Nervous System Lecture- Part II
... Cells are densely packed and intertwined Two main cell types: 1. Neurons Excitable – transmit electrical signals 2. Glial cells – support cells Also called neuroglia or simply glia Non-excitable – do not transmit electrical signals ...
... Cells are densely packed and intertwined Two main cell types: 1. Neurons Excitable – transmit electrical signals 2. Glial cells – support cells Also called neuroglia or simply glia Non-excitable – do not transmit electrical signals ...
Biology 2121 – Lecture Sheet – ANS 1. The autonomic nervous sy
... 28. The nerves that leave the sacral area via the ventral rami are called the __________________ nerves and join to form the __________________ plexus. 29. The cell bodies of the sympathetic preganglionic neurons can be found in this portion of the spinal cord: _____________. They exit via the _____ ...
... 28. The nerves that leave the sacral area via the ventral rami are called the __________________ nerves and join to form the __________________ plexus. 29. The cell bodies of the sympathetic preganglionic neurons can be found in this portion of the spinal cord: _____________. They exit via the _____ ...
Loss of orexin/NARP neurons in human narcolepsy
... of the paraventricular nucleus and reached a high density in the dorsal hypothalamic area, dorsomedial nucleus, and perifornical region. Caudally, cells were abundant in the lateral and posterior hypothalamus. Across the entire ORX field, nearly all ORX-ir neurons contained NARP-immunoreactivity. In ...
... of the paraventricular nucleus and reached a high density in the dorsal hypothalamic area, dorsomedial nucleus, and perifornical region. Caudally, cells were abundant in the lateral and posterior hypothalamus. Across the entire ORX field, nearly all ORX-ir neurons contained NARP-immunoreactivity. In ...
reading guide
... A single postsynaptic neuron can be affected by neurotransmitter molecules released by many other neurons, some releasing excitatory and some releasing inhibitory neurotransmitters. What will determine whether an action potential is generated in the postsynaptic neuron? ...
... A single postsynaptic neuron can be affected by neurotransmitter molecules released by many other neurons, some releasing excitatory and some releasing inhibitory neurotransmitters. What will determine whether an action potential is generated in the postsynaptic neuron? ...
Chapter 2: Neuroscience
... Helps impulses travel quickly Importance of the myelin sheath is seen in ...
... Helps impulses travel quickly Importance of the myelin sheath is seen in ...
Theoretical neuroscience: Single neuron dynamics and computation
... Israel (HU, 1990s) and Europe (Gatsby Unit, Bernstein Centers, 2000s) ...
... Israel (HU, 1990s) and Europe (Gatsby Unit, Bernstein Centers, 2000s) ...
LEARNING OBJECTIVE 5: Explain how an injured nerve fiber may
... that generally carry impulses toward the nerve cell body are dendrites. What would one call the portion of the neuron process which connects the dendrites to the axon? Answer: In unipolar sensory neurons, the portion of the neuron process which connects dendrites to axon conveys properties of both. ...
... that generally carry impulses toward the nerve cell body are dendrites. What would one call the portion of the neuron process which connects the dendrites to the axon? Answer: In unipolar sensory neurons, the portion of the neuron process which connects dendrites to axon conveys properties of both. ...
One difference between axons and dendrites is that
... One thing that differentiates neurons from other body cells is that only neurons A. contain mitochondria. B. have a nucleus in their cell body. C. have an outer membrane that acts as a filter. D. have axons and dendrites. One difference between axons and dendrites is that A. axons carry signals to t ...
... One thing that differentiates neurons from other body cells is that only neurons A. contain mitochondria. B. have a nucleus in their cell body. C. have an outer membrane that acts as a filter. D. have axons and dendrites. One difference between axons and dendrites is that A. axons carry signals to t ...
1. Cell body - greinerudsd
... The Resting Neuron When a neuron is at rest – There is a certain amount of ions inside & outside of cell – This difference in charges is called the resting potential (-70mV) ...
... The Resting Neuron When a neuron is at rest – There is a certain amount of ions inside & outside of cell – This difference in charges is called the resting potential (-70mV) ...
Glands
... body that can turn other kinds of energy into action potentials that the nervous system can process. 0 Sensory Nerves: nerves that carry information from the sense receptors to the central nervous system. 0 Interneurons: nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord responsible for processing information ...
... body that can turn other kinds of energy into action potentials that the nervous system can process. 0 Sensory Nerves: nerves that carry information from the sense receptors to the central nervous system. 0 Interneurons: nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord responsible for processing information ...
P312Ch04C_BeyondV1
... 3) May be a separate area in the inferotemporal lobe containing neurons which respond to face-like stimuli. The fusiform face area has been identified in humans. It’s under the temporal lobe. 4) Ramachandran has suggested that there may be as many as 30 different processing modules. Each one contain ...
