The Nervous System - riverridge210.org
... threshold. Any stimulus that is weaker than the threshold will produce no impulse. Any stimulus that is stronger than the threshold will have an impulse. ...
... threshold. Any stimulus that is weaker than the threshold will produce no impulse. Any stimulus that is stronger than the threshold will have an impulse. ...
Nervous System - IB BiologyMr. Van Roekel Salem High School
... neurons) are usually much smaller cells, with many ...
... neurons) are usually much smaller cells, with many ...
Somatic nervous system
... In invertebrates, depending on the neurotransmitter released and the type of receptor it binds, the response in the muscle fiber could either be excitatory or inhibitory. For vertebrates, however, the response of a muscle fiber to a neurotransmitter (always acetylcholine (ACh)) can only be excitator ...
... In invertebrates, depending on the neurotransmitter released and the type of receptor it binds, the response in the muscle fiber could either be excitatory or inhibitory. For vertebrates, however, the response of a muscle fiber to a neurotransmitter (always acetylcholine (ACh)) can only be excitator ...
Test 3
... each other. Nervous system, CNS, PNS, Somatic, ANS. Sensory, integration, motor 2. Describe the types of glial cells, Schwann, oligodendrocyte 3. Explain the physiological characteristics of mature neurons. 4. Discuss the function of each structure. 5. Describe the function of the myelin sheath, and ...
... each other. Nervous system, CNS, PNS, Somatic, ANS. Sensory, integration, motor 2. Describe the types of glial cells, Schwann, oligodendrocyte 3. Explain the physiological characteristics of mature neurons. 4. Discuss the function of each structure. 5. Describe the function of the myelin sheath, and ...
Nervous System ppt
... Using all the types of candy provided, make a neuron! Use your journal picture (and this one) to help you! ...
... Using all the types of candy provided, make a neuron! Use your journal picture (and this one) to help you! ...
Slide ()
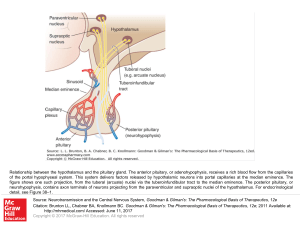
... Relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. The anterior pituitary, or adenohypophysis, receives a rich blood flow from the capillaries of the portal hypophyseal system. This system delivers factors released by hypothalamic neurons into portal capillaries at the median eminence. T ...
... Relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. The anterior pituitary, or adenohypophysis, receives a rich blood flow from the capillaries of the portal hypophyseal system. This system delivers factors released by hypothalamic neurons into portal capillaries at the median eminence. T ...
GENERAL CONCEPTS OF NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Gray matter – cell bodies and unmylenated fibers. Nuclei – clusters of cell bodies within the white matter of the central nervous system. Ganglia – collections of cell bodies outside the central nervous system. ...
... Gray matter – cell bodies and unmylenated fibers. Nuclei – clusters of cell bodies within the white matter of the central nervous system. Ganglia – collections of cell bodies outside the central nervous system. ...
Chapter 17 Review Jeopardy
... of marijuana on the nervous system? – A) THC binds to a receptor in the brain, blocking a natural neurotransmitter – B) THC interferes with short-term memory processing – C) can cause anxiety, depression, and paranoia – D) all of the above are true ...
... of marijuana on the nervous system? – A) THC binds to a receptor in the brain, blocking a natural neurotransmitter – B) THC interferes with short-term memory processing – C) can cause anxiety, depression, and paranoia – D) all of the above are true ...
CHAPTER 46 NEURONS AND NERVOUS SYSTEM
... 5. The CNS and PNS of the human nervous system are connected and work together to perform the functions of a nervous system. 39.2 Nervous Tissue A. Nervous tissue is made up of neurons and neuroglia, which supports and nourishes the neurons. B. Neurons 1. Neurons vary in size and shape but they all ...
... 5. The CNS and PNS of the human nervous system are connected and work together to perform the functions of a nervous system. 39.2 Nervous Tissue A. Nervous tissue is made up of neurons and neuroglia, which supports and nourishes the neurons. B. Neurons 1. Neurons vary in size and shape but they all ...
File
... Eliot Spitzer, the governor of New York who made his name as an aggressive prosecutor of corporate fraud and organized crime had to resign in disgrace in 2008 for being personally involved in a prostitution ring. These prostitutes charged up to $3100 an hour. ...
... Eliot Spitzer, the governor of New York who made his name as an aggressive prosecutor of corporate fraud and organized crime had to resign in disgrace in 2008 for being personally involved in a prostitution ring. These prostitutes charged up to $3100 an hour. ...
nervous system
... Up to one trillion nerve cells work together and coordinate the physical actions and mental processes that set humans apart from other species. ...
... Up to one trillion nerve cells work together and coordinate the physical actions and mental processes that set humans apart from other species. ...
Nerve Cell Physiology
... It can summate, which means if another stimulus is applied before repolarization is complete, the depolarization of the second stimulus adds onto the depolarization of the first (the 2 depolarizations sum together). رافع عاوي الفياض.د ...
... It can summate, which means if another stimulus is applied before repolarization is complete, the depolarization of the second stimulus adds onto the depolarization of the first (the 2 depolarizations sum together). رافع عاوي الفياض.د ...
Nervous System - healthsciencesMBIT
... The nervous system carries information from one part of the body to another The nervous system transmit information by nerve impulses to communicate with other parts of the body Main parts of the nervous system are the: Brain, Spinal Cord, and Nerves Regulate homeostasis and responds to disease ...
... The nervous system carries information from one part of the body to another The nervous system transmit information by nerve impulses to communicate with other parts of the body Main parts of the nervous system are the: Brain, Spinal Cord, and Nerves Regulate homeostasis and responds to disease ...
