CHAPTER Atoms
... 43 ∙∙ Why is the energy of the 3s state considerably lower than that of the 3p state for sodium, whereas in hydrogen these states have essentially the same energy? The s state, with ! = 0, is a “penetrating” state in which the probability density near the nucleus is significant. Consequently, the 3s ...
... 43 ∙∙ Why is the energy of the 3s state considerably lower than that of the 3p state for sodium, whereas in hydrogen these states have essentially the same energy? The s state, with ! = 0, is a “penetrating” state in which the probability density near the nucleus is significant. Consequently, the 3s ...
Physics 12 Class th
... When temperature of source and sink of a heat engine becomes equal, the entropy change will be __________. ...
... When temperature of source and sink of a heat engine becomes equal, the entropy change will be __________. ...
Modeling Dusty Plasma Discharges of Noble Gases Using a Self
... Neon and xenon have six excitation levels compared to argon and helium that only have one. Moreover, all of the excitation levels are at lower energies than that required for ionization. Therefore, energy losses for neon and xenon extended further into the bulk and were not contained to locations of ...
... Neon and xenon have six excitation levels compared to argon and helium that only have one. Moreover, all of the excitation levels are at lower energies than that required for ionization. Therefore, energy losses for neon and xenon extended further into the bulk and were not contained to locations of ...
What is electricity?
... protons carry a charge. The amount of the charge is the same for each particle, but opposite in sign. Electrons carry a negative charge while protons carry positive charge. The objects around us contain billions and billions of atoms, and each atom contains many protons and electrons. The protons ar ...
... protons carry a charge. The amount of the charge is the same for each particle, but opposite in sign. Electrons carry a negative charge while protons carry positive charge. The objects around us contain billions and billions of atoms, and each atom contains many protons and electrons. The protons ar ...
Physics 12: Curriculum Document Nicole Heighton, Zack MacAulay
... Concepts: the roles and evidence/ theories of scientific paradigms, development of major scientific knowledge, magnetic, electric and gravitational fields as regions of space that affect mass and charge or as lines of force. Materials: low level beta radiation source, Geiger counter, various thickne ...
... Concepts: the roles and evidence/ theories of scientific paradigms, development of major scientific knowledge, magnetic, electric and gravitational fields as regions of space that affect mass and charge or as lines of force. Materials: low level beta radiation source, Geiger counter, various thickne ...
Electrostatics, Electricity, and Magnetism
... electricity. You are familiar with the terms positive and negative and should recall that atoms are composed of positively charged protons, negatively charged electrons, as well as neutral neutrons. While studying of atoms you learned that there were positively charged protons in the nucleus and neg ...
... electricity. You are familiar with the terms positive and negative and should recall that atoms are composed of positively charged protons, negatively charged electrons, as well as neutral neutrons. While studying of atoms you learned that there were positively charged protons in the nucleus and neg ...
Accelerator Terms
... Thin aluminum foil to strip a pair of electrons from negatively charged hydrogen ions to convert them to protons for injection into a proton storage ring. ...
... Thin aluminum foil to strip a pair of electrons from negatively charged hydrogen ions to convert them to protons for injection into a proton storage ring. ...
tut8_q
... 15 Interactive Solution 18.15 provides a model for solving this type of problem. Two small objects, A and B, are fixed in place and separated by 3.00 cm in a vacuum. Object A has a charge of +2.00 µC, and object B has a charge of –2.00 µC. How many electrons must be removed from A and put onto B to ...
... 15 Interactive Solution 18.15 provides a model for solving this type of problem. Two small objects, A and B, are fixed in place and separated by 3.00 cm in a vacuum. Object A has a charge of +2.00 µC, and object B has a charge of –2.00 µC. How many electrons must be removed from A and put onto B to ...
Lecture 5 Molecular Orbital Theory Part 1 Molecular Orbital Theory
... • When the constituent AOs are in phase the result is a bonding orbital • This MO can accommodate two electrons (usually one from each atom). • The energy of the MO is lower than the energy of the two constituent AOs, so placing two electrons in such an orbital results in a net stabilisation of the ...
