http://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/jres/112/6/V112.N06.A01.pdf
... to the first) using a single-sideband mixer [12] in order to match the design frequency of the stabilization electronics. An RF tracking filter is used to improve the f0 signal-to-noise ratio (originally ∼20 dB with a 10 kHz resolution bandwidth) in order to make the measurement of this parameter mo ...
... to the first) using a single-sideband mixer [12] in order to match the design frequency of the stabilization electronics. An RF tracking filter is used to improve the f0 signal-to-noise ratio (originally ∼20 dB with a 10 kHz resolution bandwidth) in order to make the measurement of this parameter mo ...
EC312 Lecture 11
... frequencies of the signal to pass and attenuate other frequencies. We will analyze the RLC series Bandpass circuit specifically, but you should understand that all of the types of filters could be analyzed using your EE331 skills, and that you are responsible for knowing the effects the four types o ...
... frequencies of the signal to pass and attenuate other frequencies. We will analyze the RLC series Bandpass circuit specifically, but you should understand that all of the types of filters could be analyzed using your EE331 skills, and that you are responsible for knowing the effects the four types o ...
Shot Noise Suppression in an Atomic Point Contact, Part 1
... wait, it turns out that we would need to wait 1 million seconds which is about 11 days and annoyingly long. If however, we measure the fluctuations at a higher frequency, say 1 MHz, the length of time that must be waited for such a measurement of SI can be greatly reduced. However, we cannot use the ...
... wait, it turns out that we would need to wait 1 million seconds which is about 11 days and annoyingly long. If however, we measure the fluctuations at a higher frequency, say 1 MHz, the length of time that must be waited for such a measurement of SI can be greatly reduced. However, we cannot use the ...
Linear Circuit Elements
... Thus, as our signal frequency increases, the we often find that the “frequency response” G ω will in reality be different from that predicted by our circuit model—unless explicit parasitics are considered in that model. As a result, the response G ω may vary from our expectations as the signal ...
... Thus, as our signal frequency increases, the we often find that the “frequency response” G ω will in reality be different from that predicted by our circuit model—unless explicit parasitics are considered in that model. As a result, the response G ω may vary from our expectations as the signal ...
ICS660 - uri=media.digikey
... Stresses above the ratings listed below can cause permanent damage to the ICS660. These ratings, which are standard values for ICS commercially rated parts, are stress ratings only. Functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections ...
... Stresses above the ratings listed below can cause permanent damage to the ICS660. These ratings, which are standard values for ICS commercially rated parts, are stress ratings only. Functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections ...
A Low Phase Noise 10GHz Optoelectronic RF Oscillator
... It has been known for some time that an optoelectronic oscillator (OEO) can achieve better phase noise performance than traditional frequency synthesis approaches, such as phase-locked dielectric resonators, YIG, and quartz crystal oscillators [1,2]. The fundamental improvement in phase noise achiev ...
... It has been known for some time that an optoelectronic oscillator (OEO) can achieve better phase noise performance than traditional frequency synthesis approaches, such as phase-locked dielectric resonators, YIG, and quartz crystal oscillators [1,2]. The fundamental improvement in phase noise achiev ...
SGA-4386(Z)
... The information in this publication is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by RF Micro Devices, Inc. ("RFMD") for its use, nor for any infringement of patents, or other rights of third parties, resulting from its use. No license is granted by implication or ot ...
... The information in this publication is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by RF Micro Devices, Inc. ("RFMD") for its use, nor for any infringement of patents, or other rights of third parties, resulting from its use. No license is granted by implication or ot ...
Chapter 2 part IV_updated 23 july - MetaLab
... The IF amplifier has a tuned circuit that accepts components only near 455kHz, in this case 454kHz, 455kHz and 456kHz. Since the mixer maintains the same amplitude proportion that existed with the original AM signal input at 999kHz, 1000kHz and 1001kHz, the signal now passing through the IF amplifie ...
... The IF amplifier has a tuned circuit that accepts components only near 455kHz, in this case 454kHz, 455kHz and 456kHz. Since the mixer maintains the same amplitude proportion that existed with the original AM signal input at 999kHz, 1000kHz and 1001kHz, the signal now passing through the IF amplifie ...
