Brain and Neuron Quiz Key
... Fill in the blanks with the correct words from the word bank. Some words may be used more than once, and some may not be used at all. 1. The frontal lobes control motor function. ...
... Fill in the blanks with the correct words from the word bank. Some words may be used more than once, and some may not be used at all. 1. The frontal lobes control motor function. ...
Neurons Short Version
... blood- brain barrier. Since neurons are so vitally important and can’t carry out mitosis for replacement the body particularly tries to prevent dangerous substances from reaching them. Play a role in supplying the neurons with glucose. ...
... blood- brain barrier. Since neurons are so vitally important and can’t carry out mitosis for replacement the body particularly tries to prevent dangerous substances from reaching them. Play a role in supplying the neurons with glucose. ...
Slide ()
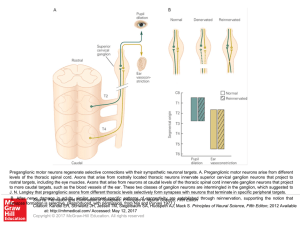
... rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons that project to more caudal targets, such as the blood vessels of the ear. These two classes of ganglion neurons are intermingled in the ganglion, which s ...
... rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons that project to more caudal targets, such as the blood vessels of the ear. These two classes of ganglion neurons are intermingled in the ganglion, which s ...
nervous system
... Sodium quick to rush in when gates open following both electrical and concentration gradients Potassium not quick to rush out only has concentration gradient to drive flow ...
... Sodium quick to rush in when gates open following both electrical and concentration gradients Potassium not quick to rush out only has concentration gradient to drive flow ...
File
... Neurons either fire maximally or not at all, this is referred to as the “all or none” response Increasing neuronal stimulation beyond a critical level will not result in an increased response Neurons response to increased stimulation by increasing the frequency of firing, not the intensity at wh ...
... Neurons either fire maximally or not at all, this is referred to as the “all or none” response Increasing neuronal stimulation beyond a critical level will not result in an increased response Neurons response to increased stimulation by increasing the frequency of firing, not the intensity at wh ...
3.E.2 Nervous System - kromko
... Two types of glial cells, oligodendrocytes and astrocytes, form the myelin sheath in the CNS. Astrocytes form the "blood-brain barrier”, separates brain cells from the blood and protects the brain from many common bacterial infections. ...
... Two types of glial cells, oligodendrocytes and astrocytes, form the myelin sheath in the CNS. Astrocytes form the "blood-brain barrier”, separates brain cells from the blood and protects the brain from many common bacterial infections. ...
overview of neural f..
... The sodium-potassium pump is an active process that returns & maintains levels of Na+ and K+ ...
... The sodium-potassium pump is an active process that returns & maintains levels of Na+ and K+ ...
The Nervous System
... 60 fibers at the same time—no neurilemma because of the absence of coiling of cells Regions of the brain and spinal cord with myelinated fibers called white matter. Gray matter contains mostly cell bodies and unmyelinated ...
... 60 fibers at the same time—no neurilemma because of the absence of coiling of cells Regions of the brain and spinal cord with myelinated fibers called white matter. Gray matter contains mostly cell bodies and unmyelinated ...
Structure of a Neuron
... Structure of a Neuron • Cell body (soma) – single, central nucleus – contains many multibranched dendrites – Which receive signals from other neurons. ...
... Structure of a Neuron • Cell body (soma) – single, central nucleus – contains many multibranched dendrites – Which receive signals from other neurons. ...
IOSR Journal of Computer Science (IOSR-JCE) e-ISSN: 2278-0661, p-ISSN: 2278-8727 PP 24-28 www.iosrjournals.org
... were able to reconstruct recognizable scenes and moving objects. Similar results in humans have since been achieved by researchers in Japan. Miguel Nicolelis, a professor at Duke University, in Durham, North Carolina, has been a prominent proponent of using multiple electrodes spread over a greater ...
... were able to reconstruct recognizable scenes and moving objects. Similar results in humans have since been achieved by researchers in Japan. Miguel Nicolelis, a professor at Duke University, in Durham, North Carolina, has been a prominent proponent of using multiple electrodes spread over a greater ...
NMSI - 1 Intro to the Nervous System
... • Dr. Rufus B. Weaver, the school's foremost anatomy professor had a special project in mind for Harriet — a project many colleagues thought impossible. • Weaver spent five exhausting months — working eight to 10 hours a day — painstakingly removing every bit of bone and flesh from the cadaver leavi ...
