NERVOUS SYSTEM REVIEW
... system is responsible for increasing the output of energy during emotion and stress (pumping you up!) ...
... system is responsible for increasing the output of energy during emotion and stress (pumping you up!) ...
Neurons and the General Layout of the Nervous System - U
... • the glial cells and satellite cells that form the myelin sheaths of axons in the CNS and PNS are oligodendroglia and Schwann cells, respectively • Only Schwann cells are regenerative. Damage is permanent if it occurs in oligodendroglia (cause of Parkinson’s, degeneration of myelin of dopaminergic ...
... • the glial cells and satellite cells that form the myelin sheaths of axons in the CNS and PNS are oligodendroglia and Schwann cells, respectively • Only Schwann cells are regenerative. Damage is permanent if it occurs in oligodendroglia (cause of Parkinson’s, degeneration of myelin of dopaminergic ...
Fill in the blanks on LB page 67-68.
... A. Many axons are covered by a myelin sheath derived in part from Schwann cells. 1. Each section of the sheath is separated from adjacent ones by a region (node of Ranvier) where the axon membrane (plentiful in gated sodium channels) is exposed. B. The myelin sheath has other functions: 1. It saves ...
... A. Many axons are covered by a myelin sheath derived in part from Schwann cells. 1. Each section of the sheath is separated from adjacent ones by a region (node of Ranvier) where the axon membrane (plentiful in gated sodium channels) is exposed. B. The myelin sheath has other functions: 1. It saves ...
neuron - Cloudfront.net
... Motor neurons: carry response impulses away from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or gland ...
... Motor neurons: carry response impulses away from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or gland ...
The Nervous System
... 2. MOTOR NEURON: (= efferent neuron) takes message away from CNS to a muscle fiber or gland. Short dendrites, long axon. 3. INTERNEURON: (= association neuron or connector neuron): completely contained within CNS. Conveys messages between parts of the system. Dendrites, axons, may be long or short. ...
... 2. MOTOR NEURON: (= efferent neuron) takes message away from CNS to a muscle fiber or gland. Short dendrites, long axon. 3. INTERNEURON: (= association neuron or connector neuron): completely contained within CNS. Conveys messages between parts of the system. Dendrites, axons, may be long or short. ...
Module 04
... The brain’s neurons cluster into work groups called neural networks. Myers is pointing out that the brain works much like a computer making many simultaneous computations. This is accomplished by neural networks, which are clusters of interconnected neurons (work groups). Neurons work with other nea ...
... The brain’s neurons cluster into work groups called neural networks. Myers is pointing out that the brain works much like a computer making many simultaneous computations. This is accomplished by neural networks, which are clusters of interconnected neurons (work groups). Neurons work with other nea ...
Lecture 1 Brain Structure
... Myelinated regions of axon are electrically insulated. Electrical charge moves along the axon rather than across the membrane. Action potentials occur only at unmyelinated regions: nodes of Ranvier. ...
... Myelinated regions of axon are electrically insulated. Electrical charge moves along the axon rather than across the membrane. Action potentials occur only at unmyelinated regions: nodes of Ranvier. ...
Sensory neurons
... • Some important nerve cells have an axon that is covered in Myelin. • Myelin is a fatty substance that acts as an insulator and allows an nerve impulse to travel very quickly. • Multiple Sclerosis is a disease where the Myelin Sheath is damaged causing some signals to ‘short-circuit’. ...
... • Some important nerve cells have an axon that is covered in Myelin. • Myelin is a fatty substance that acts as an insulator and allows an nerve impulse to travel very quickly. • Multiple Sclerosis is a disease where the Myelin Sheath is damaged causing some signals to ‘short-circuit’. ...
B- Parietal
... Which part of the nervous system is protected by bone? A- central nervous system B- peripheral nervous system C- autonomic nervous system D- none of the above are protected by bone ...
... Which part of the nervous system is protected by bone? A- central nervous system B- peripheral nervous system C- autonomic nervous system D- none of the above are protected by bone ...
Chapter 12 Notes: Nervous Tissue 2014
... conduct nerve impulses faster Saltatory conduction = nerve impulse jumps between gaps in the myelin sheath called neurofibril nodes or Nodes of Ranvier (white matter is white because neurons are myelinated; gray matter is non-myelinated neurons) Neuron = nerve cell Nerve or tract = MANY nerve cells ...
... conduct nerve impulses faster Saltatory conduction = nerve impulse jumps between gaps in the myelin sheath called neurofibril nodes or Nodes of Ranvier (white matter is white because neurons are myelinated; gray matter is non-myelinated neurons) Neuron = nerve cell Nerve or tract = MANY nerve cells ...
Vocabulary Terms
... Axon: a long, fiber-like extension of a neuron that transmits signals from the cell body to the synapse. Brain: located in the skull, it is the organ that controls all body activities through the spinal cord and peripheral nerves of the nervous system. Codeine: a naturally occurring component (alkal ...
... Axon: a long, fiber-like extension of a neuron that transmits signals from the cell body to the synapse. Brain: located in the skull, it is the organ that controls all body activities through the spinal cord and peripheral nerves of the nervous system. Codeine: a naturally occurring component (alkal ...
fleming_Oct
... a nerve cell fiber in cross section, and the upper left inset gives a more realistic picture of the shape of neurons. The nerve impulse usually travels from the dendrites and soma to the branching ends of the axon. The neuron shown here is a motor neuron. Motor neurons originate in the brain or spin ...
... a nerve cell fiber in cross section, and the upper left inset gives a more realistic picture of the shape of neurons. The nerve impulse usually travels from the dendrites and soma to the branching ends of the axon. The neuron shown here is a motor neuron. Motor neurons originate in the brain or spin ...
