Earth Science 16.1 Ocean Circulation
... It’s temperature and salinity remain relatively unchanged during the time it is in the deep ocean. Because of this, oceanographers can track the movements of density currents in the deep ocean. By knowing the temperature, density, and salinity of a water mass; scientists are able to map the slow cir ...
... It’s temperature and salinity remain relatively unchanged during the time it is in the deep ocean. Because of this, oceanographers can track the movements of density currents in the deep ocean. By knowing the temperature, density, and salinity of a water mass; scientists are able to map the slow cir ...
15.2 Diversity of Ocean Life & 15.3 Oceanic Productivity
... • Describes organisms living on or in the ocean bottom • Shallow coastal ocean floor contains a wide variety of physical conditions & nutrient levels • Deeper parts = photosynthesis can not occur – They feed on each other and whatever falls from above ...
... • Describes organisms living on or in the ocean bottom • Shallow coastal ocean floor contains a wide variety of physical conditions & nutrient levels • Deeper parts = photosynthesis can not occur – They feed on each other and whatever falls from above ...
APES Review: Earth Systems and Global Changes
... Aurorae; meteors burn up in this layer; temperature increases with height due to X-rays, gamma rays, and ultraviolet radiation from the sun ...
... Aurorae; meteors burn up in this layer; temperature increases with height due to X-rays, gamma rays, and ultraviolet radiation from the sun ...
Deep Ocean Technology & The Ocean Floor
... •A seamount is a volcanic mountain on the ocean floor. •Guyot is a submarine volcanic mountain with a flat top. •Islands are seamounts that rise above the water surface. •The mid-ocean ridge is a mountain range that runs through all the world’s oceans. It is almost 64,000 kilometers (40,000 miles) l ...
... •A seamount is a volcanic mountain on the ocean floor. •Guyot is a submarine volcanic mountain with a flat top. •Islands are seamounts that rise above the water surface. •The mid-ocean ridge is a mountain range that runs through all the world’s oceans. It is almost 64,000 kilometers (40,000 miles) l ...
Surface Currents - Mrs. Leachman Science
... Surface currents move warmer water into cooler regions and return cooler water to the warmer regions (tropics) Currents can have a cooling effect on an area’s climate or a warming effect on an area’s climate As warm water flows from the equator, heat is released into the atmosphere and the air ...
... Surface currents move warmer water into cooler regions and return cooler water to the warmer regions (tropics) Currents can have a cooling effect on an area’s climate or a warming effect on an area’s climate As warm water flows from the equator, heat is released into the atmosphere and the air ...
Tect.EQ.Oceans.S04 - SC4 Geography MainPage
... the distance that the wind travels over open water a depositional shoreline feature Abyssal plains are: flat areas that are near the coastline flat areas of the ocean floor that are on the continental shelf flat areas of the ocean floor that are in very deep water flat areas of the moon Surface wave ...
... the distance that the wind travels over open water a depositional shoreline feature Abyssal plains are: flat areas that are near the coastline flat areas of the ocean floor that are on the continental shelf flat areas of the ocean floor that are in very deep water flat areas of the moon Surface wave ...
oceans - Sir C R R College
... land inhabitants are know scattered across several continents. All these suggest that once upon a time , there was one single land ...
... land inhabitants are know scattered across several continents. All these suggest that once upon a time , there was one single land ...
4 Resources from the Ocean Critical Thinking
... living near, on, or in the ocean floor. The pelagic environment is found near the ocean surface and in the open and deep-ocean water. It gets more sunlight than any other zone, so many phytoplankton can grow. These phytoplankton act as food for other marine organisms in this zone. No sunlight reache ...
... living near, on, or in the ocean floor. The pelagic environment is found near the ocean surface and in the open and deep-ocean water. It gets more sunlight than any other zone, so many phytoplankton can grow. These phytoplankton act as food for other marine organisms in this zone. No sunlight reache ...
