Major and minor music compared to excited and subdued speech
... any songs that were annotated as being in more than one key or that were polyphonic. Applying these criteria left 6555 melodies for analysis of which 3699 were major and 2856 minor. The distribution of key signatures for these melodies is shown in Table IIB. To assess the tonal differences between t ...
... any songs that were annotated as being in more than one key or that were polyphonic. Applying these criteria left 6555 melodies for analysis of which 3699 were major and 2856 minor. The distribution of key signatures for these melodies is shown in Table IIB. To assess the tonal differences between t ...
Lesson_CCC_-_The_Min..
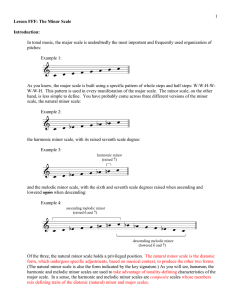
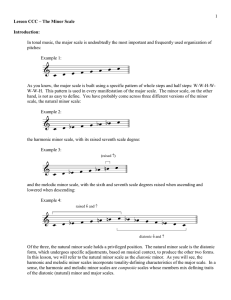
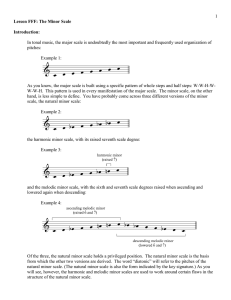
... As Example 11 shows, the raised seventh scale degree applies only to the chords built on 5 and 7, both of which have a dominant function. If these chords were built using the pitches of the natural minor scale, V would be minor (v) and vii° would be major (VII). Neither v nor VII urge toward tonic a ...
... As Example 11 shows, the raised seventh scale degree applies only to the chords built on 5 and 7, both of which have a dominant function. If these chords were built using the pitches of the natural minor scale, V would be minor (v) and vii° would be major (VII). Neither v nor VII urge toward tonic a ...
Chapter 5 - Wilson Central High School Band
... To identify the mode of a piece, think of the major key associated with the key signature. If the most stable pitch is 4, then it’s Lydian; if it’s 2, then it’s Dorian, etc. ...
... To identify the mode of a piece, think of the major key associated with the key signature. If the most stable pitch is 4, then it’s Lydian; if it’s 2, then it’s Dorian, etc. ...
ANALYSIS AND ANALYTIC TECHNIQUES IN AFRICAN MUSIC A
... It exhibits a symmetry that is amazing. The interval of a major 2nd in the centre is flanked by a minor 3rd on both sides. There appears to be a pivot in this scale, made up of the two resting notes E and D. So this may be called a pivotal scale. E may be called the upper focus (to be abbreviated UF ...
... It exhibits a symmetry that is amazing. The interval of a major 2nd in the centre is flanked by a minor 3rd on both sides. There appears to be a pivot in this scale, made up of the two resting notes E and D. So this may be called a pivotal scale. E may be called the upper focus (to be abbreviated UF ...
Melody
... minor scales, and sometimes the other scales introduced in this chapter. But many cultures base their music on entirely different scale patterns composed of tones we cannot reproduce on a keyboard, restricted as it is to half steps as the smallest interval. Microtones (lying between the tones of a h ...
... minor scales, and sometimes the other scales introduced in this chapter. But many cultures base their music on entirely different scale patterns composed of tones we cannot reproduce on a keyboard, restricted as it is to half steps as the smallest interval. Microtones (lying between the tones of a h ...
Estimation of harpsichord inharmonicity
... intonation to form perfectly consonant intervals if required, but fixed-pitch instruments such as keyboard, some fretted, and some percussion instruments, need to commit to a tuning scheme for the duration of a piece, if not an entire concert. In the Western musical tradition at least, this gives ri ...
... intonation to form perfectly consonant intervals if required, but fixed-pitch instruments such as keyboard, some fretted, and some percussion instruments, need to commit to a tuning scheme for the duration of a piece, if not an entire concert. In the Western musical tradition at least, this gives ri ...
Lesson_CCC_-_The_Min..
... of which have a dominant function. If these chords were built using the pitches of the diatonic minor, V would be minor (v) and vii° would be major (VII). Neither v nor VII pull toward tonic as do their leading-tone adjusted forms, although both appear in other functional roles in a minor key. Liste ...
