8th Grade - Astronomy
... A huge group of stars, star clusters, star systems, dust and gas bound together by Galaxy gravity. There are billions of galaxies in the universe each with billions of stars. Astronomers classify galaxies into three main categories: spiral, elliptical and irregular. Our own galaxy is called the Milk ...
... A huge group of stars, star clusters, star systems, dust and gas bound together by Galaxy gravity. There are billions of galaxies in the universe each with billions of stars. Astronomers classify galaxies into three main categories: spiral, elliptical and irregular. Our own galaxy is called the Milk ...
Multiple Choice - Secondary Science Wiki
... Sun. It contains smaller bodies that scientists think are pieces left over from the formation of the Solar System. Which of the following best states how scientists know that the Kuiper Belt is part of our solar system? A. B. C. D. ...
... Sun. It contains smaller bodies that scientists think are pieces left over from the formation of the Solar System. Which of the following best states how scientists know that the Kuiper Belt is part of our solar system? A. B. C. D. ...
Lecture 1
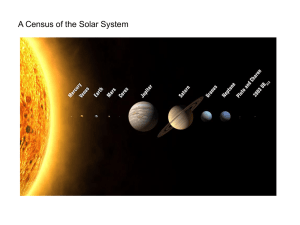
... The Solar System The Sun — An average star at the center of the solar system. The Sun is a G-class star with a surface temperature of 5’800 K and a central temperature of 15 million K. The Planets — Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune The Asteroid Belt — A ring of small ...
... The Solar System The Sun — An average star at the center of the solar system. The Sun is a G-class star with a surface temperature of 5’800 K and a central temperature of 15 million K. The Planets — Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune The Asteroid Belt — A ring of small ...
Name Period ______ Astronomy Unit Study Guide 1. _____
... G. a pattern of stars in the sky H. Greek astronomer who developed a geocentric model of planetary motion I. the idea that the earth is the center of the universe J. he developed a law that other galaxies are moving away from us ...
... G. a pattern of stars in the sky H. Greek astronomer who developed a geocentric model of planetary motion I. the idea that the earth is the center of the universe J. he developed a law that other galaxies are moving away from us ...
PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES HOMEWORK
... Solar wind particles traveling at 400 km/s (give your answer in days) A CME moving with a velocity of 1500 km/sec (give your answer in days) A jet aircraft traveling at 220 m/s (give your answer in years) ...
... Solar wind particles traveling at 400 km/s (give your answer in days) A CME moving with a velocity of 1500 km/sec (give your answer in days) A jet aircraft traveling at 220 m/s (give your answer in years) ...
Year 7 Gravity and Space
... The speed and direction of galaxies can be measured using light. It show that the Universe is expanding ...
... The speed and direction of galaxies can be measured using light. It show that the Universe is expanding ...
NEBULAR HYPOTHESIS
... inward due to gravitational forces ⦿ At the beginning of this collapse we form a SOLAR NEBULA. ...
... inward due to gravitational forces ⦿ At the beginning of this collapse we form a SOLAR NEBULA. ...
5-SolarSystem
... Fundamental Properties of the solar System 1. Planets and their satellites all lie in the same plane - the excliptic – to within a few degrees 2. Sun’s rotational equator aligned with ecliptic 3. Planetary orbits are nearly circular ellipses 4. Planets all revolve in same W -> E direction 5. Sun an ...
... Fundamental Properties of the solar System 1. Planets and their satellites all lie in the same plane - the excliptic – to within a few degrees 2. Sun’s rotational equator aligned with ecliptic 3. Planetary orbits are nearly circular ellipses 4. Planets all revolve in same W -> E direction 5. Sun an ...
The Sun
... • Class G • Color Yellow • Surface Temperature 5,000 – 6,000 ºC • Elements hydrogen and helium • Greek word for Sun is Helios ...
... • Class G • Color Yellow • Surface Temperature 5,000 – 6,000 ºC • Elements hydrogen and helium • Greek word for Sun is Helios ...
ASTR100 Fall 2009: Exam #2 Review Sheet EXAM IS THURSDAY
... 1] There are four main factors that affect surfaces. Name them: _________, _________, ________, _________. Which of these are found on Venus? ______________________ 2] Name some unique features of Earth that support life (Page 216 is helpful). _______ ________________________________________________ ...
... 1] There are four main factors that affect surfaces. Name them: _________, _________, ________, _________. Which of these are found on Venus? ______________________ 2] Name some unique features of Earth that support life (Page 216 is helpful). _______ ________________________________________________ ...
