Abyssal Plain:
... mountain range found along the ocean floor (Only the peaks, if any, of the mid-ocean ridge are visible above the ocean's surface.) an underwater sea mountain ...
... mountain range found along the ocean floor (Only the peaks, if any, of the mid-ocean ridge are visible above the ocean's surface.) an underwater sea mountain ...
Quiz (with answers)
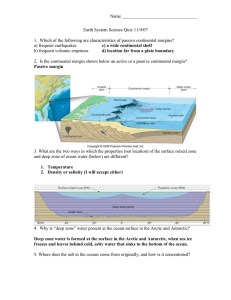
... 3. What are the two ways in which the properties (not location) of the surface mixed zone and deep zone of ocean water (below) are different? 1. Temperature 2. Density or salinity (I will accept either) ...
... 3. What are the two ways in which the properties (not location) of the surface mixed zone and deep zone of ocean water (below) are different? 1. Temperature 2. Density or salinity (I will accept either) ...
Gr.8-Ch.2-Review-Sheet-2014
... deposited into the ocean basins. 18. _____ move changing the position of the continents. 19. _____ is a force of erosion in the development of continental drainage systems. 20. Water on earth came from_____ and _____. 21. Water collected in the lowest parts of the Earth’s surface known as the _____. ...
... deposited into the ocean basins. 18. _____ move changing the position of the continents. 19. _____ is a force of erosion in the development of continental drainage systems. 20. Water on earth came from_____ and _____. 21. Water collected in the lowest parts of the Earth’s surface known as the _____. ...
pressure and ocean currents
... 8. Describe adaptations marine organisms evolved to cope with pressure changes in the water column. 9. Describe the Coriolis Effect and how it effects the Earth. 10. Describe what variables/factors effect tides. 11. Identify the components of a wave. 12. Describe what a fetch is AND how it effects w ...
... 8. Describe adaptations marine organisms evolved to cope with pressure changes in the water column. 9. Describe the Coriolis Effect and how it effects the Earth. 10. Describe what variables/factors effect tides. 11. Identify the components of a wave. 12. Describe what a fetch is AND how it effects w ...
The Characteristics and Uncertainties of Sea Level Change due to
... In the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 30-‐50% of the projected global-‐mean sea-‐level rise by 2100 is due to expansion of sea water as the ocean ...
... In the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 30-‐50% of the projected global-‐mean sea-‐level rise by 2100 is due to expansion of sea water as the ocean ...
ocean floor and life
... 1.) Organisms in the ocean use less energy for movement due to buoyancy. 2.) Temperature changes are less drastic than on land. 3.) There is never a lack of water. 4.) Waste disposal is easy and cleaner. 5.) External fertilization is carried out very easily. ...
... 1.) Organisms in the ocean use less energy for movement due to buoyancy. 2.) Temperature changes are less drastic than on land. 3.) There is never a lack of water. 4.) Waste disposal is easy and cleaner. 5.) External fertilization is carried out very easily. ...
Unit 11 Oceans Concepts of Earth Science Key Concepts and
... temperature impact the amount of dissolved gasses and salinity? 4. How do salinity and temperature affect the density of ocean water? 5. How does ocean temperature change with depth? 6. Be able to identify and describe the features of the ocean floor. 7. What mineral and food resources can be extrac ...
... temperature impact the amount of dissolved gasses and salinity? 4. How do salinity and temperature affect the density of ocean water? 5. How does ocean temperature change with depth? 6. Be able to identify and describe the features of the ocean floor. 7. What mineral and food resources can be extrac ...
11.1 OCEAN BASINS - STUDENT NOTES
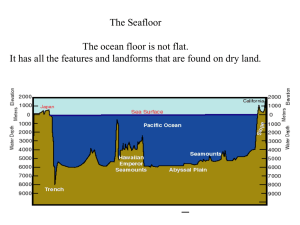
... Although the word “__________” makes it sound flat, many features found on land, including mountain ranges, valleys, flat plains, canyons, and volcanoes also exist on the _____________ _________________________. The __________ is the large, flat middle part, while the ___________________________ ...
... Although the word “__________” makes it sound flat, many features found on land, including mountain ranges, valleys, flat plains, canyons, and volcanoes also exist on the _____________ _________________________. The __________ is the large, flat middle part, while the ___________________________ ...
Grade 8 Science
... Moving _____________________ are forced to Earth’s continents turn when they ______________ a _____________ surface. ...
... Moving _____________________ are forced to Earth’s continents turn when they ______________ a _____________ surface. ...
Chapter 1- Introduction to Castro Part 1
... Goals for Course • Learn nature of marine environment • Learn diversity of marine organisms • Learn ecosystems • Guide to issues in human-marine interactions • Provide info that can inform policy decisions ...
... Goals for Course • Learn nature of marine environment • Learn diversity of marine organisms • Learn ecosystems • Guide to issues in human-marine interactions • Provide info that can inform policy decisions ...
1 Introduction to Marine Ecology jh part 2 2009
... – wind friction on water – uneven sea surface, starts water moving – Coriolis effect deflection – contact with the continents deflect currents, creating giant oceanic current circles or gyres. ...
... – wind friction on water – uneven sea surface, starts water moving – Coriolis effect deflection – contact with the continents deflect currents, creating giant oceanic current circles or gyres. ...
Ocean Environment (Salt Water)
... Oceans are large bodies of salt water divided by continents. Since ocean water is constantly moving, the characteristics of the waters are constantly changing. ...
... Oceans are large bodies of salt water divided by continents. Since ocean water is constantly moving, the characteristics of the waters are constantly changing. ...