... 3) May be a separate area in the inferotemporal lobe containing neurons which respond to face-like stimuli. The fusiform face area has been identified in humans. It’s under the temporal lobe. 4) Ramachandran has suggested that there may be as many as 30 different processing modules. Each one contain ...
The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 PowerPoint
... 3. Which type of cell communicates within the central nervous system and processes information between incoming and outgoing messages? ANSWER A. B. C. D. ...
... 3. Which type of cell communicates within the central nervous system and processes information between incoming and outgoing messages? ANSWER A. B. C. D. ...
KKDP4: The role of neurotransmitters in the transmission of neural
... A postsynaptic neuron may have many different shaped receptor sites on its dendrites and may therefore be able to receive several different neurotransmitters. ...
... A postsynaptic neuron may have many different shaped receptor sites on its dendrites and may therefore be able to receive several different neurotransmitters. ...
nervous system 2012 - Junction Hill C
... nervous system. Humans have about 100 billion neurons in their brain alone! While variable in size and shape, all neurons have three parts. Dendrites receive information from another cell and transmit the message to the cell body. The cell body contains the nucleus. The axon conducts messages away f ...
... nervous system. Humans have about 100 billion neurons in their brain alone! While variable in size and shape, all neurons have three parts. Dendrites receive information from another cell and transmit the message to the cell body. The cell body contains the nucleus. The axon conducts messages away f ...
Slide ()
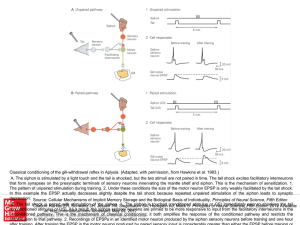
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
13.2 part 2
... In this example, stimuli of less than 2 mV does not produce any muscle contraction, whereas anything 2 mv and over produces the same force of muscle contraction. This experiment shows us two important things: All neurons have a threshold level or a minimum level that must be reached in order for an ...
... In this example, stimuli of less than 2 mV does not produce any muscle contraction, whereas anything 2 mv and over produces the same force of muscle contraction. This experiment shows us two important things: All neurons have a threshold level or a minimum level that must be reached in order for an ...
There are about 3 million miles of axons in the human brain. The
... include controlling responses to sight, eye Movement, pupil dilation, hearing and body movement ...
... include controlling responses to sight, eye Movement, pupil dilation, hearing and body movement ...
Finding the missing fundamental
... top-down influences from centres associated with complex functions in frontal or parietal lobes are also significant. This last point is relevant, because one technical advantage of this work is that the animals tested were awake rather than anaesthetized, meaning that attentional and other cognitiv ...
... top-down influences from centres associated with complex functions in frontal or parietal lobes are also significant. This last point is relevant, because one technical advantage of this work is that the animals tested were awake rather than anaesthetized, meaning that attentional and other cognitiv ...
PIPE CLEANER NEURON LESSON PLAN Part A
... Teacher leads students through a review of the function of the parts of the neuron by using arm of their body. Arm should bent at elbow with fingers pointing upwards. Palm – Cell body/Neuron – Creates the message Fingers – Dendrites – Receives the message Elbow – Synaptic Terminal/Axon Terminal – Se ...
... Teacher leads students through a review of the function of the parts of the neuron by using arm of their body. Arm should bent at elbow with fingers pointing upwards. Palm – Cell body/Neuron – Creates the message Fingers – Dendrites – Receives the message Elbow – Synaptic Terminal/Axon Terminal – Se ...
Lecture Suggestions and Guidelines
... remission and exacerbation. What might be a probable diagnosis? Answer: A chronic, progressive disease of unknown origin which affects the central nervous system by the degeneration of the protective myelin sheath called Multiple Sclerosis would be a possible diagnosis which should be confirmed via ...
... remission and exacerbation. What might be a probable diagnosis? Answer: A chronic, progressive disease of unknown origin which affects the central nervous system by the degeneration of the protective myelin sheath called Multiple Sclerosis would be a possible diagnosis which should be confirmed via ...
NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION
... called neurons which transmit messages (nerve impulses) from one part of the body to another. The human nervous system is most highly complex and integrated by receiving stimuli, sending impulses and controls different functions of the body. The nervous system is very simple in lower invertebrates ( ...
... called neurons which transmit messages (nerve impulses) from one part of the body to another. The human nervous system is most highly complex and integrated by receiving stimuli, sending impulses and controls different functions of the body. The nervous system is very simple in lower invertebrates ( ...
1: Nervous System II: Anatomy Review
... The neuron conducting the impulse toward the synapse is called the __________________ neuron. The axon terminal contains ___________ ____________ filled with ______________________. An action potential in the axon terminal of the _____________ neuron causes the chemical transmitter, also known as a ...
... The neuron conducting the impulse toward the synapse is called the __________________ neuron. The axon terminal contains ___________ ____________ filled with ______________________. An action potential in the axon terminal of the _____________ neuron causes the chemical transmitter, also known as a ...