its temperature The vertical position represents the star's luminosity (absolute magnitude). The horizontal position represents the star's surface temperature ...
... uses data from lots of stars, so there are lots of dots. The position of each dot on the diagram corresponds to the star's luminosity and its temperature The vertical position represents the star's luminosity (absolute magnitude). The horizontal position represents the star's surface temperature ...
Astronomy Learning Objectives and Study Questions for Chapter 12
... 5. At the end of its main-sequence life, H-fusion in a medium mass star like Sol will shift to a shell outside the core and the star will become a _____. A. red dwarf B. red giant C. white dwarf D. blue-white supergiant E. supernova 6. The period during which an RR Lyrae or Cepheid variable star bri ...
... 5. At the end of its main-sequence life, H-fusion in a medium mass star like Sol will shift to a shell outside the core and the star will become a _____. A. red dwarf B. red giant C. white dwarf D. blue-white supergiant E. supernova 6. The period during which an RR Lyrae or Cepheid variable star bri ...
Stars Part 2 - westscidept
... • How bright a star looks in the sky from Earth is called apparent magnitude. • A dim star might look bright to us on Earth if it is close. At the same time, we may barely be able to see a very bright star if it is too far away. • Betelgeuse which is one of the brightest stars in the sky is 310 lig ...
... • How bright a star looks in the sky from Earth is called apparent magnitude. • A dim star might look bright to us on Earth if it is close. At the same time, we may barely be able to see a very bright star if it is too far away. • Betelgeuse which is one of the brightest stars in the sky is 310 lig ...
Star Life Cycles
... light a star gives off determines the star’s brightness. Stars close to Earth can appear bright, even if they do not give off much light. Additionally, very bright stars may appear faint if they are far away. Parallax – the apparent shift in position of an object when ...
... light a star gives off determines the star’s brightness. Stars close to Earth can appear bright, even if they do not give off much light. Additionally, very bright stars may appear faint if they are far away. Parallax – the apparent shift in position of an object when ...
1 - Quia
... c. the Milky Way. b. an asteroid belt. d. the moon’s orbit. 26. Which of the following is not a characteristic of gas giants? a. thick, gaseous atmospheres c. ring structures b. many satellites d. rocky surfaces 27. The moon orbits Earth at a distance of about ____________ kilometers. a. 4000 c. 400 ...
... c. the Milky Way. b. an asteroid belt. d. the moon’s orbit. 26. Which of the following is not a characteristic of gas giants? a. thick, gaseous atmospheres c. ring structures b. many satellites d. rocky surfaces 27. The moon orbits Earth at a distance of about ____________ kilometers. a. 4000 c. 400 ...
t2 images part 1
... Once all the hydrogen fuel is used up, gravity begins to crush the star. Stars die in spectacular fashion, either by expelling their outer layers or as huge super nova explosions. So much heat and energy is produced by these events that all of the heavier elements are formed. Large star ...
... Once all the hydrogen fuel is used up, gravity begins to crush the star. Stars die in spectacular fashion, either by expelling their outer layers or as huge super nova explosions. So much heat and energy is produced by these events that all of the heavier elements are formed. Large star ...
The “Big Bang” Theory
... • Matter started to “clump” back together • This was due to gravity • The galaxies, stars and planets formed from these clumps of dust and gas • There are billions of galaxies in the universe and each galaxy consists of billions of stars ...
... • Matter started to “clump” back together • This was due to gravity • The galaxies, stars and planets formed from these clumps of dust and gas • There are billions of galaxies in the universe and each galaxy consists of billions of stars ...
Microsoft Word Document
... 1. If a supernova occurred within a few dozen lightyears of earth, how would it affect life on our ...
... 1. If a supernova occurred within a few dozen lightyears of earth, how would it affect life on our ...
Ch 28 Fact Sheet
... _________________ 16. Type of spectrum that glowing neon gas produces in a spectroscope. _________________ 17. Type of spectrum produced by the atmosphere of a planet. _________________ 18. Type of pitch (high or low) produced as a car approaches you. _________________ 19. Shift question 28 is an ex ...
