Electricity and Magnetism Reading Assignment: Read the entire
... magnetic field. The part of the magnet that will align toward the north pole of earth is called the north pole of the magnet. Some atoms, depending on their electronic structure, act like magnets and have a north and south pole. In most matter, there is no alignment of the poles of the atoms. In a b ...
... magnetic field. The part of the magnet that will align toward the north pole of earth is called the north pole of the magnet. Some atoms, depending on their electronic structure, act like magnets and have a north and south pole. In most matter, there is no alignment of the poles of the atoms. In a b ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... magnetic field. The part of the magnet that will align toward the north pole of earth is called the north pole of the magnet. Some atoms, depending on their electronic structure, act like magnets and have a north and south pole. In most matter, there is no alignment of the poles of the atoms. In a b ...
... magnetic field. The part of the magnet that will align toward the north pole of earth is called the north pole of the magnet. Some atoms, depending on their electronic structure, act like magnets and have a north and south pole. In most matter, there is no alignment of the poles of the atoms. In a b ...
AP Physics Daily Problem #107
... Three 5.0g particles each have a charge of 5.0C and are located 0.3m apart as shown here. Note that the lower charge is negative. Draw your estimate of the net force vector on each particle. ...
... Three 5.0g particles each have a charge of 5.0C and are located 0.3m apart as shown here. Note that the lower charge is negative. Draw your estimate of the net force vector on each particle. ...
Document
... 3.1 The simplest approximation To ignore all interactions between electrons and consider each electron as moving under the action only of the nucleus (considered to be a point charge). The wave function for each electron is a function like those for the hydrogen atom, specified by four quantum numbe ...
... 3.1 The simplest approximation To ignore all interactions between electrons and consider each electron as moving under the action only of the nucleus (considered to be a point charge). The wave function for each electron is a function like those for the hydrogen atom, specified by four quantum numbe ...
Word
... Ephoton = hf (The equation is given in Table 1of the IB Data booklet). h is Planck’s constant (Table 2 of the IB Data booklet). ...
... Ephoton = hf (The equation is given in Table 1of the IB Data booklet). h is Planck’s constant (Table 2 of the IB Data booklet). ...
H2 PHYSICS SET B PAPER 2 THE PHYSICS CAFE
... If you wish to get the maximum power transfer from, say a battery to an electrical appliance, what sort of resistance should the appliance have? At first sight a small resistance seems sensible, because then a large current will flow, but unfortunately drawing a large current from a supply lowers it ...
... If you wish to get the maximum power transfer from, say a battery to an electrical appliance, what sort of resistance should the appliance have? At first sight a small resistance seems sensible, because then a large current will flow, but unfortunately drawing a large current from a supply lowers it ...
Document
... They fill all the lower energy levels of an atom. Outer electrons are those in the highest energy level (highest n value). They spend most of their time farthest from the nucleus. Valence electrons are those involved in forming compounds. Among main group elements, the valence electrons are the oute ...
... They fill all the lower energy levels of an atom. Outer electrons are those in the highest energy level (highest n value). They spend most of their time farthest from the nucleus. Valence electrons are those involved in forming compounds. Among main group elements, the valence electrons are the oute ...
Energy Loss of a Charged Particle Traversing Ionized Gas and
... The energy loss due to free electrons thus derived is added to the contribution from ions and neutral atoms. Then the total energy loss is expressed in terms of the degree of ionization, a. The fractional excess energy loss is found to be of the order of ajZ, where Z is the atomic number of the medi ...
... The energy loss due to free electrons thus derived is added to the contribution from ions and neutral atoms. Then the total energy loss is expressed in terms of the degree of ionization, a. The fractional excess energy loss is found to be of the order of ajZ, where Z is the atomic number of the medi ...
PDF version
... that Vstop did not depend at all on the intensity of the light! Doubling the light intensity doubled the number of electrons emitted, but did not affect the energies of the emitted electrons. The more powerful oscillating field ejected more electrons, but the maximum individual energy of the ejected ...
... that Vstop did not depend at all on the intensity of the light! Doubling the light intensity doubled the number of electrons emitted, but did not affect the energies of the emitted electrons. The more powerful oscillating field ejected more electrons, but the maximum individual energy of the ejected ...
Paper II
... 23. An aeroplane flies horizontally at a low altitude with a constant speed of 300ms-1. It transmits a radio signal of frequency 30 MHz as it passes a receiving station. What is the difference in the frequencies received a long time before and a long time after the passage of the plane? A. 10 Hz B. ...
... 23. An aeroplane flies horizontally at a low altitude with a constant speed of 300ms-1. It transmits a radio signal of frequency 30 MHz as it passes a receiving station. What is the difference in the frequencies received a long time before and a long time after the passage of the plane? A. 10 Hz B. ...