Missing Geothermal Flux
... of thermal convection occur in these ocean floor zones. The complete Geothermal Flux is the sum of hot elemental gas phase change to liquid along tens of thousands of miles of ocean rifts and the convective exchange across millions of square miles ocean floor. The change in just a fraction of a degr ...
... of thermal convection occur in these ocean floor zones. The complete Geothermal Flux is the sum of hot elemental gas phase change to liquid along tens of thousands of miles of ocean rifts and the convective exchange across millions of square miles ocean floor. The change in just a fraction of a degr ...
ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION Earth is heated unevenly by the
... Coriolis affects the direction of winds and currents Coriolis occurs because the Earth is a sphere rotating around its pole Earth rotates about its axis every 24 hours Distance around the equator is ~25,000 miles travelling east at ~ 1,000 miles per hour Distance around the Earth at 40o N (Buffalo, ...
... Coriolis affects the direction of winds and currents Coriolis occurs because the Earth is a sphere rotating around its pole Earth rotates about its axis every 24 hours Distance around the equator is ~25,000 miles travelling east at ~ 1,000 miles per hour Distance around the Earth at 40o N (Buffalo, ...
Hydrothermal Vents - The Corn Group Unicorn Web Site
... on the ocean floor. The instrument combines a portable focusing lens with a potent laser to examine minerals, gases and liquids – even seawater itself. Pasteris' group and their MBARI colleagues are using Raman spectroscopy to see what carbon dioxide in either a pure liquid or a complex solid phase ...
... on the ocean floor. The instrument combines a portable focusing lens with a potent laser to examine minerals, gases and liquids – even seawater itself. Pasteris' group and their MBARI colleagues are using Raman spectroscopy to see what carbon dioxide in either a pure liquid or a complex solid phase ...
Oceans - sabresocials.com
... plants will become extinct, breaking the food chain. For example, polar bears live on ice, but when the ice melts, they can’t survive in the glacier water and must be in cold climates to live, resulting in death, and the fish amounts will grow because there is one less predator eating them. ...
... plants will become extinct, breaking the food chain. For example, polar bears live on ice, but when the ice melts, they can’t survive in the glacier water and must be in cold climates to live, resulting in death, and the fish amounts will grow because there is one less predator eating them. ...
SEA FLOOR SPREADING Mid
... • Deep ocean trenches are swallowing more oceanic crust than the mid-ocean ridge can produce. Thus, the width of the Pacific will shrink. • The Atlantic is expanding. It has short trenches. In some places, the oceanic crust is attached to the continental crust which moves the continents. ...
... • Deep ocean trenches are swallowing more oceanic crust than the mid-ocean ridge can produce. Thus, the width of the Pacific will shrink. • The Atlantic is expanding. It has short trenches. In some places, the oceanic crust is attached to the continental crust which moves the continents. ...
What does abiotic mean? Non-living The base of the ocean`s food
... 26. What does abiotic mean? Non-living 27. The base of the ocean's food chains is formed by: Plankton 28. What are the abiotic factors in marine ecosystems? 1. Water temp. 2. Water depth 3. Amount of sunlight 29. Name and describe the 4 levels of the ocean: (only have to describe 1 & 4) 1 intertidal ...
... 26. What does abiotic mean? Non-living 27. The base of the ocean's food chains is formed by: Plankton 28. What are the abiotic factors in marine ecosystems? 1. Water temp. 2. Water depth 3. Amount of sunlight 29. Name and describe the 4 levels of the ocean: (only have to describe 1 & 4) 1 intertidal ...
Jeopardy - Effingham County Schools
... The focus is inside the earth and the epicenter is on the surface ...
... The focus is inside the earth and the epicenter is on the surface ...
Marine Ecosystems - Distribution Access
... special adaptations. Hard shells of animals and a gooey coating on seaweed serve as protections against drying out in the hot sun. Mussels, barnacles and other shellfish anchor themselves to rocks with strong threads, while ghost crabs burrow into the sand to keep from being washed away by powerful ...
