Chapter 13 NUCLEAR FUSION
... the process that accounts for the hydrogen bomb, a proven weapon of enormous explosive power well exceeding that of the atomic bombs which, in World War II, destroyed Nagasaki and Hiroshimo. I have, in Part I of this work, made it quite clear that the Sun is not powered by a nuclear furnace. I well ...
... the process that accounts for the hydrogen bomb, a proven weapon of enormous explosive power well exceeding that of the atomic bombs which, in World War II, destroyed Nagasaki and Hiroshimo. I have, in Part I of this work, made it quite clear that the Sun is not powered by a nuclear furnace. I well ...
Electronic Structure of Atoms
... 4. understand and be able to describe what the photoelectric effect is. 5. understand and be able to describe the emission of light from atoms. 6. understand and be able to describe the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom and its historical significance; be able to mathematically relate the wavelength a ...
... 4. understand and be able to describe what the photoelectric effect is. 5. understand and be able to describe the emission of light from atoms. 6. understand and be able to describe the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom and its historical significance; be able to mathematically relate the wavelength a ...
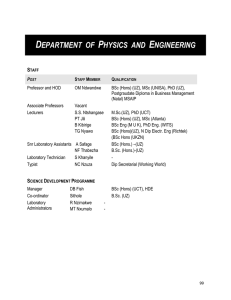
department of physics and engineering
... MSc (Physics) [QUALIFICATION CODE SMSC11, MODULE CODE SPHY700] This course consists of a dissertation on an approved topic, or of a dissertation plus coursework on theory on which examination papers will be written, as arranged with the supervisor appointed in consultation with the Head of Departmen ...
... MSc (Physics) [QUALIFICATION CODE SMSC11, MODULE CODE SPHY700] This course consists of a dissertation on an approved topic, or of a dissertation plus coursework on theory on which examination papers will be written, as arranged with the supervisor appointed in consultation with the Head of Departmen ...
nuclear fusion
... TWa equals 1012 Watts per year), of which 3.8 TWa is the electric energy. The energy consumption on average per head is 2.2 kWa: in Europe 5.9 kWa, in the USA 10.9 kWa, in China 0.83 kWa, and in India 0.32 kWa. Annually 6% energy is produced in nuclear power stations and 7% in hydroelectric power st ...
... TWa equals 1012 Watts per year), of which 3.8 TWa is the electric energy. The energy consumption on average per head is 2.2 kWa: in Europe 5.9 kWa, in the USA 10.9 kWa, in China 0.83 kWa, and in India 0.32 kWa. Annually 6% energy is produced in nuclear power stations and 7% in hydroelectric power st ...
Electromagnetic Theory, Photons and Light • Introduction – Maxwell
... ∗ Ground states and excited states. ∗ When atoms interact with light, they jump from initial to excited states and since these energy states have well defined energies, the amount of energy that can be absorbed by an atom from light is quantized. ∗ The lifetime of the atom in this excited state is s ...
... ∗ Ground states and excited states. ∗ When atoms interact with light, they jump from initial to excited states and since these energy states have well defined energies, the amount of energy that can be absorbed by an atom from light is quantized. ∗ The lifetime of the atom in this excited state is s ...
Energy Loss by Charge Particles Passing Through Matter
... One of the most important problems in experimental physics is the problem of understanding how particles slow down as they pass through matter. Consider a massive charged particle (e.g. a proton or muon) passing through matter. As it passes an electron, it will be minimally deflected (little momentu ...
... One of the most important problems in experimental physics is the problem of understanding how particles slow down as they pass through matter. Consider a massive charged particle (e.g. a proton or muon) passing through matter. As it passes an electron, it will be minimally deflected (little momentu ...
File
... Important facts about atoms 1. Every atom has a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons. 2. All electrons are identical. 3. The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. All protons are identical; similarly, all neutrons are identical. 4. Atoms usually have as many ...
... Important facts about atoms 1. Every atom has a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons. 2. All electrons are identical. 3. The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. All protons are identical; similarly, all neutrons are identical. 4. Atoms usually have as many ...