Document
... Traveling waves vs standing waves • Can think of standing waves as sums of left traveling and right traveling waves • The time to go from zero to max depends on the time for the wave to travel a distance of 1 wavelength smaller wavelengths have faster oscillation periods (frequencies) ...
... Traveling waves vs standing waves • Can think of standing waves as sums of left traveling and right traveling waves • The time to go from zero to max depends on the time for the wave to travel a distance of 1 wavelength smaller wavelengths have faster oscillation periods (frequencies) ...
A SIGE LOW PHASE NOISE PUSH
... to the inductor at the base terminal a varactor is placed in order to allow a tuning of the oscillation frequency. For this purpose we employ the capacitance of a base-collector junction as a tuning varactor. By connecting the two emitter networks the common output terminal is realized. Thus the pha ...
... to the inductor at the base terminal a varactor is placed in order to allow a tuning of the oscillation frequency. For this purpose we employ the capacitance of a base-collector junction as a tuning varactor. By connecting the two emitter networks the common output terminal is realized. Thus the pha ...
High-coherence mid-infrared frequency comb
... obtained by mixing two OFCS-locked CW NIR lasers, have been recently reported [12, 13]. Relatively high-power CW MIR sources have been obtained by using intracavity difference frequency generation (DFG) [14], optical parametric oscillators (OPOs) [15–17], and OFCSreferenced QCLs [18,19]. Alternative ...
... obtained by mixing two OFCS-locked CW NIR lasers, have been recently reported [12, 13]. Relatively high-power CW MIR sources have been obtained by using intracavity difference frequency generation (DFG) [14], optical parametric oscillators (OPOs) [15–17], and OFCSreferenced QCLs [18,19]. Alternative ...
Abbreviations, annotations and conventions used
... A motion in which the acceleration/force is proportional to the displacement; directed towards the centre of oscillation/equilibrium position/AW or a " -x or a = -#2x or a = -4$2f2x; ...
... A motion in which the acceleration/force is proportional to the displacement; directed towards the centre of oscillation/equilibrium position/AW or a " -x or a = -#2x or a = -4$2f2x; ...
High-speed Digital Architectures
... One cost of this approach is the added complexity both in terms of added hardware and in terms of signal formatting for output ...
... One cost of this approach is the added complexity both in terms of added hardware and in terms of signal formatting for output ...
Chapter 11 Frequency Response
... Video signals without sufficient bandwidth become fuzzy as they fail to abruptly change the contrast of pictures from complete white into complete black. CH 11 Frequency Response ...
... Video signals without sufficient bandwidth become fuzzy as they fail to abruptly change the contrast of pictures from complete white into complete black. CH 11 Frequency Response ...
paper
... receiver is locked to the input clock frequency, V in crosses the differential zero point V o, and causes the node reset to switch from low to high after a certain delay. This closes the switches connecting the last differential pair DIF F 3 to the input nodes, applying a downwards slope to V in, ac ...
... receiver is locked to the input clock frequency, V in crosses the differential zero point V o, and causes the node reset to switch from low to high after a certain delay. This closes the switches connecting the last differential pair DIF F 3 to the input nodes, applying a downwards slope to V in, ac ...
SGA6486Z 数据资料DataSheet下载
... The information in this publication is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by RF Micro Devices, Inc. ("RFMD") for its use, nor for any infringement of patents, or other rights of third parties, resulting from its use. No license is granted by implication or ot ...
... The information in this publication is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by RF Micro Devices, Inc. ("RFMD") for its use, nor for any infringement of patents, or other rights of third parties, resulting from its use. No license is granted by implication or ot ...
SIMPLE LOW PASS AND HIGH PASS FILTER
... The frequencies 1 and 2 at which the output power drops to one half of its values at the resonant frequency are called the half-power frequencies. At these frequencies also known as cutoff frequencies or corner frequencies, the output voltage is | Vo ( c ) | 0.707 | Vo ( o ) | . This circuit w ...
