Non-Cell-Autonomous Effect of Human SOD1G37R
... markers such as Pax6, Nestin, Olig2, and Islet1 after 2–3 weeks of differentiation (Figures 1A–1D). After 4 weeks under differentiation conditions, the cells started to express panneuronal markers such as TuJ1, and after 6–8 weeks, the cells exhibited motor neuron postmitotic lineage-specific marker ...
... markers such as Pax6, Nestin, Olig2, and Islet1 after 2–3 weeks of differentiation (Figures 1A–1D). After 4 weeks under differentiation conditions, the cells started to express panneuronal markers such as TuJ1, and after 6–8 weeks, the cells exhibited motor neuron postmitotic lineage-specific marker ...
Bidirectional propagation of Action potentials
... Signal propagation can be described uniform for neurons, regardsless of different neuron shapes and functions, in a model neuron. A signal travelling through the neuron can be seen as a linkage between four components. A input component, a trigger component, a long-distance component and a secretory ...
... Signal propagation can be described uniform for neurons, regardsless of different neuron shapes and functions, in a model neuron. A signal travelling through the neuron can be seen as a linkage between four components. A input component, a trigger component, a long-distance component and a secretory ...
Olfactory processing: maps, time and codes Gilles Laurent
... topography often disappears [21,22], probably because, at this scale, the cortex trades positional information for other attributes, such as orientation. Yet, this area represents a foveal visual angle much greater than the visual resolution limit. Thus, position in the topographic map does not carr ...
... topography often disappears [21,22], probably because, at this scale, the cortex trades positional information for other attributes, such as orientation. Yet, this area represents a foveal visual angle much greater than the visual resolution limit. Thus, position in the topographic map does not carr ...
Inhibition and Epilepsy
... blockade of both hyperpolarizing and depolarizing spontaneous postsynaptic potentials recorded with a K-acetate/QX314-filled electrode from a CA3 pyramidal neuron treated with 4aminopyridine. This effect is reversed by applying the GABAB receptor antagonist CGP-35348. In C, paired-pulse depression o ...
... blockade of both hyperpolarizing and depolarizing spontaneous postsynaptic potentials recorded with a K-acetate/QX314-filled electrode from a CA3 pyramidal neuron treated with 4aminopyridine. This effect is reversed by applying the GABAB receptor antagonist CGP-35348. In C, paired-pulse depression o ...
Nerve Cell Communication - URMC
... called dendrites that receive chemical signals. Receptor proteins on the cell membranes of dendrites can attach to chemical signal molecules. Also attached to the cell body is a long conducting branch called an axon. The axon conducts electrical signals called impulses over long distances. Th ...
... called dendrites that receive chemical signals. Receptor proteins on the cell membranes of dendrites can attach to chemical signal molecules. Also attached to the cell body is a long conducting branch called an axon. The axon conducts electrical signals called impulses over long distances. Th ...
Expression and Functional Interaction of Hepatocyte Growth Factor
... Chomczynski and Sacchi (1987). Control cultures received either 30 ng/ml of nerve growth factor (NGF) purified from mouse submandibular gland (Berninger et al., 1993) or an equal volume of bovine serum albumin. RNA electrophoresis and hybridization were performed as described earlier (Lindholm et al ...
... Chomczynski and Sacchi (1987). Control cultures received either 30 ng/ml of nerve growth factor (NGF) purified from mouse submandibular gland (Berninger et al., 1993) or an equal volume of bovine serum albumin. RNA electrophoresis and hybridization were performed as described earlier (Lindholm et al ...
Zebrafish and motor control over the last decade
... the head associated with activation of the entire serial set of cells and the weaker escapes produced by stimuli to the tail involving only the activation of the Mauthner cell. The implication of this work is that serially repeated hindbrain neurons may form functional groups associated with particu ...
... the head associated with activation of the entire serial set of cells and the weaker escapes produced by stimuli to the tail involving only the activation of the Mauthner cell. The implication of this work is that serially repeated hindbrain neurons may form functional groups associated with particu ...
Axons break in animals lacking β-spectrin
... The proximal end has initiated a new growth cone (open arrowhead). At 48 h, the secondary growth has reached the dorsal cord, albeit by an aberrant posterior route (open arrowheads). (The new dorsal and posterior neuron is DVB [asterisks], which arises postembryonically and sends an axon ventrally t ...
... The proximal end has initiated a new growth cone (open arrowhead). At 48 h, the secondary growth has reached the dorsal cord, albeit by an aberrant posterior route (open arrowheads). (The new dorsal and posterior neuron is DVB [asterisks], which arises postembryonically and sends an axon ventrally t ...