OUR SOLAR SYSTEM
... contains more elements heavier than hydrogen and helium ("metals" in astronomical parlance) than older population II stars. Elements heavier than hydrogen and helium were formed in the cores of ancient and exploding stars, so the first generation of stars had to die before the universe could be enri ...
... contains more elements heavier than hydrogen and helium ("metals" in astronomical parlance) than older population II stars. Elements heavier than hydrogen and helium were formed in the cores of ancient and exploding stars, so the first generation of stars had to die before the universe could be enri ...
answers_exam_review_space
... Gas Giants – the outer planets, furthest from the sun with atmospheres that consist mostly of gases such as hydrogen and helium Orbit – the path an object takes as it moves around another object i.e. planets orbit around the sun Fill in the blanks for each of the following questions: 1. universe 20. ...
... Gas Giants – the outer planets, furthest from the sun with atmospheres that consist mostly of gases such as hydrogen and helium Orbit – the path an object takes as it moves around another object i.e. planets orbit around the sun Fill in the blanks for each of the following questions: 1. universe 20. ...
BABYLON and SUMERIA 3000BC
... the heavenly spheres and heavenly bodies (stars and planets). Each of the four earthly elements has its natural place. All that is earthly tends toward the center of the universe, i.e., the center of the Earth. Water tends toward a sphere surrounding the center. Air tends toward a sphere surrounding ...
... the heavenly spheres and heavenly bodies (stars and planets). Each of the four earthly elements has its natural place. All that is earthly tends toward the center of the universe, i.e., the center of the Earth. Water tends toward a sphere surrounding the center. Air tends toward a sphere surrounding ...
Unit 2
... Abundant water – 70% is covered with water. The water keeps the Earth at a temperature that allows life. ...
... Abundant water – 70% is covered with water. The water keeps the Earth at a temperature that allows life. ...
Planetarium Field Guide 2015-2016 Third Grade
... How many planets are there in our solar system? Is it eight or nine? What is the difference between the Sun and the planets? How are the inner planets different than the outer planets? Program: “Nine Planets and Counting” The program takes students on a tour to explore the many objects that populate ...
... How many planets are there in our solar system? Is it eight or nine? What is the difference between the Sun and the planets? How are the inner planets different than the outer planets? Program: “Nine Planets and Counting” The program takes students on a tour to explore the many objects that populate ...
Slides
... take place at the core of the sun. The entire supply of hydrogen will have been turned to helium. Once this happens, the sun will go from being a main sequence star to a red giant. The diameter of a red giant is typically 260 times larger than that of a main sequence star. The sun will decrease in t ...
... take place at the core of the sun. The entire supply of hydrogen will have been turned to helium. Once this happens, the sun will go from being a main sequence star to a red giant. The diameter of a red giant is typically 260 times larger than that of a main sequence star. The sun will decrease in t ...
Components of the Solar System Learning Targets
... Mercury no atmosphere, closest to sun, shortest year, 59 earth day rotation, cratered like moon, layers, volcanic activity, no moons, largest difference in temperature Venus hottest, greenhouse effect, dense atmosphere, rotates opposite of other planets, Earth’s sister (because of size only), layers ...
... Mercury no atmosphere, closest to sun, shortest year, 59 earth day rotation, cratered like moon, layers, volcanic activity, no moons, largest difference in temperature Venus hottest, greenhouse effect, dense atmosphere, rotates opposite of other planets, Earth’s sister (because of size only), layers ...
Monday – October 29th - East Hanover Township School District
... With over 63 moons, you might say I have a lot. Look with a telescope to see my big, red spot. The spot is a wind storm, swirling around. High in the night sky is where I can be found. Which planet am I? ...
... With over 63 moons, you might say I have a lot. Look with a telescope to see my big, red spot. The spot is a wind storm, swirling around. High in the night sky is where I can be found. Which planet am I? ...
Astro 101-001 Summer 2013 (Howard) Assignment #3 Due: Wed
... objects, as cold as Pluto; (c) They are extremely hot, but cooler than the surrounding areas of the Sun; (d) They are solid bodies floating on the surface of the Sun; (e) They are associated with areas of very low magnetic fields. 6. The primary source of the Sun's energy is: (a) oxidation of carbon ...
... objects, as cold as Pluto; (c) They are extremely hot, but cooler than the surrounding areas of the Sun; (d) They are solid bodies floating on the surface of the Sun; (e) They are associated with areas of very low magnetic fields. 6. The primary source of the Sun's energy is: (a) oxidation of carbon ...
The Solar System
... Nebular Model, as the best supported explanation • It explains why… – Planets are so far apart – In the same plane – orbit in the same direction – They have nearly circular orbits – Why some are terrestrial and some gaseous ...
