New Harmonic Resources
... Chords may be constructed of intervals other than thirds (triadic harmony):! 3rds (tertian)! Extensions of traditional triads: ! 7th, 9th, 11th, and 13th chords.! diatonic! ...
... Chords may be constructed of intervals other than thirds (triadic harmony):! 3rds (tertian)! Extensions of traditional triads: ! 7th, 9th, 11th, and 13th chords.! diatonic! ...
Curriculum Map Symphony Band Unit 1
... evaluate their success using feedback from ensemble peers and other sources to refine performances MU:Re8.1.E.8a Identify and support interpretations of the expressive intent and meaning of musical works, citing as evidence the treatment of the elements of music, contexts, and (when appropriate) the ...
... evaluate their success using feedback from ensemble peers and other sources to refine performances MU:Re8.1.E.8a Identify and support interpretations of the expressive intent and meaning of musical works, citing as evidence the treatment of the elements of music, contexts, and (when appropriate) the ...
answer key - Belmont University
... 5. Identify the key of the melody. Remember, key is based on how the music sounds, not on what key signature is used. These exercises don’t always end on tonic. Look at the whole melody and decide what scale is being used, what accidentals might imply leading tones, and what tone would sound like to ...
... 5. Identify the key of the melody. Remember, key is based on how the music sounds, not on what key signature is used. These exercises don’t always end on tonic. Look at the whole melody and decide what scale is being used, what accidentals might imply leading tones, and what tone would sound like to ...
Glossary Commonly Used Musical Terms and
... bass clef A sign placed on t h e fourth line (F) of the bass s t a f f ; also called the F Clef. ...
... bass clef A sign placed on t h e fourth line (F) of the bass s t a f f ; also called the F Clef. ...
THE BLUES SCALE Phillip Pedler This scale is so often overlooked
... United States (Allen, Ware & Garrison, 1867). I quote this passage from the introduction: "...The best that we can do, however, with paper and types, or even with voices, will convey but a faint shadow of the original. The voices of the coloured people have a peculiar quality that nothing can imitat ...
... United States (Allen, Ware & Garrison, 1867). I quote this passage from the introduction: "...The best that we can do, however, with paper and types, or even with voices, will convey but a faint shadow of the original. The voices of the coloured people have a peculiar quality that nothing can imitat ...
69s and pentatonics
... Used against a major chord or a dominant seventh built on the lowest note we get the 3 blues notes - the minor 7th, flattened 5th and the minor 3rd. Sometimes the major 3rd can also be used as indeed can the natural 5th. (If the natural 5th is used with a minor 3rd we have the minor pentatonic scal ...
... Used against a major chord or a dominant seventh built on the lowest note we get the 3 blues notes - the minor 7th, flattened 5th and the minor 3rd. Sometimes the major 3rd can also be used as indeed can the natural 5th. (If the natural 5th is used with a minor 3rd we have the minor pentatonic scal ...
On Serial Music
... especially with perfect intervals that imply a cadence or a succession of minor thirds that imply a diminished chord; whereas some rows lead to more dissonant harmonies than others and so on. There are various sub-classes of tone row available to the composer: all-interval (where all the possible in ...
... especially with perfect intervals that imply a cadence or a succession of minor thirds that imply a diminished chord; whereas some rows lead to more dissonant harmonies than others and so on. There are various sub-classes of tone row available to the composer: all-interval (where all the possible in ...
important overtones are higher
... • 2/3 of basilar membrane accounts for range of 100-4000 Hz. • Membrane has a logarithmic scale; jump of one octave anywhere in range is about the same jump on membrane (3.5-4 mm) ...
... • 2/3 of basilar membrane accounts for range of 100-4000 Hz. • Membrane has a logarithmic scale; jump of one octave anywhere in range is about the same jump on membrane (3.5-4 mm) ...
Whole tone scale
... The whole tone scale has no leading tone and because all tones are the same distance apart, "no single tone stands out, [and] the scale creates a blurred, indistinct effect". This effect is especially emphasized by the fact that triads built on such scale tones are augmented. Indeed, one can play al ...
... The whole tone scale has no leading tone and because all tones are the same distance apart, "no single tone stands out, [and] the scale creates a blurred, indistinct effect". This effect is especially emphasized by the fact that triads built on such scale tones are augmented. Indeed, one can play al ...