ES Unit 5 standards - Springfield Public Schools
... and compare it to land. Explain the formation of new ocean floor at ...
... and compare it to land. Explain the formation of new ocean floor at ...
Weather and Climate Test Review Sheet (6th Grade)
... Earth’s oceans cover nearly ¾ (75%) of Earth’s surface. Water for Earth’s oceans originally came from water vapor from volcanoes. Photosynthesis is a process that needs sunlight as a source of energy to make food. The thermocline is the layer in the ocean where temperature varies with depth. You are ...
... Earth’s oceans cover nearly ¾ (75%) of Earth’s surface. Water for Earth’s oceans originally came from water vapor from volcanoes. Photosynthesis is a process that needs sunlight as a source of energy to make food. The thermocline is the layer in the ocean where temperature varies with depth. You are ...
11.2 OCEAN CURRENTS
... it. This creates wind. As the wind passes along the surface of the water, it bumps the water molecules and moves them along in the same ___________________. • ___________________________ Earth spins from West to East (counter clockwise) The________________ effect deflects winds and currents to ...
... it. This creates wind. As the wind passes along the surface of the water, it bumps the water molecules and moves them along in the same ___________________. • ___________________________ Earth spins from West to East (counter clockwise) The________________ effect deflects winds and currents to ...
Slide 1 - OnCourse
... • They expect one that causes major damage about once every seven years • Alaska is another high risk area with an average of one every 1.75 years and a major damageof causer every seven years • Warnings are via seismograph records • These help determine the location of where a submarine earthquake ...
... • They expect one that causes major damage about once every seven years • Alaska is another high risk area with an average of one every 1.75 years and a major damageof causer every seven years • Warnings are via seismograph records • These help determine the location of where a submarine earthquake ...
20.1 Reading Guide
... 2. What percent of the world is covered by oceans? Pg 389 3. Why is earth called the “water planet”? ...
... 2. What percent of the world is covered by oceans? Pg 389 3. Why is earth called the “water planet”? ...
Water Systems on Earth
... Wind....... • Air movement caused by uneven heating resulting in air energy. • The result is friction to the water molecules . ...
... Wind....... • Air movement caused by uneven heating resulting in air energy. • The result is friction to the water molecules . ...
Here is an example formatted abstract
... Decadal change of the deep and upper ocean heat content of the north-east Atlantic KING, MCDONAGH, GARRY We examine the vertical distribution of trends in heat content of the north-east basin of the Atlantic Ocean since the late 1980s. The 2010 analysis of Purkey and Johnson identified this basin as ...
... Decadal change of the deep and upper ocean heat content of the north-east Atlantic KING, MCDONAGH, GARRY We examine the vertical distribution of trends in heat content of the north-east basin of the Atlantic Ocean since the late 1980s. The 2010 analysis of Purkey and Johnson identified this basin as ...
Currents and Climate
... toward these areas, much of its heat is lost and is carried to northern Europe by the atmosphere, warming the climate there. An important factor influencing sinking is the salinity, or saltiness, of the water. Salt increases the density, or mass per unit volume, of water. The warm water transported ...
... toward these areas, much of its heat is lost and is carried to northern Europe by the atmosphere, warming the climate there. An important factor influencing sinking is the salinity, or saltiness, of the water. Salt increases the density, or mass per unit volume, of water. The warm water transported ...
Chapter 19
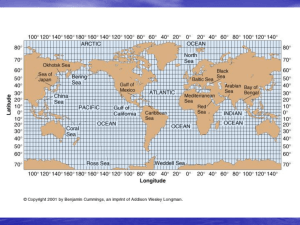
... Chapter 19 – The Ocean Basins Today nearly ¾ of Earth’s surface is covered by oceans. The global ocean can be divided into three or four major oceans: the Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, and Arctic (sometimes considered part of the Atlantic). The deepest and therefore coldest is the Pacific. It is also t ...
... Chapter 19 – The Ocean Basins Today nearly ¾ of Earth’s surface is covered by oceans. The global ocean can be divided into three or four major oceans: the Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, and Arctic (sometimes considered part of the Atlantic). The deepest and therefore coldest is the Pacific. It is also t ...
Ocean water moves in currents
... Ocean Currents Ocean water moves in currents What causes ocean currents? How do ocean currents distribute heat around the globe and interact with climate and weather? ...
... Ocean Currents Ocean water moves in currents What causes ocean currents? How do ocean currents distribute heat around the globe and interact with climate and weather? ...
Ocean tides result mainly from
... Compare and contrast surface currents to density currents in terms of their location, temperature, and salinity. ...
... Compare and contrast surface currents to density currents in terms of their location, temperature, and salinity. ...
Study Guide for Oceanography Test 2016
... A wave is the movement of energy through a medium Waves slow down when they approach the shore due to friction with the bottom of the ocean As salinity increases the density of water increases Sodium Chloride is the most abundant salt in ocean water As depth increases so does the pressure ...
... A wave is the movement of energy through a medium Waves slow down when they approach the shore due to friction with the bottom of the ocean As salinity increases the density of water increases Sodium Chloride is the most abundant salt in ocean water As depth increases so does the pressure ...
Post Test Study Guide Answer Key 1. HMS Challenger: first voyage
... buoyancy. It is easier to float in the Dead Sea than in Lake Erie because of this ...
... buoyancy. It is easier to float in the Dead Sea than in Lake Erie because of this ...
Physical oceanography

Physical oceanography is the study of physical conditions and physical processes within the ocean, especially the motions and physical properties of ocean waters.Physical oceanography is one of several sub-domains into which oceanography is divided. Others include biological, chemical and geological oceanographies.