... of which have a dominant function. If these chords were built using the pitches of the diatonic minor, V would be minor (v) and vii° would be major (VII). Neither v nor VII pull toward tonic as do their leading-tone adjusted forms, although both appear in other functional roles in a minor key. Liste ...
Lorenz Composer
... constitute an octave. These pitches are: C, C#, D, D#, E, F, F#, G, G#, A, A#, and B. After B, the sequence repeats itself with the C from the octave above. The tones in music can be understood as sine waves of varying frequencies. The frequency of a pitch is twice that of the pitch in the octave be ...
... constitute an octave. These pitches are: C, C#, D, D#, E, F, F#, G, G#, A, A#, and B. After B, the sequence repeats itself with the C from the octave above. The tones in music can be understood as sine waves of varying frequencies. The frequency of a pitch is twice that of the pitch in the octave be ...
Real-time Melodic Accompaniment System for Indian Music Using
... period. Hence first we store the local minima occurring in a frame in increasing order. Then a value for the threshold and the number of minima points to look for is set from experimental observation. Now out of the first n number of local minima after arranging in the increasing order (7 in the abo ...
... period. Hence first we store the local minima occurring in a frame in increasing order. Then a value for the threshold and the number of minima points to look for is set from experimental observation. Now out of the first n number of local minima after arranging in the increasing order (7 in the abo ...
hw4
... classes that consist of elements that are equivalent to one another. For example, if our set is the integers {…, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, …} and the equivalence relation is equivalence mod 4, then the integers split into four equivalence classes: {…, -8, -4, 0, 4, 8, …} (integers that are equivalent t ...
... classes that consist of elements that are equivalent to one another. For example, if our set is the integers {…, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, …} and the equivalence relation is equivalence mod 4, then the integers split into four equivalence classes: {…, -8, -4, 0, 4, 8, …} (integers that are equivalent t ...
Lesson_CCC_-_The_Min..
... Popup box: As you may have noticed, the raised seventh scale degree does not apply to the chord built on scale degree 3. If the seventh scale degree were to be raised in a III chord, the result would be an augmented triad (the triad on three relative major and this should not be subverted). Due to ...
... Popup box: As you may have noticed, the raised seventh scale degree does not apply to the chord built on scale degree 3. If the seventh scale degree were to be raised in a III chord, the result would be an augmented triad (the triad on three relative major and this should not be subverted). Due to ...
A Brief History of the Establishment of International Standard
... transposition by every player of a wind instrument or fixed-pitch instrument would have been risky — and because human voices have unchanging tessituras, the tuning of a fixed pitch instrument or the construction of any other instrument could thereafter vary only within practical limits, these limit ...
... transposition by every player of a wind instrument or fixed-pitch instrument would have been risky — and because human voices have unchanging tessituras, the tuning of a fixed pitch instrument or the construction of any other instrument could thereafter vary only within practical limits, these limit ...
Non-Harmonic Tones Harmonic Tones
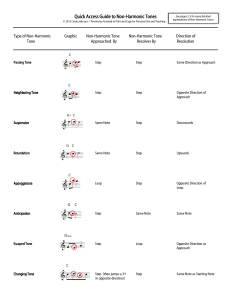
... Have you ever looked at music and wondered why there may be notes which don’t appear to belong to a chord? Notes that are not part of a chord are called Non-Harmonic Tones and are usually found melodically between two harmonic tones (notes that belong to a chord). Most may appear on the beat or in b ...
... Have you ever looked at music and wondered why there may be notes which don’t appear to belong to a chord? Notes that are not part of a chord are called Non-Harmonic Tones and are usually found melodically between two harmonic tones (notes that belong to a chord). Most may appear on the beat or in b ...
12 Music Hacks
... in the west. Whether you’re working with a keyboard, guitar, voice, MIDI sequencer, or any other instrument, you’re already experiencing this tuning system. Equal temperament divides the octave into twelve equal steps, known as semitones. A semitone is the smallest space between notes in western mus ...
... in the west. Whether you’re working with a keyboard, guitar, voice, MIDI sequencer, or any other instrument, you’re already experiencing this tuning system. Equal temperament divides the octave into twelve equal steps, known as semitones. A semitone is the smallest space between notes in western mus ...
