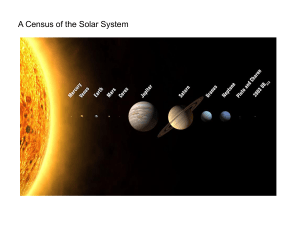
A Census of the Solar System
... 1. Planets and their satellites all lie in the same plane - the ecliptic – to within a few degrees 2. Sun’s rotational equator aligned with ecliptic 3. Planetary orbits are nearly circular ellipses 4. Planets all revolve in same W -> E direction 5. Sun and planets all rotate on axes in same W –E dir ...
... 1. Planets and their satellites all lie in the same plane - the ecliptic – to within a few degrees 2. Sun’s rotational equator aligned with ecliptic 3. Planetary orbits are nearly circular ellipses 4. Planets all revolve in same W -> E direction 5. Sun and planets all rotate on axes in same W –E dir ...
Benchmark One Study Guide: Science Benchmark Wed
... 4. How far from the center bulge is our Sun? 5. What unit of measure do we use to measure distance within the Milky Way Galaxy? 6. Identify and describe each type of galaxy below. ...
... 4. How far from the center bulge is our Sun? 5. What unit of measure do we use to measure distance within the Milky Way Galaxy? 6. Identify and describe each type of galaxy below. ...
TY Course Day 2 Friday Solar System
... While the asteroid belt is composed largely of rocky or metal objects, EKB and Oort cloud objects are mostly icy, comprising dust and frozen volatiles such as water, methane, carbon dioxide and ammonia (termed "ices”). ...
... While the asteroid belt is composed largely of rocky or metal objects, EKB and Oort cloud objects are mostly icy, comprising dust and frozen volatiles such as water, methane, carbon dioxide and ammonia (termed "ices”). ...
20081 Study Guide_77-120
... 2. the orbit period of the planet; if you know a planet’s distance from the sun, you can determine the orbit period using Kepler’s third law. 3. The dark surface of asteroids composed of carbon would reflect little light; the metallic surface of asteroids composed of iron and nickel would reflect li ...
... 2. the orbit period of the planet; if you know a planet’s distance from the sun, you can determine the orbit period using Kepler’s third law. 3. The dark surface of asteroids composed of carbon would reflect little light; the metallic surface of asteroids composed of iron and nickel would reflect li ...
Lecture7 - UCSB Physics
... Many planets about the size of Jupiter orbit closer to their star than Mercury does to our Sun! Early studies subject to a selection bias. Most sensitive to short period planets. ...
... Many planets about the size of Jupiter orbit closer to their star than Mercury does to our Sun! Early studies subject to a selection bias. Most sensitive to short period planets. ...
Big Bang
... • An Extrasolar planet, or exoplanet, is a planet outside the Solar System. • First exoplanet was confirmed indirectly at G-type star 51 Pegasi in 1995 • So far, about 500 planets were confirmed through the astronomical observations. • Exoplanets are an extremely fainter than those of central stars ...
... • An Extrasolar planet, or exoplanet, is a planet outside the Solar System. • First exoplanet was confirmed indirectly at G-type star 51 Pegasi in 1995 • So far, about 500 planets were confirmed through the astronomical observations. • Exoplanets are an extremely fainter than those of central stars ...
Chapter 4: The Solar System
... orbits of Mars and Jupiter. • Comets are icy, and are believed to have formed early in the solar system’s life. • Major planets orbit Sun in same sense, and all but Venus rotate in that sense as well. • Planetary orbits lie almost in the same plane. ...
... orbits of Mars and Jupiter. • Comets are icy, and are believed to have formed early in the solar system’s life. • Major planets orbit Sun in same sense, and all but Venus rotate in that sense as well. • Planetary orbits lie almost in the same plane. ...
Quiz # 2
... Bonus. The spectrum of a star shows an equivalent set of dark absorption lines to those of the Sun, but with one exception. Every line appears at a slightly longer wavelength, shifted toward the red end of the spectrum. What conclusion can be drawn from this observation? A) A cloud of cold gas and ...
... Bonus. The spectrum of a star shows an equivalent set of dark absorption lines to those of the Sun, but with one exception. Every line appears at a slightly longer wavelength, shifted toward the red end of the spectrum. What conclusion can be drawn from this observation? A) A cloud of cold gas and ...
The Solar System - 3rdgrade-libertyschool
... • Saturn is best known for its rings • The rings around Saturn are made up of frozen gases, water ice and rock. So the rings are not solid bands around the planet • There are 31 moons orbiting Saturn ...