... _________________ 16. Type of spectrum that glowing neon gas produces in a spectroscope. _________________ 17. Type of spectrum produced by the atmosphere of a planet. _________________ 18. Type of pitch (high or low) produced as a car approaches you. _________________ 19. Shift question 28 is an ex ...
Search for Life in the Universe
... • Indirect detection of effect on parent star – Extrasolar planets around main sequence stars discovered in 1995 – Planets around neutron stars discovered previously – Spectroscopy (>100 cases): detect Doppler shift of stellar motion around center of mass – Astrometry (1 case): detect angular motion ...
... • Indirect detection of effect on parent star – Extrasolar planets around main sequence stars discovered in 1995 – Planets around neutron stars discovered previously – Spectroscopy (>100 cases): detect Doppler shift of stellar motion around center of mass – Astrometry (1 case): detect angular motion ...
Questions for this book (Word format)
... present understanding of hydrogen fusion in main-sequence stars. 2. The observed properties of a star are its surface temperature, its chemical composition and its radius (deduced from luminosity and surface temperature). Theoretical astrophysicists study stellar structure by constructing computer m ...
... present understanding of hydrogen fusion in main-sequence stars. 2. The observed properties of a star are its surface temperature, its chemical composition and its radius (deduced from luminosity and surface temperature). Theoretical astrophysicists study stellar structure by constructing computer m ...
File
... moon orbits the earth, affecting the ocean tides, and slowing the Earth’s rotation with its gravity. The Earth and its solar system are part of a bigger area of space called the Milky Way galaxy. The Milky Way is a galaxy named this way because it appears in the sky as a “Milky” glowing band. In 161 ...
... moon orbits the earth, affecting the ocean tides, and slowing the Earth’s rotation with its gravity. The Earth and its solar system are part of a bigger area of space called the Milky Way galaxy. The Milky Way is a galaxy named this way because it appears in the sky as a “Milky” glowing band. In 161 ...
MBuzaTalk2
... Importance of Stars and their role in the universe. Overview of all stars, and basic characteristics. Stellar Evolution: Start finish Path to a Neutron Star. Further work being done. ...
... Importance of Stars and their role in the universe. Overview of all stars, and basic characteristics. Stellar Evolution: Start finish Path to a Neutron Star. Further work being done. ...
Earth in the Universe
... the mass was pulled to the center and formed our sun. • After Earth and other planets were formed, their gravity pulled on other smaller objects causing them to collide with the planets. This is called an impact event. Where is there evidence for this? ...
... the mass was pulled to the center and formed our sun. • After Earth and other planets were formed, their gravity pulled on other smaller objects causing them to collide with the planets. This is called an impact event. Where is there evidence for this? ...
Sample final
... 17. An object orbits the Sun with a period of 350 years. What is its semi-major axis? How would you classify (composition or type) this object? In other words, what is it? Essay section part one Choose two of the following discoveries, and determine if they are surprising (not consistent with curren ...
... 17. An object orbits the Sun with a period of 350 years. What is its semi-major axis? How would you classify (composition or type) this object? In other words, what is it? Essay section part one Choose two of the following discoveries, and determine if they are surprising (not consistent with curren ...
Ch 28 Vocab cnp
... Chapter 28: Stars and Galaxies A halo of gases that is formed by the expelled layers of a star’s atmosphere The brightness of a star The measure of how bright a star would be if it were located 10 parsecs from Earth A group of millions, or even billions of stars held together by gravity A unit of me ...
... Chapter 28: Stars and Galaxies A halo of gases that is formed by the expelled layers of a star’s atmosphere The brightness of a star The measure of how bright a star would be if it were located 10 parsecs from Earth A group of millions, or even billions of stars held together by gravity A unit of me ...
Science 9 Unit E Section 1.0
... most useful information about it has come from the Hubble Space Telescope. One of the greatest debates among planetary astronomers currently is whether Pluto is a planet or not. It is a frozen ball of methane smaller than our moon. It doesn’t fit the pattern of the outer planets, which tend to be la ...
... most useful information about it has come from the Hubble Space Telescope. One of the greatest debates among planetary astronomers currently is whether Pluto is a planet or not. It is a frozen ball of methane smaller than our moon. It doesn’t fit the pattern of the outer planets, which tend to be la ...