The History of Tuning
... Refer to Figure 3, Greek music was mostly religious poetry that was sung and a string instrument was used to back the voice. The above example is a religious poem (in Classical Greek) the smaller symbols above the text poem are the notes that are intended to be sounded when the poem is sung. Pythag ...
... Refer to Figure 3, Greek music was mostly religious poetry that was sung and a string instrument was used to back the voice. The above example is a religious poem (in Classical Greek) the smaller symbols above the text poem are the notes that are intended to be sounded when the poem is sung. Pythag ...
Music Theory & Ear Training for Busy Adults
... guitars are tempered instruments. Tempering means to tune each half-step to be exactly equal--in contrast to just tuning, which makes one key (for example, C major) sound wonderful at the expense of all other keys. For any given pitch, the difference between just tuning and tempered tuning may be as ...
... guitars are tempered instruments. Tempering means to tune each half-step to be exactly equal--in contrast to just tuning, which makes one key (for example, C major) sound wonderful at the expense of all other keys. For any given pitch, the difference between just tuning and tempered tuning may be as ...
How to Play the Chromatic Scale
... chromatic scale can be easily represented by what we call the chromatic number line: ...
... chromatic scale can be easily represented by what we call the chromatic number line: ...
A Psychophysical Explanation for Why Major Chords are “Bright
... harmonic tension will lead to the positive affect of a major chord or to the negative affect of a minor chord, depending solely on the direction of pitch change. ...
... harmonic tension will lead to the positive affect of a major chord or to the negative affect of a minor chord, depending solely on the direction of pitch change. ...
What is Tonality - California State University, Los Angeles
... which is symmetrical in two respects: it divides the octave by equal intervals. and it is self-invertible.+ The symmetry inherent in the semitonal scale implies a new kind of musicd equivalence. whereas in the diatonic context thers is only intervallic equir alence, in the twelve-tone context there ...
... which is symmetrical in two respects: it divides the octave by equal intervals. and it is self-invertible.+ The symmetry inherent in the semitonal scale implies a new kind of musicd equivalence. whereas in the diatonic context thers is only intervallic equir alence, in the twelve-tone context there ...
AP Theory Syllabus - Pequannock Township High School
... f. Harmonize a melody with appropriate chords using good voice leading. g. Analyze the chords of a musical composition by number and letter name. h. Transpose a composition from one key to another. i. Express musical ideas by composing and arranging. j. Understand and recognize basic musical forms: ...
... f. Harmonize a melody with appropriate chords using good voice leading. g. Analyze the chords of a musical composition by number and letter name. h. Transpose a composition from one key to another. i. Express musical ideas by composing and arranging. j. Understand and recognize basic musical forms: ...
Just intonation

In music, just intonation (sometimes abbreviated as JI) or pure intonation is any musical tuning in which the frequencies of notes are related by ratios of small whole numbers. Any interval tuned in this way is called a pure or just interval. The two notes in any just interval are members of the same harmonic series. Frequency ratios involving large integers such as 1024:927 are not generally said to be justly tuned. ""Just intonation is the tuning system of the later ancient Greek modes as codified by Ptolemy; it was the aesthetic ideal of the Renaissance theorists; and it is the tuning practice of a great many musical cultures worldwide, both ancient and modern.""Just intonation can be contrasted and compared with equal temperament, which dominates Western instruments of fixed pitch (e.g., piano or organ) and default MIDI tuning on electronic keyboards. In equal temperament, all intervals are defined as multiples of the same basic interval, or more precisely, the intervals are ratios which are integer powers of the smallest step ratio, so two notes separated by the same number of steps always have exactly the same frequency ratio. However, except for doubling of frequencies (one or more octaves), no other intervals are exact ratios of small integers. Each just interval differs a different amount from its analogous, equally tempered interval.Justly tuned intervals can be written as either ratios, with a colon (for example, 3:2), or as fractions, with a solidus (3 ⁄ 2). For example, two tones, one at 300 Hertz (cycles per second), and the other at 200 hertz are both multiples of 100 Hz and as such members of the harmonic series built on 100 Hz. Thus 3/2, known as a perfect fifth, may be defined as the musical interval (the ratio) between the second and third harmonics of any fundamental pitch.