... special adaptations. Hard shells of animals and a gooey coating on seaweed serve as protections against drying out in the hot sun. Mussels, barnacles and other shellfish anchor themselves to rocks with strong threads, while ghost crabs burrow into the sand to keep from being washed away by powerful ...
Tides--their Nature and Impacts (MSL F693H)
... tides are related to large sea level changes and strong currents in the coastal regions, they also impact on many phenomena such as, vertical mixing rates of waters and, hence, on biology, sedimentation and thermal balance. These subjects have broader implications beyond the context of tides. Our ge ...
... tides are related to large sea level changes and strong currents in the coastal regions, they also impact on many phenomena such as, vertical mixing rates of waters and, hence, on biology, sedimentation and thermal balance. These subjects have broader implications beyond the context of tides. Our ge ...
Central America Landforms
... that most people associate with rainforests, but it also has other distinct geographic features, due to its location between the temperate northern and tropical southern regions of the Americas. The Belize Rainforest is home to thousands of mountainous and underground caves, herb trails, river valle ...
... that most people associate with rainforests, but it also has other distinct geographic features, due to its location between the temperate northern and tropical southern regions of the Americas. The Belize Rainforest is home to thousands of mountainous and underground caves, herb trails, river valle ...
Central America Landforms
... that most people associate with rainforests, but it also has other distinct geographic features, due to its location between the temperate northern and tropical southern regions of the Americas. The Belize Rainforest is home to thousands of mountainous and underground caves, herb trails, river valle ...
... that most people associate with rainforests, but it also has other distinct geographic features, due to its location between the temperate northern and tropical southern regions of the Americas. The Belize Rainforest is home to thousands of mountainous and underground caves, herb trails, river valle ...
EXAMPLE PROBLEMS: Bob is in the middle of the ocean and
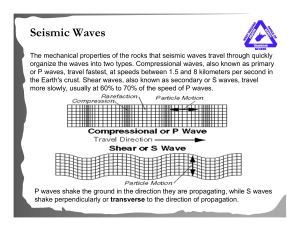
... sound. Seismic events such as earthquakes produce acoustic signatures that can be used to get information about the Earth. But first, they have to figure out where the quake started! Earthquakes produce two types of waves called P- and S-waves. P stands for primary waves and are longitudinal waves t ...
... sound. Seismic events such as earthquakes produce acoustic signatures that can be used to get information about the Earth. But first, they have to figure out where the quake started! Earthquakes produce two types of waves called P- and S-waves. P stands for primary waves and are longitudinal waves t ...
Background Information
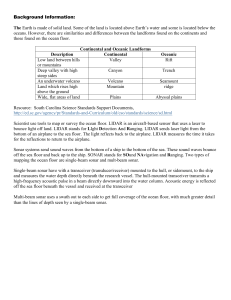
... Background Information: The Earth is made of solid land. Some of the land is located above Earth’s water and some is located below the oceans. However, there are similarities and differences between the landforms found on the continents and those found on the ocean floor. ...
... Background Information: The Earth is made of solid land. Some of the land is located above Earth’s water and some is located below the oceans. However, there are similarities and differences between the landforms found on the continents and those found on the ocean floor. ...
Marine Provinces
... Describe features of the sea floor Identify a passive vs. an active continental margin ...
... Describe features of the sea floor Identify a passive vs. an active continental margin ...
Chapter 10: Siliciclastic Marine Environments The Shelf
... Wind-forced currents: unidirectional currents generated by wind-shear stress as wind blows across the water surface, gradually putting into motion deeper and deeper layer of water (Ekman transport). ...
... Wind-forced currents: unidirectional currents generated by wind-shear stress as wind blows across the water surface, gradually putting into motion deeper and deeper layer of water (Ekman transport). ...
Physical oceanography

Physical oceanography is the study of physical conditions and physical processes within the ocean, especially the motions and physical properties of ocean waters.Physical oceanography is one of several sub-domains into which oceanography is divided. Others include biological, chemical and geological oceanographies.