Twelve Tone Serialism - Mathematics and Computer Science
... incorporation of three, four, or even six voices. Eventually instruments were included as well. Although, they were originally used as a background noise, a drone that would enhance certain notes but not add anything on its own (Forney, 75). As more instruments were used in composition, music gained ...
... incorporation of three, four, or even six voices. Eventually instruments were included as well. Although, they were originally used as a background noise, a drone that would enhance certain notes but not add anything on its own (Forney, 75). As more instruments were used in composition, music gained ...
Pitch Perception
... • AP can be a negative: playing or singing in a key other than written or in a group which strays off pitch; constant awareness of pitch labels hurts enjoyment of music ...
... • AP can be a negative: playing or singing in a key other than written or in a group which strays off pitch; constant awareness of pitch labels hurts enjoyment of music ...
Appendix I: Microtonality in 20 Century Western Art Music: A
... when composers pushed the boundaries of their pitch systems ever closer to an (at least theoretical) equality of all common intervals, it was a logical conclusion to consider applying intervals smaller than a semitone to the newly discovered chromatic pitch systems in which notes increasingly relate ...
... when composers pushed the boundaries of their pitch systems ever closer to an (at least theoretical) equality of all common intervals, it was a logical conclusion to consider applying intervals smaller than a semitone to the newly discovered chromatic pitch systems in which notes increasingly relate ...
Pitch is directly related to frequency and my analysis of ragas is
... C octave' (also called the Middle C scale). We have no need to have just twelve keys in an octave. In fact, the traditional Indian music system over thousands of years is based on a 22 key per octave system. We do not have an 'Equally tempered scale'. One can locate one’s frequencies based on some o ...
... C octave' (also called the Middle C scale). We have no need to have just twelve keys in an octave. In fact, the traditional Indian music system over thousands of years is based on a 22 key per octave system. We do not have an 'Equally tempered scale'. One can locate one’s frequencies based on some o ...
Perception of musical consonance and dissonance
... major sixth major third minor third minor sixth major second major seventh minor seventh minor second tritone ...
... major sixth major third minor third minor sixth major second major seventh minor seventh minor second tritone ...
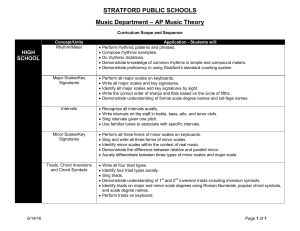
AP Music Theory - Stratford Public Schools
... Write cadences in 3 and 4 part harmony. Analyze music in terms of phrases and periods aurally and in written form. Create diagrams of musical form based on phrases, periods, and cadences. Recognize a motive and how it is developed in a composition. ...
... Write cadences in 3 and 4 part harmony. Analyze music in terms of phrases and periods aurally and in written form. Create diagrams of musical form based on phrases, periods, and cadences. Recognize a motive and how it is developed in a composition. ...
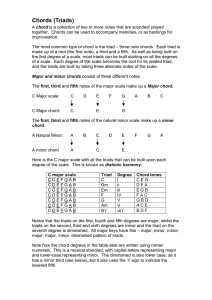
Chords Triads
... Notice that the triads on the first, fourth and fifth degrees are major, whilst the triads on the second, third and sixth degrees are minor and the triad on the seventh degree is diminished. All major keys have this – major, minor, minor, major, major, minor, diminished pattern of triads. Note how t ...
... Notice that the triads on the first, fourth and fifth degrees are major, whilst the triads on the second, third and sixth degrees are minor and the triad on the seventh degree is diminished. All major keys have this – major, minor, minor, major, major, minor, diminished pattern of triads. Note how t ...
UNVIERSIDAD NACIONAL DE QUILMES
... For centuries, scales have been used to arrange and give context to pitches. A scale is simply a set of pitches. They are usually arranged …………………………………to pitch in ascending or descending order. Pretty much all of the music you listen to is based on scales, and the song 'Do-Re-Mi' from The Sound of ...
... For centuries, scales have been used to arrange and give context to pitches. A scale is simply a set of pitches. They are usually arranged …………………………………to pitch in ascending or descending order. Pretty much all of the music you listen to is based on scales, and the song 'Do-Re-Mi' from The Sound of ...
ATTAINMENT TARGET
... b) play a steady G major scale & arpeggio a) understand repeat signs b) understand 3/4 time c) understand slurs d) read notes learned so far ...