... • When the constituent AOs are in phase the result is a bonding orbital • This MO can accommodate two electrons (usually one from each atom). • The energy of the MO is lower than the energy of the two constituent AOs, so placing two electrons in such an orbital results in a net stabilisation of the ...
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
... The absorption-emission mechanism:When a laser beam (of suitable frequency) collides an atom moving toward the beam, the atom may absorb the laser photon energy, and recoil. This leads to the slowing of the atom. In the proves, the electron in the atom will jump up to a higher level. Then, it sponta ...
... The absorption-emission mechanism:When a laser beam (of suitable frequency) collides an atom moving toward the beam, the atom may absorb the laser photon energy, and recoil. This leads to the slowing of the atom. In the proves, the electron in the atom will jump up to a higher level. Then, it sponta ...
Physics 3 - Bangor University
... 2. The incident angle θ1 equal to the critical angle and so the light ray passes along the surface of the boundary. 3. The incident angle is greater than the critical angle and so the light ray is reflected back into the water. This phenomenon is known as total internal reflection. θ1 = θ2 ...
... 2. The incident angle θ1 equal to the critical angle and so the light ray passes along the surface of the boundary. 3. The incident angle is greater than the critical angle and so the light ray is reflected back into the water. This phenomenon is known as total internal reflection. θ1 = θ2 ...
Course Objectives - Seattle Public Schools
... From the Washington State K-12 Science Learning Standards, June 2009 ...
... From the Washington State K-12 Science Learning Standards, June 2009 ...
SDW`s
... of the cubic unit cell (Corliss et al., PRL 3 (1959), p211) . These results came on the moment that neutron diffraction techniques became a suitable tool for determining magnetic structures. We come to that later. Anyhow, there was a problem how to explain these results. ...
... of the cubic unit cell (Corliss et al., PRL 3 (1959), p211) . These results came on the moment that neutron diffraction techniques became a suitable tool for determining magnetic structures. We come to that later. Anyhow, there was a problem how to explain these results. ...
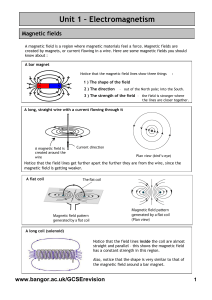
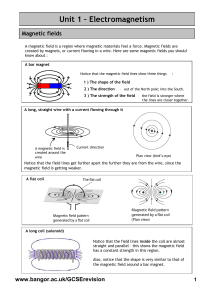
Unit 1 – Electromagnetism
... 2. The incident angle θ1 equal to the critical angle and so the light ray passes along the surface of the boundary. 3. The incident angle is greater than the critical angle and so the light ray is reflected back into the water. This phenomenon is known as total internal reflection. θ1 = θ2 ...
... 2. The incident angle θ1 equal to the critical angle and so the light ray passes along the surface of the boundary. 3. The incident angle is greater than the critical angle and so the light ray is reflected back into the water. This phenomenon is known as total internal reflection. θ1 = θ2 ...
Chapter 1 Introduction: Physical Quantities, Units and Mathematical
... The sciences of electricity and magnetism developed separately for centuries – until 1820 when Oersted found an electric current in a wire can deflect a magnetic compass needle. The new science of electromagnetism (the combination of electrical and magnetic phenomena) was developed further by resear ...
... The sciences of electricity and magnetism developed separately for centuries – until 1820 when Oersted found an electric current in a wire can deflect a magnetic compass needle. The new science of electromagnetism (the combination of electrical and magnetic phenomena) was developed further by resear ...
Physics 2220 - University of Utah
... Electric flux through closed surface is proportional to the amount of electric charge inside (electric monopoles). ...
... Electric flux through closed surface is proportional to the amount of electric charge inside (electric monopoles). ...