Briefed by: Dr. Hayder The human nervous system, by far the most
... A single long process called axon extending from the cells body to a specialized terminal (synapse) that transmits impulses from the cells body into the synapse. Axon varies in length from 1 mm to 1 meter. All axons originate from a pyramidal-shaped region called axonal hillock that arises from peri ...
... A single long process called axon extending from the cells body to a specialized terminal (synapse) that transmits impulses from the cells body into the synapse. Axon varies in length from 1 mm to 1 meter. All axons originate from a pyramidal-shaped region called axonal hillock that arises from peri ...
Unit 10 Chapter 36 The Nervous System
... to the spinal cord & brain Motor neurons carry impulses from the spinal cord & brain to the body Interneurons are found within the spinal cord & brain, pass response impulses between sensory & motor ...
... to the spinal cord & brain Motor neurons carry impulses from the spinal cord & brain to the body Interneurons are found within the spinal cord & brain, pass response impulses between sensory & motor ...
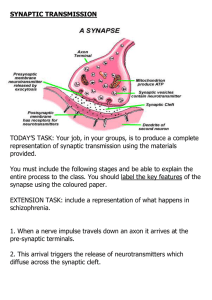
SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION
... Synaptic transmission: Additional Information Neurotransmitters include: dopamine, acetylcholine and serotonin. These can all influence the post-synaptic neuron to respond in an inhibitory way (decreases the firing of a cell) or an excitatory way (increases the firing of a cell). Schizophrenia, ...
... Synaptic transmission: Additional Information Neurotransmitters include: dopamine, acetylcholine and serotonin. These can all influence the post-synaptic neuron to respond in an inhibitory way (decreases the firing of a cell) or an excitatory way (increases the firing of a cell). Schizophrenia, ...
The Nervous System - OCPS TeacherPress
... Serotonin: control of mood, appetite, and the induction of sleep. Nitric oxide: causes vasodilation. Lowers bp and causes erection in penis. (viagra enhances the effect of NO) Endorphins: natural painkillers, feelings of ...
... Serotonin: control of mood, appetite, and the induction of sleep. Nitric oxide: causes vasodilation. Lowers bp and causes erection in penis. (viagra enhances the effect of NO) Endorphins: natural painkillers, feelings of ...
The Nervous System
... Functions of astrocytes: 1. Connect neurons to capillaries. This makes up the “blood-brain barrier”. 2. Maintain the the electrochemical environment ...
... Functions of astrocytes: 1. Connect neurons to capillaries. This makes up the “blood-brain barrier”. 2. Maintain the the electrochemical environment ...
Nervous System
... Cells of the Nervous System • Neurons (primary cells) – Consist of a cell body and two types of processes • Dendrites: Short, often highly branched cytoplasmic extensions that are tapered from their bases at the neuron cell body to their tips • Axons: long cell process extending from the neuron cel ...
... Cells of the Nervous System • Neurons (primary cells) – Consist of a cell body and two types of processes • Dendrites: Short, often highly branched cytoplasmic extensions that are tapered from their bases at the neuron cell body to their tips • Axons: long cell process extending from the neuron cel ...
The Nerve Impulse - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... If the overall results are excitatory, impulses are transmitted down the axon to the next set of synapses. If the results are inhibitory, no impulses are transmitted. Much of the complex behaviour of an organism results from the great number and variety of synaptic circuits formed when neurons are ...
... If the overall results are excitatory, impulses are transmitted down the axon to the next set of synapses. If the results are inhibitory, no impulses are transmitted. Much of the complex behaviour of an organism results from the great number and variety of synaptic circuits formed when neurons are ...
Real Neurons for Engineers
... their membranes. This changes ion concentrations and the potential across their membrane. The ions then function in various ways to cause changes in the neuron. • Bob will teach this. I will show you how to model it. ...
... their membranes. This changes ion concentrations and the potential across their membrane. The ions then function in various ways to cause changes in the neuron. • Bob will teach this. I will show you how to model it. ...
nervous system
... Body: Contains nucleus, control center of the cell. Regulates production of protein within the cell. Neurons ...
... Body: Contains nucleus, control center of the cell. Regulates production of protein within the cell. Neurons ...
The nervous system
... Schwann cells are part of the peripheral nervous system (PNS.) They have two major functions, they produce the myelin sheath which covers the Schwann cell, which helps to repair and regenerate nerves that have been damaged. In addition, they help the nerve impulse to be passed on quicker so that the ...
... Schwann cells are part of the peripheral nervous system (PNS.) They have two major functions, they produce the myelin sheath which covers the Schwann cell, which helps to repair and regenerate nerves that have been damaged. In addition, they help the nerve impulse to be passed on quicker so that the ...
The human brain
... Defined the cerebral cortex into 52 distinct regions on the basis of their cytoarchitectonic characteristics. ...
... Defined the cerebral cortex into 52 distinct regions on the basis of their cytoarchitectonic characteristics. ...
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the electrical impulse travels along an axon from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction causes many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons.An axon is one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being dendrites. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites usually receive signals while axons usually transmit them). All of these rules have exceptions, however.Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other. Most axons branch, in some cases very profusely.Axons make contact with other cells—usually other neurons but sometimes muscle or gland cells—at junctions called synapses. At a synapse, the membrane of the axon closely adjoins the membrane of the target cell, and special molecular structures serve to transmit electrical or electrochemical signals across the gap. Some synaptic junctions appear partway along an axon as it extends—these are called en passant (""in passing"") synapses. Other synapses appear as terminals at the ends of axonal branches. A single axon, with all its branches taken together, can innervate multiple parts of the brain and generate thousands of synaptic terminals.