13.3 Ocean Water Chemistry
... a. Temperatures at the surface of the ocean vary with locations and seasons. Gases vary as well. b. Temperature of Ocean Water i. The surface of the ocean absorbs energy from the sun 1. Near the equator, surface water reaches 25°C ii. Warm water is less dense than cold water 1. Warm water forms a th ...
... a. Temperatures at the surface of the ocean vary with locations and seasons. Gases vary as well. b. Temperature of Ocean Water i. The surface of the ocean absorbs energy from the sun 1. Near the equator, surface water reaches 25°C ii. Warm water is less dense than cold water 1. Warm water forms a th ...
World Geography Fall Final 2010 Review
... Uplands- hills or very low mountains found on the European continent Arctic Circle-area of the world that experiences winter days during which the sun does not rise Zuider Zee-changed from an arm of the sea into a fresh water lake North Atlantic Drift-flows near Europe’s west coast and contributes t ...
... Uplands- hills or very low mountains found on the European continent Arctic Circle-area of the world that experiences winter days during which the sun does not rise Zuider Zee-changed from an arm of the sea into a fresh water lake North Atlantic Drift-flows near Europe’s west coast and contributes t ...
Guided Reading on Sections 23.3 and 23.4
... together as part of a larger land mass. 7. He proposed that the geological boundary of each continent lay not at its ________________ but at the edge of its __________________ ___________ (the gently sloping platform between the shoreline and the steep slope that leads to the deep ocean floor). 8. W ...
... together as part of a larger land mass. 7. He proposed that the geological boundary of each continent lay not at its ________________ but at the edge of its __________________ ___________ (the gently sloping platform between the shoreline and the steep slope that leads to the deep ocean floor). 8. W ...
The Oceans
... Salts accumulate beneath the ice which increasing the density of the seawater The dense seawater sinks and moves toward the equator. This is called a density current ...
... Salts accumulate beneath the ice which increasing the density of the seawater The dense seawater sinks and moves toward the equator. This is called a density current ...
CH 3 - 4
... Only substance that can exist as solid, liquid, or gas Has the ability to dissolve into ...
... Only substance that can exist as solid, liquid, or gas Has the ability to dissolve into ...
Ocean Topography presentation
... How do submarine canyons form? Thought to be fast moving currents and underwater landslides. ...
... How do submarine canyons form? Thought to be fast moving currents and underwater landslides. ...
SEA-FLOOR SPREADING
... sunlight • Cold---temp near freezing • Areas where there is space between the plates allows water down into the crust, then brings it back up. • These warm areas provide a great area for life to thrive, and support information given by Wegener’s “continental drift” theory. ...
... sunlight • Cold---temp near freezing • Areas where there is space between the plates allows water down into the crust, then brings it back up. • These warm areas provide a great area for life to thrive, and support information given by Wegener’s “continental drift” theory. ...
Chapter 23
... Sound signals are sent through the water to the sea floor. By tracking how long it takes for them to bounce back, the depth can be determined. ______________________________ Bouncing back signals from space can map the area. The waves can not penetrate to the sea floor, but they still can create a h ...
... Sound signals are sent through the water to the sea floor. By tracking how long it takes for them to bounce back, the depth can be determined. ______________________________ Bouncing back signals from space can map the area. The waves can not penetrate to the sea floor, but they still can create a h ...
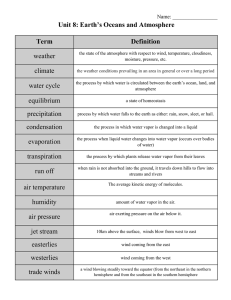
Unit 8: Earth`s Oceans and Atmosphere
... the process when liquid water changes into water vapor (occurs over bodies of water) ...
... the process when liquid water changes into water vapor (occurs over bodies of water) ...
Lecture 3
... • Again, Coriolis Effect causes the surface waters to track toward the right (N. hemisphere). • Progressive spiraling caused by shallower currents pushing on deeper currents results in Ekman Spirals. • As spirals continue, wind shear becomes less and less at depth. • Eventually, deep currents travel ...
... • Again, Coriolis Effect causes the surface waters to track toward the right (N. hemisphere). • Progressive spiraling caused by shallower currents pushing on deeper currents results in Ekman Spirals. • As spirals continue, wind shear becomes less and less at depth. • Eventually, deep currents travel ...
process of forming new oceanic crust from magma rising to the
... Which process adds new crust to the surface? ______Sea Floor ...
... Which process adds new crust to the surface? ______Sea Floor ...
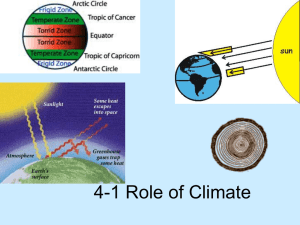
4-1 Role of Climate
... 3. This unequal heating creates 3 different zones. 4. Polar zone A. Located in the areas around the North and South poles, between 66.5º and 90º north and south latitudes. B. Sun’s rays are at a very low angle. 5. Temperate zones A. Sit between the polar zones and the tropic zones, because this z ...
... 3. This unequal heating creates 3 different zones. 4. Polar zone A. Located in the areas around the North and South poles, between 66.5º and 90º north and south latitudes. B. Sun’s rays are at a very low angle. 5. Temperate zones A. Sit between the polar zones and the tropic zones, because this z ...