... • Saturn is best known for its rings • The rings around Saturn are made up of frozen gases, water ice and rock. So the rings are not solid bands around the planet • There are 31 moons orbiting Saturn ...
Star Constellations - rosedalegrade9astronomy
... Astronomy is the study of the universe and the objects in it. The Universe is all the matter and energy that exists everywhere. The universe includes: o All stars and constellations, galaxies ...
... Astronomy is the study of the universe and the objects in it. The Universe is all the matter and energy that exists everywhere. The universe includes: o All stars and constellations, galaxies ...
The Planets in the Solar System There are an uncountable number
... formed during the collapse of a nebula into a thin disk of gas and dust. A proto-star (proto = early) forms at the core, surrounded by a rotating proto-planetary disk. Through a process called accretion (i.e., sticky collision) dust particles in the disk steadily accumulate mass to form ever-larger ...
... formed during the collapse of a nebula into a thin disk of gas and dust. A proto-star (proto = early) forms at the core, surrounded by a rotating proto-planetary disk. Through a process called accretion (i.e., sticky collision) dust particles in the disk steadily accumulate mass to form ever-larger ...
Science 9 Test Review-Space Answers 1. pg 434 2a
... Constellations – a group of stars that forms shapes or patterns Probe – an unmanned space craft sent into space to obtain data and complete research Satellite – a large natural object that travels in an orbit around a planet Asteroids – small rocky objects Asteroid belt – made up of thousands of ast ...
... Constellations – a group of stars that forms shapes or patterns Probe – an unmanned space craft sent into space to obtain data and complete research Satellite – a large natural object that travels in an orbit around a planet Asteroids – small rocky objects Asteroid belt – made up of thousands of ast ...
The Sun
... Nuclear reaction for stars on the "main sequence" (hydrogen-burning stars) 4 H ----> 1 He + energy Expected lifetime of the Sun as a "main-sequence" star is 12 × 109 years. We're now at about 4.5 × 109 yr, i.e. less than half gone. After leaving the main sequence, Sun will become a red giant, then a ...
... Nuclear reaction for stars on the "main sequence" (hydrogen-burning stars) 4 H ----> 1 He + energy Expected lifetime of the Sun as a "main-sequence" star is 12 × 109 years. We're now at about 4.5 × 109 yr, i.e. less than half gone. After leaving the main sequence, Sun will become a red giant, then a ...
What is the difference between geocentric and heliocentric theories?
... model to explain all the planetary motions. • His model had the planets move in little circles that also moved in bigger circles. • This belief persisted for about 1500 years. ...
... model to explain all the planetary motions. • His model had the planets move in little circles that also moved in bigger circles. • This belief persisted for about 1500 years. ...
Science 9 Test Review-Space Answers 1. pg 434 2a
... Constellations – a group of stars that forms shapes or patterns Probe – an unmanned space craft sent into space to obtain data and complete research Satellite – a large natural object that travels in an orbit around a planet Asteroids – small rocky objects Asteroid belt – made up of thousands of ast ...
... Constellations – a group of stars that forms shapes or patterns Probe – an unmanned space craft sent into space to obtain data and complete research Satellite – a large natural object that travels in an orbit around a planet Asteroids – small rocky objects Asteroid belt – made up of thousands of ast ...
PSC101-lecture12
... • Within the disk, material is constantly colliding with one another. If the collisions are not too violent material may stick together. • In the outer parts of the Solar Nebula the planets become large enough to have a significant gravitational pull and collect gas around them. • Planets in the inn ...
... • Within the disk, material is constantly colliding with one another. If the collisions are not too violent material may stick together. • In the outer parts of the Solar Nebula the planets become large enough to have a significant gravitational pull and collect gas around them. • Planets in the inn ...
Terms - HULK SCIENCE
... A round object that has cleared its orbit of all other objects A smaller body that orbits a planet An object (natural or man-made) that orbits a larger object A force determined by mass. The greater the mass, the greater the gravity The pathway a satellite takes around another object Our local star ...
... A round object that has cleared its orbit of all other objects A smaller body that orbits a planet An object (natural or man-made) that orbits a larger object A force determined by mass. The greater the mass, the greater the gravity The pathway a satellite takes around another object Our local star ...
Our Solar System - Livingstone High School
... Discovered through math 7 known moons Triton largest moon Great Dark Spot thought to be a hole, similar to the hole in the ozone layer on Earth ...