... b) play a steady G major scale & arpeggio a) understand repeat signs b) understand 3/4 time c) understand slurs d) read notes learned so far ...
Mathematical Harmonies Write-up
... not in any other key. For example, in the key of D the first ratio is 1.111, but it needs to be 1.125. With just temperament, your flute is only good in one key! Just temperament instruments were the standard until the 1700s. A flutist would have had to own several flutes each tuned to a different k ...
... not in any other key. For example, in the key of D the first ratio is 1.111, but it needs to be 1.125. With just temperament, your flute is only good in one key! Just temperament instruments were the standard until the 1700s. A flutist would have had to own several flutes each tuned to a different k ...
e-Workbook TECHNIQUES AND MATERIALS OF MUSIC Part I
... perhaps discuss in class) the implied harmonic rhythm and the harmonic and cadential implications of the given line; if an unfigured bass, analyze and discuss the harmonic implications of each note in the bass, paying close attention to typical bass-line scaledegree idioms; if a texture/stylistic ex ...
... perhaps discuss in class) the implied harmonic rhythm and the harmonic and cadential implications of the given line; if an unfigured bass, analyze and discuss the harmonic implications of each note in the bass, paying close attention to typical bass-line scaledegree idioms; if a texture/stylistic ex ...
Appendix 1 Musical Terms
... raised a half step, resulting in half steps between 2 and 3 and between 7 and 8. In the descending form, the sixth and seventh notes are lowered a half step, resulting in a return to the natural form of the minor scale. Melody The horizontal succession of pitches. Additional elements include rhythm ...
... raised a half step, resulting in half steps between 2 and 3 and between 7 and 8. In the descending form, the sixth and seventh notes are lowered a half step, resulting in a return to the natural form of the minor scale. Melody The horizontal succession of pitches. Additional elements include rhythm ...
TONE VS. MODE by Stan Takis More than once I have been
... In music, a scale is an ordered series of musical intervals, which, along with the key or tonic, define the pitches. However, mode is usually used in the sense of scale applied only to the specific diatonic scales found below. The use of more than one mode is polymodal, such as with polymodal chroma ...
... In music, a scale is an ordered series of musical intervals, which, along with the key or tonic, define the pitches. However, mode is usually used in the sense of scale applied only to the specific diatonic scales found below. The use of more than one mode is polymodal, such as with polymodal chroma ...
Tuning Systems
... size pitch change. (To a scientist or engineer, "equally-spaced" means that the ratio of the frequencies of the two notes in any half step is always the same.) This tuning system is very convenient for some instruments, such as the piano, and also makes it very easy to change key14 without retuning ...
... size pitch change. (To a scientist or engineer, "equally-spaced" means that the ratio of the frequencies of the two notes in any half step is always the same.) This tuning system is very convenient for some instruments, such as the piano, and also makes it very easy to change key14 without retuning ...
Just intonation

In music, just intonation (sometimes abbreviated as JI) or pure intonation is any musical tuning in which the frequencies of notes are related by ratios of small whole numbers. Any interval tuned in this way is called a pure or just interval. The two notes in any just interval are members of the same harmonic series. Frequency ratios involving large integers such as 1024:927 are not generally said to be justly tuned. ""Just intonation is the tuning system of the later ancient Greek modes as codified by Ptolemy; it was the aesthetic ideal of the Renaissance theorists; and it is the tuning practice of a great many musical cultures worldwide, both ancient and modern.""Just intonation can be contrasted and compared with equal temperament, which dominates Western instruments of fixed pitch (e.g., piano or organ) and default MIDI tuning on electronic keyboards. In equal temperament, all intervals are defined as multiples of the same basic interval, or more precisely, the intervals are ratios which are integer powers of the smallest step ratio, so two notes separated by the same number of steps always have exactly the same frequency ratio. However, except for doubling of frequencies (one or more octaves), no other intervals are exact ratios of small integers. Each just interval differs a different amount from its analogous, equally tempered interval.Justly tuned intervals can be written as either ratios, with a colon (for example, 3:2), or as fractions, with a solidus (3 ⁄ 2). For example, two tones, one at 300 Hertz (cycles per second), and the other at 200 hertz are both multiples of 100 Hz and as such members of the harmonic series built on 100 Hz. Thus 3/2, known as a perfect fifth, may be defined as the musical interval (the ratio) between the second and third harmonics of any fundamental pitch.