Guided Notes on Seafloor Spreading
... SONAR, uses sound waves to measure water depth. The sound waves bounce off the ocean floor and back to a receiver. ...
... SONAR, uses sound waves to measure water depth. The sound waves bounce off the ocean floor and back to a receiver. ...
Salinity of Ocean water Salty ocean waters constitute 97% of all the
... Salty ocean waters constitute 97% of all the water on the earth and only 3% of water left in the earth is fresh. Most of the fresh water exists as ice sheet with only about 0.04% found in lakes, rivers and reservoirs. Interestingly, the volume of waters on the earth (around 1.3 billion cubic kilomet ...
... Salty ocean waters constitute 97% of all the water on the earth and only 3% of water left in the earth is fresh. Most of the fresh water exists as ice sheet with only about 0.04% found in lakes, rivers and reservoirs. Interestingly, the volume of waters on the earth (around 1.3 billion cubic kilomet ...
Features of the Ocean Floor
... Everest, which is the tallest point on earth at 8,850 meters (29,035 feet), were set in the Mariana Trench, there would still be 2,183 meters (7,166 feet) of water left above it. ...
... Everest, which is the tallest point on earth at 8,850 meters (29,035 feet), were set in the Mariana Trench, there would still be 2,183 meters (7,166 feet) of water left above it. ...
Water Masses and Density Currents
... movement of water masses is called Thermohaline circulation. Heat transport y moving water masses, likened to huge conveyor belts, is an important control of global climate. Water masses of different densities tend not to mix. This lack of mixing means that each water-mass layer retains its original ...
... movement of water masses is called Thermohaline circulation. Heat transport y moving water masses, likened to huge conveyor belts, is an important control of global climate. Water masses of different densities tend not to mix. This lack of mixing means that each water-mass layer retains its original ...
Unit 7 Chapter 23 Powerpoint
... Sound signals are sent through the water to the sea floor. By tracking how long it takes for them to bounce back, the depth can be determined. ...
... Sound signals are sent through the water to the sea floor. By tracking how long it takes for them to bounce back, the depth can be determined. ...
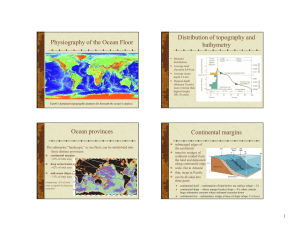
Physiography of the Ocean Floor Distribution of topography and
... abyssal hills – elongated dome-shaped hills of oceanic crust seamounts – abyssal mountains, largely volcanic (active and extinct); includes flat-topped guyots formed by wave erosion deep sea trenches – deepest regions on Earth, found close to land ...
... abyssal hills – elongated dome-shaped hills of oceanic crust seamounts – abyssal mountains, largely volcanic (active and extinct); includes flat-topped guyots formed by wave erosion deep sea trenches – deepest regions on Earth, found close to land ...
The Three Voices
... 1. Compare the poem ‘The Three Voices’ to the Robert Service ballad ‘The Men That Don’t Fit In’. Discuss the message and warning. 2. What are the three voices? Circle or highlight the three voices to see how the poem is organized. ...
... 1. Compare the poem ‘The Three Voices’ to the Robert Service ballad ‘The Men That Don’t Fit In’. Discuss the message and warning. 2. What are the three voices? Circle or highlight the three voices to see how the poem is organized. ...
Chapter 2 – Plate Tectonics
... 71% of the earth’s surface is water. Two thirds of earth’s crust is in the northern hemisphere. 80% of the southern hemisphere is ocean. ...
... 71% of the earth’s surface is water. Two thirds of earth’s crust is in the northern hemisphere. 80% of the southern hemisphere is ocean. ...
Study Guide – Social Studies Test 1 Lesson 1 Continent
... Lesson 2 Identify Geographic features on a map Tributary – a river or stream that flows into a larger river Plain – a mostly flat, low area of land Plateau – a flat, high area of land Peninsula – piece of land bordered by water on three sides (almost an island) Elevation – height above sea level or ...
... Lesson 2 Identify Geographic features on a map Tributary – a river or stream that flows into a larger river Plain – a mostly flat, low area of land Plateau – a flat, high area of land Peninsula – piece of land bordered by water on three sides (almost an island) Elevation – height above sea level or ...
Chapter One: An Introduction to “Our Country`s
... California is 280 feet below sea level. Basin: Low bowl shaped land with high land all around it. ...
... California is 280 feet below sea level. Basin: Low bowl shaped land with high land all around it. ...
File
... •Huge lone wave with very high crests and low troughs. –Formed when 2 or more large waves unite. ...
... •Huge lone wave with very high crests and low troughs. –Formed when 2 or more large waves unite. ...
Marine Life zones and biotic and abiotic factors chart information
... *From surface down to about 200 ft. *Affected by currents and waves *Low water pressure *Special structures that allow for attaching to the reef (some of them) ...
... *From surface down to about 200 ft. *Affected by currents and waves *Low water pressure *Special structures that allow for attaching to the reef (some of them) ...
Physical oceanography

Physical oceanography is the study of physical conditions and physical processes within the ocean, especially the motions and physical properties of ocean waters.Physical oceanography is one of several sub-domains into which oceanography is divided. Others include biological, chemical and geological oceanographies.