... Nebular Model, as the best supported explanation • It explains why… – Planets are so far apart – In the same plane – orbit in the same direction – They have nearly circular orbits – Why some are terrestrial and some gaseous ...
Our Solar System ppt
... All planets orbit the sun in almost-circular elliptical orbits on approximately the same plane (the ecliptic). Dwarf Planets, comets, asteroids, and meteoroids also orbit the sun Most Satellites/Moons orbit planets (some orbit dwarf planets or even asteroids) Almost all planets, dwarf planets, and m ...
... All planets orbit the sun in almost-circular elliptical orbits on approximately the same plane (the ecliptic). Dwarf Planets, comets, asteroids, and meteoroids also orbit the sun Most Satellites/Moons orbit planets (some orbit dwarf planets or even asteroids) Almost all planets, dwarf planets, and m ...
Earth Science SOL Review Sheet #1
... classic planets, dwarf planets, comets, and asteroids. The sun is made of mostly hydrogen gas and its energy comes from nuclear fusion reactions. Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are terrestrial planets. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are gas giants. The asteroid belt is located between Mars ...
... classic planets, dwarf planets, comets, and asteroids. The sun is made of mostly hydrogen gas and its energy comes from nuclear fusion reactions. Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are terrestrial planets. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are gas giants. The asteroid belt is located between Mars ...
Unit 3 *The Solar System* 6th Grade Space Science
... Key Concept In general, the farther away a planet is from ...
... Key Concept In general, the farther away a planet is from ...
Space Flight to the Stars - Laureate International College
... Beyond the asteroid belt lie the four gas giant planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. ...
... Beyond the asteroid belt lie the four gas giant planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. ...
Unit 5: THE SOLAR SYSTEM 1.THE SOLAR SYSTEM
... 1.2. Our Solar System The Solar System is our Planetary System. The Solar System is about five billion years old. It is an exciting place made up of a star we call the Sun, and celestial bodies, such as planets, dwarf planets, moons or satellites, asteroids, comets, and many other smaller bodies. Th ...
... 1.2. Our Solar System The Solar System is our Planetary System. The Solar System is about five billion years old. It is an exciting place made up of a star we call the Sun, and celestial bodies, such as planets, dwarf planets, moons or satellites, asteroids, comets, and many other smaller bodies. Th ...
Solar System

The Solar System comprises the Sun and the planetary system that orbits it, either directly or indirectly. Of those objects that orbit the Sun directly, the largest eight are the planets, with the remainder being significantly smaller objects, such as dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies such as comets and asteroids. Of those that orbit the Sun indirectly, two are larger than the smallest planet.The Solar System formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar molecular cloud. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun, with most of the remaining mass contained in Jupiter. The four smaller inner planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars, are terrestrial planets, being primarily composed of rock and metal. The four outer planets are giant planets, being substantially more massive than the terrestrials. The two largest, Jupiter and Saturn, are gas giants, being composed mainly of hydrogen and helium; the two outermost planets, Uranus and Neptune, are ice giants, being composed largely of substances with relatively high melting points compared with hydrogen and helium, called ices, such as water, ammonia and methane. All planets have almost circular orbits that lie within a nearly flat disc called the ecliptic.The Solar System also contains smaller objects. The asteroid belt, which lies between Mars and Jupiter, mostly contains objects composed, like the terrestrial planets, of rock and metal. Beyond Neptune's orbit lie the Kuiper belt and scattered disc, populations of trans-Neptunian objects composed mostly of ices, and beyond them a newly discovered population of sednoids. Within these populations are several dozen to possibly tens of thousands of objects large enough to have been rounded by their own gravity. Such objects are categorized as dwarf planets. Identified dwarf planets include the asteroid Ceres and the trans-Neptunian objects Pluto and Eris. In addition to these two regions, various other small-body populations, including comets, centaurs and interplanetary dust, freely travel between regions. Six of the planets, at least three of the dwarf planets, and many of the smaller bodies are orbited by natural satellites, usually termed ""moons"" after the Moon. Each of the outer planets is encircled by planetary rings of dust and other small objects.The solar wind, a stream of charged particles flowing outwards from the Sun, creates a bubble-like region in the interstellar medium known as the heliosphere. The heliopause is the point at which pressure from the solar wind is equal to the opposing pressure of interstellar wind; it extends out to the edge of the scattered disc. The Oort cloud, which is believed to be the source for long-period comets, may also exist at a distance roughly a thousand times further than the heliosphere. The Solar System is located in the Orion Arm, 26,000 light-years from the center of the Milky Way.