... • Dr. Rufus B. Weaver, the school's foremost anatomy professor had a special project in mind for Harriet — a project many colleagues thought impossible. • Weaver spent five exhausting months — working eight to 10 hours a day — painstakingly removing every bit of bone and flesh from the cadaver leavi ...
nervous system ppt
... Dendrite - extend from the cell body; receive information Neurofibrils - fibers within the axon ...
... Dendrite - extend from the cell body; receive information Neurofibrils - fibers within the axon ...
Ch 11 Part 1 - Groch Biology
... Supporting cells found in the CNS are called neuroglia. ___ _______________ Neurons are mitotic. ___ ____________________ Schwann cells and satellite cells are found only in the CNS. ___ ________________ Ependymal cells show irritability and conductivity. ___ ____________________ Almost 50% of the v ...
... Supporting cells found in the CNS are called neuroglia. ___ _______________ Neurons are mitotic. ___ ____________________ Schwann cells and satellite cells are found only in the CNS. ___ ________________ Ependymal cells show irritability and conductivity. ___ ____________________ Almost 50% of the v ...
Chapter 3 Notes (part 1) 1. Basic Elements of the Nervous System (a
... selectively-permeable membrane which separates the cytoplasm from the extracellular matrix contains ion channels and protein pumps which manage the flow of ions (charged particles) into and out of the cell C. Axon The part of the cell which carries the electrical signal (action potential); in ...
... selectively-permeable membrane which separates the cytoplasm from the extracellular matrix contains ion channels and protein pumps which manage the flow of ions (charged particles) into and out of the cell C. Axon The part of the cell which carries the electrical signal (action potential); in ...
Neurons
... • Neural crest – cranial, spinal, autonomic ganglia, neuroendocrine cells (APUD), Shwann cells of neuroglia • Monoblast – microglia ...
... • Neural crest – cranial, spinal, autonomic ganglia, neuroendocrine cells (APUD), Shwann cells of neuroglia • Monoblast – microglia ...
eating spaghetti!
... nerve impulse in the second neuron. The electrical signal is changing from positive to negative, and it moves the nerve impulse along a neuron. Neurons are in a fiber-like bundle called a nerve, and the impulses are all traveling in the same direction. ...
... nerve impulse in the second neuron. The electrical signal is changing from positive to negative, and it moves the nerve impulse along a neuron. Neurons are in a fiber-like bundle called a nerve, and the impulses are all traveling in the same direction. ...
Full-Text PDF
... overcome this limitation, studies using two-photon or multi-photon microscopy as imaging tools have been underway since the late 1990s [7–9]. Such non-linear microscopies are becoming standard tools for defining molecular mechanisms in the field of cell-based engineering and bio-medical research. Mo ...
... overcome this limitation, studies using two-photon or multi-photon microscopy as imaging tools have been underway since the late 1990s [7–9]. Such non-linear microscopies are becoming standard tools for defining molecular mechanisms in the field of cell-based engineering and bio-medical research. Mo ...
Nerve tissue for stu..
... Part of the perikaryon from which axon extends is called axon hillock. It is an area free of rER and GA. ...
... Part of the perikaryon from which axon extends is called axon hillock. It is an area free of rER and GA. ...
Slide ()
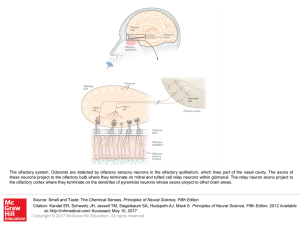
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
Neuron (Nerve Cell)
... By the time of its birth, a baby's brain consists of around 10 million nerve cells. ...
... By the time of its birth, a baby's brain consists of around 10 million nerve cells. ...
Nerve cells - Dr Magrann
... receptors. They are carried by nerve fibers of PNS to the CNS Motor (efferent) signals are carried away from the CNS. They innervate muscles and glands 1. Receive a signal. Can be any type of stimulus (change in environment, signal from another neuron, etc). 2. Transmit a signal to another location. ...
... receptors. They are carried by nerve fibers of PNS to the CNS Motor (efferent) signals are carried away from the CNS. They innervate muscles and glands 1. Receive a signal. Can be any type of stimulus (change in environment, signal from another neuron, etc). 2. Transmit a signal to another location. ...
No Slide Title
... During voluntary activation, recruitment and temporal summation are two mechanisms that regulate the strenght of muscle contraction, and usually these mechanisms act simultaneously ...
... During voluntary activation, recruitment and temporal summation are two mechanisms that regulate the strenght of muscle contraction, and usually these mechanisms act simultaneously ...