... Discovered through math 7 known moons Triton largest moon Great Dark Spot thought to be a hole, similar to the hole in the ozone layer on Earth ...
The Solar System PPT
... The four inner planets are called terrestrial planets because their surfaces are solid (and, as the name implies, somewhat similar to Earth — although the term can be misleading because each of the four has vastly different environments). They’re made up mostly of heavy metals such as iron and nick ...
... The four inner planets are called terrestrial planets because their surfaces are solid (and, as the name implies, somewhat similar to Earth — although the term can be misleading because each of the four has vastly different environments). They’re made up mostly of heavy metals such as iron and nick ...
Document
... sun? More than 1 AU from the sun? How long does sunlight take to reach the Earth? 9. What is a comet? (p. 500) Where is the asteroid belt? (pg. 502) 10. What is the difference between a meteor, meteoroid and meteorite? P.503 ...
... sun? More than 1 AU from the sun? How long does sunlight take to reach the Earth? 9. What is a comet? (p. 500) Where is the asteroid belt? (pg. 502) 10. What is the difference between a meteor, meteoroid and meteorite? P.503 ...
Science 9 Unit E Section 1.0
... a century and a half later, Voyager 2 flew to Neptune to collect more information. The composition and size of Neptune make it very similar in appearance to Uranus. Another gas giant composed of hydrogen, helium, and methane, Neptune (like Uranus) is bluish in colour. Very little of the Sun’s energy ...
... a century and a half later, Voyager 2 flew to Neptune to collect more information. The composition and size of Neptune make it very similar in appearance to Uranus. Another gas giant composed of hydrogen, helium, and methane, Neptune (like Uranus) is bluish in colour. Very little of the Sun’s energy ...
The Sun, the closest star - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... • The luminosity of the Sun = 3.85E+26 Watts • The age of the Sun (how could we know this?) • Comparison with other objects (Vega, Arcturus, stars in M13, etc) ...
... • The luminosity of the Sun = 3.85E+26 Watts • The age of the Sun (how could we know this?) • Comparison with other objects (Vega, Arcturus, stars in M13, etc) ...
Solar System

The Solar System comprises the Sun and the planetary system that orbits it, either directly or indirectly. Of those objects that orbit the Sun directly, the largest eight are the planets, with the remainder being significantly smaller objects, such as dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies such as comets and asteroids. Of those that orbit the Sun indirectly, two are larger than the smallest planet.The Solar System formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar molecular cloud. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun, with most of the remaining mass contained in Jupiter. The four smaller inner planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars, are terrestrial planets, being primarily composed of rock and metal. The four outer planets are giant planets, being substantially more massive than the terrestrials. The two largest, Jupiter and Saturn, are gas giants, being composed mainly of hydrogen and helium; the two outermost planets, Uranus and Neptune, are ice giants, being composed largely of substances with relatively high melting points compared with hydrogen and helium, called ices, such as water, ammonia and methane. All planets have almost circular orbits that lie within a nearly flat disc called the ecliptic.The Solar System also contains smaller objects. The asteroid belt, which lies between Mars and Jupiter, mostly contains objects composed, like the terrestrial planets, of rock and metal. Beyond Neptune's orbit lie the Kuiper belt and scattered disc, populations of trans-Neptunian objects composed mostly of ices, and beyond them a newly discovered population of sednoids. Within these populations are several dozen to possibly tens of thousands of objects large enough to have been rounded by their own gravity. Such objects are categorized as dwarf planets. Identified dwarf planets include the asteroid Ceres and the trans-Neptunian objects Pluto and Eris. In addition to these two regions, various other small-body populations, including comets, centaurs and interplanetary dust, freely travel between regions. Six of the planets, at least three of the dwarf planets, and many of the smaller bodies are orbited by natural satellites, usually termed ""moons"" after the Moon. Each of the outer planets is encircled by planetary rings of dust and other small objects.The solar wind, a stream of charged particles flowing outwards from the Sun, creates a bubble-like region in the interstellar medium known as the heliosphere. The heliopause is the point at which pressure from the solar wind is equal to the opposing pressure of interstellar wind; it extends out to the edge of the scattered disc. The Oort cloud, which is believed to be the source for long-period comets, may also exist at a distance roughly a thousand times further than the heliosphere. The Solar System is located in the Orion Arm, 26,000 light-years from the center of the Milky Way.