Title: 공학도를 위한 생물학 (2)
... to be explained by a general theory. And because ir performs too many computational functions to be explained by any single theory. So the computational fuction, so their major computational function do not give, explain the all ?[09:26]. And another common answer: we don't yet have enough about it, ...
... to be explained by a general theory. And because ir performs too many computational functions to be explained by any single theory. So the computational fuction, so their major computational function do not give, explain the all ?[09:26]. And another common answer: we don't yet have enough about it, ...
5. Discussion - UvA-DARE - University of Amsterdam
... Last, when exposed to an environment containing multiple visual patterns, an organism will benefit from the ability to differentially represent behaviorally relevant stimuli. Orientation-tuned cells can increase their ability of discriminating two very similar orientations by sharpening their tuning ...
... Last, when exposed to an environment containing multiple visual patterns, an organism will benefit from the ability to differentially represent behaviorally relevant stimuli. Orientation-tuned cells can increase their ability of discriminating two very similar orientations by sharpening their tuning ...
Protein Interacting with Never in Mitosis A
... differentiating into a variety of cell lineages such as odontoblasts, osteoblasts, adipocytes, and hepatocytes (1–3). In addition, hDPSCs were able to differentiate into glial or neuronal cells on the basis of cellular morphology, expression of the neural progenitor marker nestin, and expression of ...
... differentiating into a variety of cell lineages such as odontoblasts, osteoblasts, adipocytes, and hepatocytes (1–3). In addition, hDPSCs were able to differentiate into glial or neuronal cells on the basis of cellular morphology, expression of the neural progenitor marker nestin, and expression of ...
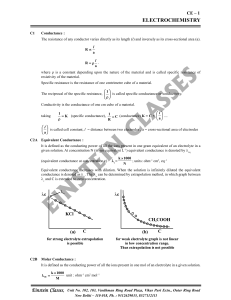
electrochemistry - einstein classes
... The standard reduction potential of Cu | Cu and Cu | Cu are 0.337 and 0.153 V respectively. The standard electrode potential of Cu+ | Cu half cell is (a) ...
... The standard reduction potential of Cu | Cu and Cu | Cu are 0.337 and 0.153 V respectively. The standard electrode potential of Cu+ | Cu half cell is (a) ...
Cell division and migration in a `genotype` for neural networks (Cell
... simulation experiments by Dawkins, 1986). This is a very important property that may allow the search space to be explored by the evolutionary process without exponential increase with increasing complexity of the phenotype. Kitano (1990) has criticized literal encodings for neural networks such as ...
... simulation experiments by Dawkins, 1986). This is a very important property that may allow the search space to be explored by the evolutionary process without exponential increase with increasing complexity of the phenotype. Kitano (1990) has criticized literal encodings for neural networks such as ...
Loading “EBSCOhost”
... http://web.ebscohost.com/ehost/delivery?vid=8&hid=104&sid=7d847e1c-c834-4ceb-a47b-7bcf28470435%40sessionmgr104 ...
... http://web.ebscohost.com/ehost/delivery?vid=8&hid=104&sid=7d847e1c-c834-4ceb-a47b-7bcf28470435%40sessionmgr104 ...
Cell division and migration in a `genotype` for neural
... simulation experiments by Dawkins, 1986). This is a very important property that may allow the search space to be explored by the evolutionary process without exponential increase with increasing complexity of the phenotype. Kitano (1990) has criticized literal encodings for neural networks such as ...
... simulation experiments by Dawkins, 1986). This is a very important property that may allow the search space to be explored by the evolutionary process without exponential increase with increasing complexity of the phenotype. Kitano (1990) has criticized literal encodings for neural networks such as ...
Expression of Neurofilament Subunits in Neurons of the Central and
... and Sternberger, 1983).Other explanations,suchaslimitations in the methods used to identify NF subunits in situ, are also possible(Hickey et al., 1983). Immunohistochemical studiesof the in situ distribution of NF subunitshave appeared(Dahl, 1983;Goldstein et al., 1983; Gown and Vogel, 1984; Hickey ...
... and Sternberger, 1983).Other explanations,suchaslimitations in the methods used to identify NF subunits in situ, are also possible(Hickey et al., 1983). Immunohistochemical studiesof the in situ distribution of NF subunitshave appeared(Dahl, 1983;Goldstein et al., 1983; Gown and Vogel, 1984; Hickey ...
Loss of Notch Activity in the Developing Central Nervous System
... cells, little is known about the potential function of Notch signaling in the survival of more mature neurons undergoing differentiation. To distinguish between the effects of Notch on neural progenitors and differentiating neurons, we immunostained mutant and wild-type forebrains with the Tuj1 anti ...