H local
... Hlocal: local field induced by the external field Hlocal: Electrons in a chemical bond are considered to be in motion and are charged. This induces a local magnetic field which can shield (oppose) or deshield (enhance) the magnetic field experienced by the nucleus. Since the precessional frequency o ...
... Hlocal: local field induced by the external field Hlocal: Electrons in a chemical bond are considered to be in motion and are charged. This induces a local magnetic field which can shield (oppose) or deshield (enhance) the magnetic field experienced by the nucleus. Since the precessional frequency o ...
Division I students, START HERE.
... A gas is enclosed in a cylindrical piston. When the gas is heated from 0o C to 100o C, the piston is allowed to move to maintain a constant pressure. According to the Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Matter A) the mass of the gas will increase B) the number of molecules of gas must increase C) the size o ...
... A gas is enclosed in a cylindrical piston. When the gas is heated from 0o C to 100o C, the piston is allowed to move to maintain a constant pressure. According to the Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Matter A) the mass of the gas will increase B) the number of molecules of gas must increase C) the size o ...
Document
... q Electrons were discovered ~1900 by J. J. Thomson q Protons being confined in a nucleus was put forth ~1905 q Neutrons discovered 1932 by James Chadwick q Quantum theory of radiation had become “widely accepted”, although even Einstein had his doubts ...
... q Electrons were discovered ~1900 by J. J. Thomson q Protons being confined in a nucleus was put forth ~1905 q Neutrons discovered 1932 by James Chadwick q Quantum theory of radiation had become “widely accepted”, although even Einstein had his doubts ...
pdf x1 - Department of Physics
... • University Academic/athletic conflicts • Medical emergency • Legal obligations ...
... • University Academic/athletic conflicts • Medical emergency • Legal obligations ...
Solutions - American Association of Physics Teachers
... What constraint does this fact place on z? e. In which of the reaction steps is the energy carried by any given product the same every time the step occurs? Assume that the kinetic energy carried in by the reactants in each step is negligible, and that the products are in the ground state. ...
... What constraint does this fact place on z? e. In which of the reaction steps is the energy carried by any given product the same every time the step occurs? Assume that the kinetic energy carried in by the reactants in each step is negligible, and that the products are in the ground state. ...
Nuclear Physics 1 NWNC
... for use by DOE category A reactors. The subject areas, subject matter content, and level of detail of the Reactor Operator Fundamentals Manuals were determined from several sources. DOE Category A reactor training managers determined which materials should be included, and served as a primary refere ...
... for use by DOE category A reactors. The subject areas, subject matter content, and level of detail of the Reactor Operator Fundamentals Manuals were determined from several sources. DOE Category A reactor training managers determined which materials should be included, and served as a primary refere ...
Chemistry Syllabus
... e. Measure and calculate the magnitude of gravitational forces. f. Measure and calculate two-dimensional motion (projectile and circular) by using component vectors. g. Measure and calculate centripetal force. h. Determine the conditions required to maintain a body in a state of static equilibrium a ...
... e. Measure and calculate the magnitude of gravitational forces. f. Measure and calculate two-dimensional motion (projectile and circular) by using component vectors. g. Measure and calculate centripetal force. h. Determine the conditions required to maintain a body in a state of static equilibrium a ...
Name
... Overshot mill is a potential energy device. The water falls onto the wheel, the rate is controlled by a gate. The water strikes the wheel slightly in front the midpoint. The weight of the water causes the wheel to turn. The turning wheel generates mechanical energy that is transferred to the inner w ...
... Overshot mill is a potential energy device. The water falls onto the wheel, the rate is controlled by a gate. The water strikes the wheel slightly in front the midpoint. The weight of the water causes the wheel to turn. The turning wheel generates mechanical energy that is transferred to the inner w ...
Developing a test procedure for neutron detection/non detection
... to be the worlds highest intensity neutron source. Using a linear accelerator, protons will be accelerated towards a target consisting of a neutron rich material, like tungsten, and neutrons are emitted through the process of spallation. The neutrons are collected and moderated before ending up at v ...
... to be the worlds highest intensity neutron source. Using a linear accelerator, protons will be accelerated towards a target consisting of a neutron rich material, like tungsten, and neutrons are emitted through the process of spallation. The neutrons are collected and moderated before ending up at v ...