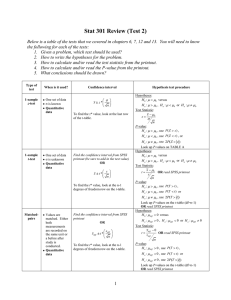
Student`s t-test
... 9. If the calculated t value exceeds the tabulated value we say that the means are significantly different at that level of probability. 10. A significant difference at p = 0.05 means that if the null hypothesis were correct (i.e. the samples or treatments do not differ) then we would expect to get ...
... 9. If the calculated t value exceeds the tabulated value we say that the means are significantly different at that level of probability. 10. A significant difference at p = 0.05 means that if the null hypothesis were correct (i.e. the samples or treatments do not differ) then we would expect to get ...
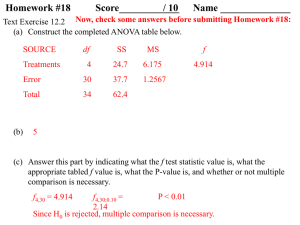
One-Way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
... Knowing which group the person is in takes you 5 points closer to their actual score. This deviation of 5 points is a deviation we can account for because we can explain where it comes from. It comes from the fact that people who get a lot of tutoring have scores that are 5 points higher, on average ...
... Knowing which group the person is in takes you 5 points closer to their actual score. This deviation of 5 points is a deviation we can account for because we can explain where it comes from. It comes from the fact that people who get a lot of tutoring have scores that are 5 points higher, on average ...
lecture 6 hypothesis tests II
... Two surveys of mortgage payment protection insurance (MPPI) are carried out, one on single parents with 1 child and one on single parents with 3 children. Amongst the first group, 67 out of a sample of 300 were found to have taken out MPPI, compared with 15 out of a sample of 101 in the second group ...
... Two surveys of mortgage payment protection insurance (MPPI) are carried out, one on single parents with 1 child and one on single parents with 3 children. Amongst the first group, 67 out of a sample of 300 were found to have taken out MPPI, compared with 15 out of a sample of 101 in the second group ...
t-test
... Suppose that a new product was test marketed in the United States and in Japan. The company hypothesizes that customers in both countries would consume the product at the same rate. A sample of 500 in the U.S. used an average of 200 kilograms a year (sd = 20), while a sample of 400 in Japan used an ...
... Suppose that a new product was test marketed in the United States and in Japan. The company hypothesizes that customers in both countries would consume the product at the same rate. A sample of 500 in the U.S. used an average of 200 kilograms a year (sd = 20), while a sample of 400 in Japan used an ...
Summer Research Opportunities Program Statistics Boot Camp
... Some processes may have more measurement error than others Too expensive Unrealistic to survey all of the population Too time-consuming ...
... Some processes may have more measurement error than others Too expensive Unrealistic to survey all of the population Too time-consuming ...
lecture6_na
... of 64.64 inches; the 10 people born on even days had heights of 71.15 inches. Height is roughly normally distributed. Which of the following best represents the correct statistical test for these data? a. Z 71.1 64.6 6.5 1.44; p ns ...
... of 64.64 inches; the 10 people born on even days had heights of 71.15 inches. Height is roughly normally distributed. Which of the following best represents the correct statistical test for these data? a. Z 71.1 64.6 6.5 1.44; p ns ...
File - TAU R Workshop 2015
... We can see here that our models: 24 months, 9271 ₪ and 173 cm are not very successful The Residual Is how much a certain value is far from the prediction of the model . Omri Caspi is far away in 32 cm from the model “Israeli = 173” and in 29 cm from the more complicated model: “Israeli man = 177, Is ...
... We can see here that our models: 24 months, 9271 ₪ and 173 cm are not very successful The Residual Is how much a certain value is far from the prediction of the model . Omri Caspi is far away in 32 cm from the model “Israeli = 173” and in 29 cm from the more complicated model: “Israeli man = 177, Is ...
Document
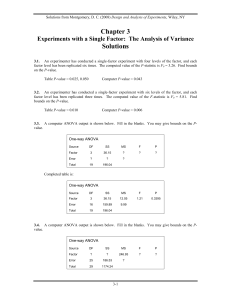
... Since the quantitative variable breaking strength is being compared for three rope types, three contiguous box plots is an appropriate graphical display. (i) Summarize the results (Step 4) of Levene’s f test to see if there is sufficient evidence at the 0.05 level that the standard deviation of brea ...
... Since the quantitative variable breaking strength is being compared for three rope types, three contiguous box plots is an appropriate graphical display. (i) Summarize the results (Step 4) of Levene’s f test to see if there is sufficient evidence at the 0.05 level that the standard deviation of brea ...
parametric statistics version 2[1].
... This does not mean we fix the value of the observation, but simply that for various statistics we have to calculate the number of observations that are free to vary. This number is called: Degrees of freedom and it must be one less than the sample size (N-1). ...
... This does not mean we fix the value of the observation, but simply that for various statistics we have to calculate the number of observations that are free to vary. This number is called: Degrees of freedom and it must be one less than the sample size (N-1). ...
PSYCHOLOGICAL STATISTICS B Sc COUNSELLING PSYCHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT IV Semester
... aptitude’. In the case of finding whether the variables X and Y are related or not, the null hypothesis will be ‘the two variables X and Y are not related’ or ‘there is no significant relationship between the variables X and Y’. If the population mean score of a variable X is 60, one can test whethe ...
... aptitude’. In the case of finding whether the variables X and Y are related or not, the null hypothesis will be ‘the two variables X and Y are not related’ or ‘there is no significant relationship between the variables X and Y’. If the population mean score of a variable X is 60, one can test whethe ...
Analysis of variance

Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a collection of statistical models used to analyze the differences among group means and their associated procedures (such as ""variation"" among and between groups), developed by statistician and evolutionary biologist Ronald Fisher. In the ANOVA setting, the observed variance in a particular variable is partitioned into components attributable to different sources of variation. In its simplest form, ANOVA provides a statistical test of whether or not the means of several groups are equal, and therefore generalizes the t-test to more than two groups. As doing multiple two-sample t-tests would result in an increased chance of committing a statistical type I error, ANOVAs are useful for comparing (testing) three or more means (groups or variables) for statistical significance.














![parametric statistics version 2[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002643361_1-f1ac5a1364ee6a2d4038d7b36f236808-300x300.png)