... cells, little is known about the potential function of Notch signaling in the survival of more mature neurons undergoing differentiation. To distinguish between the effects of Notch on neural progenitors and differentiating neurons, we immunostained mutant and wild-type forebrains with the Tuj1 anti ...
File
... Propagation - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pbg5E9GCNVE T6.5.6 - Propagation of nerve impulses is the result of local currents that cause each successive part of the axon to reach the threshold potential. Propagation of nerve impulses along the axon results from the diffusion of Na+ ions from th ...
... Propagation - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pbg5E9GCNVE T6.5.6 - Propagation of nerve impulses is the result of local currents that cause each successive part of the axon to reach the threshold potential. Propagation of nerve impulses along the axon results from the diffusion of Na+ ions from th ...
Activity 2 The Brain and Drugs - URMC
... 10. What happens in the receiving nerve cell after neurotransmitters have attached to receptors on the receiving cell? The receiving neuron makes a new impulse. ...
... 10. What happens in the receiving nerve cell after neurotransmitters have attached to receptors on the receiving cell? The receiving neuron makes a new impulse. ...
Culture of primary rat hippocampal neurons
... the cell. For example, growth cones at the tips of axons are sensitive to directional cues provided by gradients of chemoattractants and chemorepellants, which guide the axons to their targets (Oliva et al. 2003). Axons are also susceptible to local damage, a common cause of neurodegeneration. Axons ...
... the cell. For example, growth cones at the tips of axons are sensitive to directional cues provided by gradients of chemoattractants and chemorepellants, which guide the axons to their targets (Oliva et al. 2003). Axons are also susceptible to local damage, a common cause of neurodegeneration. Axons ...
State-dependent computations - Frankfurt Institute for Advanced
... network is not straightforward, and it will thus be useful to distinguish between two components, which we will refer to as the active and the hidden states. Active and hidden internal states. Traditionally, the internal state of a network is defined as the population of active neurons — we will ref ...
... network is not straightforward, and it will thus be useful to distinguish between two components, which we will refer to as the active and the hidden states. Active and hidden internal states. Traditionally, the internal state of a network is defined as the population of active neurons — we will ref ...
Dynamic computation in a recurrent network of heterogeneous
... of the clusters are unconstrained and have an equal likelihood of existing at any position. Therefore, clusters in a homogeneous network move in a random walk, constrained only by their interactions with nearby clusters [1]. In contrast, networks with heterogeneous neurons tend to bias the locations ...
... of the clusters are unconstrained and have an equal likelihood of existing at any position. Therefore, clusters in a homogeneous network move in a random walk, constrained only by their interactions with nearby clusters [1]. In contrast, networks with heterogeneous neurons tend to bias the locations ...
Cholinergic modulation of synaptic properties of cortical layer VI
... other thalamic nuclei as well. The functional role of cholinergic modulation of corticothalamic synapses might be to enhance the dynamic gain control mechanism previously proposed for the corticothalamic feedback (Lindström and Wróbel 1990, Granseth et al. 2002, Granseth 2004). According to this hyp ...
... other thalamic nuclei as well. The functional role of cholinergic modulation of corticothalamic synapses might be to enhance the dynamic gain control mechanism previously proposed for the corticothalamic feedback (Lindström and Wróbel 1990, Granseth et al. 2002, Granseth 2004). According to this hyp ...
The Biological Bases of Time-to
... ated by an approaching stimulus object is the critical stimulus variable that optimally fires these cells. The allocation of the LGMD - DCMD neurons to cell 4 of our schema presented in Table 1 is justified by their connection to pre-motor interneurons and motor-neurons known to be involved in flyin ...
... ated by an approaching stimulus object is the critical stimulus variable that optimally fires these cells. The allocation of the LGMD - DCMD neurons to cell 4 of our schema presented in Table 1 is justified by their connection to pre-motor interneurons and motor-neurons known to be involved in flyin ...
Robo1 Regulates the Migration and Laminar Distribution of Upper
... Indeed, an increasing number of genes have been identified that control the early phase of radial migration (Caviness and Rakic 1978; Gupta et al. 2002; Nadarajah and Parnavelas 2002; Tsai and Gleeson 2005; Cooper 2008; Huang 2009; Honda et al. 2011). In contrast, much less is known about how the ter ...
... Indeed, an increasing number of genes have been identified that control the early phase of radial migration (Caviness and Rakic 1978; Gupta et al. 2002; Nadarajah and Parnavelas 2002; Tsai and Gleeson 2005; Cooper 2008; Huang 2009; Honda et al. 2011). In contrast, much less is known about how the ter ...