Nervous System - Buck Mountain Central School
... bodies are located in clusters called ganglion located outside the spinal cord. • Interneurons – link neurons to other neurons. Found only in the brain and spinal cords, known as associated neurons connect sensory neurons to motor neurons. • Motor neurons – known as efferent relay info to effectors, ...
... bodies are located in clusters called ganglion located outside the spinal cord. • Interneurons – link neurons to other neurons. Found only in the brain and spinal cords, known as associated neurons connect sensory neurons to motor neurons. • Motor neurons – known as efferent relay info to effectors, ...
Nervous System Objectives
... 10. Label a diagram of a synaptic region and tell where neurotransmitters are released, direction of impulse travel, ion flow, and fusion of the neurotransmitter occur. 11. Identify the types of receptors and the structures found in the vision and hearing receptors. 12. Elaborate on the nervous syst ...
... 10. Label a diagram of a synaptic region and tell where neurotransmitters are released, direction of impulse travel, ion flow, and fusion of the neurotransmitter occur. 11. Identify the types of receptors and the structures found in the vision and hearing receptors. 12. Elaborate on the nervous syst ...
Action potential - Solon City Schools
... pressure or chemical messages (neurotransmitters) from other neurons. 2. Signals from other neurons are either ...
... pressure or chemical messages (neurotransmitters) from other neurons. 2. Signals from other neurons are either ...
Nervous System Exam Review
... Know the 5 types of neuroglia cell --- where are they found, what do they do. Identify neurons by structural classification and functional classification. Explain how an impulse travels and the ions involved. Terms: action potential resting membrane potential repolarization depolarization sodium-pot ...
... Know the 5 types of neuroglia cell --- where are they found, what do they do. Identify neurons by structural classification and functional classification. Explain how an impulse travels and the ions involved. Terms: action potential resting membrane potential repolarization depolarization sodium-pot ...
The Nervous System
... Cell body largest part contains the nucleus and much of the cytoplasm Dendrites branched extensions that spread out from the cell body receive impulses from other neurons and carry impulses to the cell body Axon the long fiber that carries impulses away from the cell body ends in a series of sma ...
... Cell body largest part contains the nucleus and much of the cytoplasm Dendrites branched extensions that spread out from the cell body receive impulses from other neurons and carry impulses to the cell body Axon the long fiber that carries impulses away from the cell body ends in a series of sma ...
Intro Nervous System and Neurons
... specialized to transmit messages – structures may differ, but all neurons have: PARTS: 1. Cell body –contains transparent nucleus –large conspicuous nucleolus –metabolic center of the cell ...
... specialized to transmit messages – structures may differ, but all neurons have: PARTS: 1. Cell body –contains transparent nucleus –large conspicuous nucleolus –metabolic center of the cell ...
summing-up - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... generates a resting membrane potential that is maintained by the action of proteins in the membrane. ...
... generates a resting membrane potential that is maintained by the action of proteins in the membrane. ...
Neuroscience Course Conference
... c. What might be the side effects of such a drug? 3. Although gNa increases as a graded function of membrane depolarization (Fig. 9-6 of textbook), the action potential has a discrete voltage threshold. Why? 4. During epileptic seizures, massive synchronous bursts of activity in cortical neurons cau ...
... c. What might be the side effects of such a drug? 3. Although gNa increases as a graded function of membrane depolarization (Fig. 9-6 of textbook), the action potential has a discrete voltage threshold. Why? 4. During epileptic seizures, massive synchronous bursts of activity in cortical neurons cau ...
Nervous System - Holy Trinity Diocesan High School
... Axon: Tail of the neuron that carries electrical information away from the body towards the next neuron Insulated with myelin ...
... Axon: Tail of the neuron that carries electrical information away from the body towards the next neuron Insulated with myelin ...
Slide ()
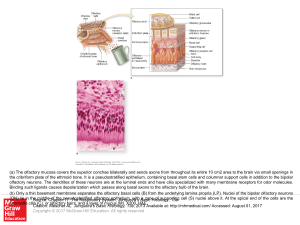
... (a) The olfactory mucosa covers the superior conchae bilaterally and sends axons from throughout its entire 10 cm2 area to the brain via small openings in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. It is a pseudostratified epithelium, containing basal stem cells and columnar support cells in addition ...
... (a) The olfactory mucosa covers the superior conchae bilaterally and sends axons from throughout its entire 10 cm2 area to the brain via small openings in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. It is a pseudostratified epithelium, containing basal stem cells and columnar support cells in addition ...
Nervous Regulation
... __________________. The junction between nerves and muscles is called a ______________ junction. ____________________ relay impulses from one neuron to another in the brain and spinal cord. The Synapse The axon ends in a __________________ which contains special chemicals called ________________ ...
... __________________. The junction between nerves and muscles is called a ______________ junction. ____________________ relay impulses from one neuron to another in the brain and spinal cord. The Synapse The axon ends in a __________________ which contains special chemicals called ________________ ...
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the electrical impulse travels along an axon from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction causes many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons.An axon is one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being dendrites. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites usually receive signals while axons usually transmit them). All of these rules have exceptions, however.Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other. Most axons branch, in some cases very profusely.Axons make contact with other cells—usually other neurons but sometimes muscle or gland cells—at junctions called synapses. At a synapse, the membrane of the axon closely adjoins the membrane of the target cell, and special molecular structures serve to transmit electrical or electrochemical signals across the gap. Some synaptic junctions appear partway along an axon as it extends—these are called en passant (""in passing"") synapses. Other synapses appear as terminals at the ends of axonal branches. A single axon, with all its branches taken together, can innervate multiple parts of the brain and generate thousands of synaptic terminals.