Physics - WordPress.com
... Electrical charge 2.19 identify common materials which are electrical conductors or insulators, including metals and plastics – Materials that conduct electricity are conductors. – Usually metallic: copper, silver, gold. – Materials that cannot conduct electricity are insulators – Usually non-metal ...
... Electrical charge 2.19 identify common materials which are electrical conductors or insulators, including metals and plastics – Materials that conduct electricity are conductors. – Usually metallic: copper, silver, gold. – Materials that cannot conduct electricity are insulators – Usually non-metal ...
Electron Effective Mass, m*
... (ions and core electrons) AND external forces such as electric fields • In a crystal lattice, the net force may be opposite the external force, however: Fext =-qE Fint =-dEp/dx ...
... (ions and core electrons) AND external forces such as electric fields • In a crystal lattice, the net force may be opposite the external force, however: Fext =-qE Fint =-dEp/dx ...
Physical Properties of Elements and Semiconductors
... To understand the location and energy of each electron in an atom, one must have the knowledge of following four quantum numbers: (i) Principal Quantum Number (n). This characterises the average distance of an electron from the nucleus and corresponds to the principal energy level in which electron ...
... To understand the location and energy of each electron in an atom, one must have the knowledge of following four quantum numbers: (i) Principal Quantum Number (n). This characterises the average distance of an electron from the nucleus and corresponds to the principal energy level in which electron ...
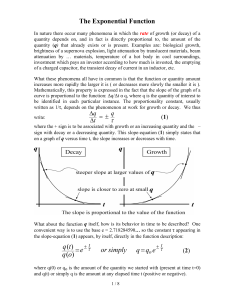
Exponential Function
... The base e is used because in many situations the rate of change of the function (the slope) is known in terms of the constant τ, but the function itself is not known. Thus whenever equation (1) is obeyed by some phenomenon, it is then a simple matter to describe the function itself immediately wit ...
... The base e is used because in many situations the rate of change of the function (the slope) is known in terms of the constant τ, but the function itself is not known. Thus whenever equation (1) is obeyed by some phenomenon, it is then a simple matter to describe the function itself immediately wit ...
Modern
... When potassium ions are examined by this mass spectrometer, the detector registers a peak current when the accelerating p.d. is 613 V with another much smaller peak at 583 V. A student comments that this is due to the presence of isotopes. Explain why the above phenomenon may be explained by the pre ...
... When potassium ions are examined by this mass spectrometer, the detector registers a peak current when the accelerating p.d. is 613 V with another much smaller peak at 583 V. A student comments that this is due to the presence of isotopes. Explain why the above phenomenon may be explained by the pre ...
Physics 103 Hour Exam #2 Solution Point values are given for each
... will diffuse into one another. This means that, over a long period of time, the gases will combine to form a uniform mixture of A and B molecules. There are various ways of measuring the diffusion rate. For example, you could measure how much time it takes for 25% of the A molecules to be in the rig ...
... will diffuse into one another. This means that, over a long period of time, the gases will combine to form a uniform mixture of A and B molecules. There are various ways of measuring the diffusion rate. For example, you could measure how much time it takes for 25% of the A molecules to be in the rig ...
Chapter 2 – The Structure of the Atom Since the book assumes you
... nucleus and protons in the early 20th century required a model of the atom classical physics could not provide. The first real model to describe the atom with some accuracy was proposed by Neils Bohr and is the familiar electron traveling around a nucleus in circular orbits. This model employed seve ...
... nucleus and protons in the early 20th century required a model of the atom classical physics could not provide. The first real model to describe the atom with some accuracy was proposed by Neils Bohr and is the familiar electron traveling around a nucleus in circular orbits. This model employed seve ...
Charge Carriers in Semiconductors.
... Intrinsic Semiconductors: Thermal ionization: Valence electron---each silicon atom has four valence electrons Covalent bond---two valence electrons from different two silicon atoms form the covalent bond Be intact at sufficiently low temperature Be broken at room temperature Free electron ...
... Intrinsic Semiconductors: Thermal ionization: Valence electron---each silicon atom has four valence electrons Covalent bond---two valence electrons from different two silicon atoms form the covalent bond Be intact at sufficiently low temperature Be broken at room temperature Free electron ...
What is Electricity? - SparkFun Learn
... rule when it comes to making circuits is they can’t have any insulating gaps in them. If you have a wire full of copper atoms and want to induce a flow of electrons through it,all free electrons need somewhere to flow in the same general direction. Copper is a great conductor, perfect for making cha ...
... rule when it comes to making circuits is they can’t have any insulating gaps in them. If you have a wire full of copper atoms and want to induce a flow of electrons through it,all free electrons need somewhere to flow in the same general direction. Copper is a great conductor, perfect for making cha ...