... The frequencies 1 and 2 at which the output power drops to one half of its values at the resonant frequency are called the half-power frequencies. At these frequencies also known as cutoff frequencies or corner frequencies, the output voltage is | Vo ( c ) | 0.707 | Vo ( o ) | . This circuit w ...
HWS400 - Hexawave
... The HWS400 is a GaAs MMIC SPDT terminated (non-reflective) switch in a low cost QFN12L (3x3 mm) plastic package and can be used in both 50 ohm and 75 ohm systems. The HWS400 features low insertion loss and high isolation with very low DC ...
... The HWS400 is a GaAs MMIC SPDT terminated (non-reflective) switch in a low cost QFN12L (3x3 mm) plastic package and can be used in both 50 ohm and 75 ohm systems. The HWS400 features low insertion loss and high isolation with very low DC ...
VersaSync Rugged Time and Frequency Reference
... • Sensor support (radar, sonar, optronics, electronic warfare) • Communication networks • Offshore/DSO platforms • Buoys ...
... • Sensor support (radar, sonar, optronics, electronic warfare) • Communication networks • Offshore/DSO platforms • Buoys ...
Wein Bridge Oscillators
... update the circuit using a form of amplitude stabilization. There are a couple of available design methods, but one of the better schemes involves the introduction diodes into the circuit. Along with the diodes, two additional resistors are added to form an amplitude control network. The schematic f ...
... update the circuit using a form of amplitude stabilization. There are a couple of available design methods, but one of the better schemes involves the introduction diodes into the circuit. Along with the diodes, two additional resistors are added to form an amplitude control network. The schematic f ...
Problem #1 - aresgate.net
... We chose the cutoff frequency to be fo= 1 kHz because if we chose the cutoff frequency to be less than 1kHz, it only filter out a portion of that band and if we chose the cutoff frequency to be 1kHz, it will filter more than half of the band, which is good for the design. We chose Q=0.707. Because i ...
... We chose the cutoff frequency to be fo= 1 kHz because if we chose the cutoff frequency to be less than 1kHz, it only filter out a portion of that band and if we chose the cutoff frequency to be 1kHz, it will filter more than half of the band, which is good for the design. We chose Q=0.707. Because i ...
Video Transcript - Rose
... A series RLC circuit is given in this problem. This is a bandreject filter with a center frequency of 1 radian per second. We want to scale the circuit to make the center frequency shift to 100,000 radians per second. We assume that there is a one-nanofarad capacitor available for the new circuit. L ...
... A series RLC circuit is given in this problem. This is a bandreject filter with a center frequency of 1 radian per second. We want to scale the circuit to make the center frequency shift to 100,000 radians per second. We assume that there is a one-nanofarad capacitor available for the new circuit. L ...
7 - Cypress Semiconductor
... 3. Crystal aging: Crystals are prone to aging, with a +/-2ppm to +/-5ppm error per every few years, caused by impurities in the crystal material and on the crystal surface, as well as mechanical stresses between the crystal material and the deposited electrodes. This error may cause slow system-wide ...
... 3. Crystal aging: Crystals are prone to aging, with a +/-2ppm to +/-5ppm error per every few years, caused by impurities in the crystal material and on the crystal surface, as well as mechanical stresses between the crystal material and the deposited electrodes. This error may cause slow system-wide ...
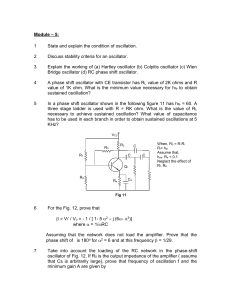
Module – 5
... Show that a transistor with a small signal common emitter short circuit gain less than 44.5 can not be used in the phase shift oscillator of Fig. 17 ...
... Show that a transistor with a small signal common emitter short circuit gain less than 44.5 can not be used in the phase shift oscillator of Fig. 17 ...
Atomic clock

An atomic clock is a clock device that uses an electronic transition frequency in the microwave, optical, or ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum of atoms as a frequency standard for its timekeeping element. Atomic clocks are the most accurate time and frequency standards known, and are used as primary standards for international time distribution services, to control the wave frequency of television broadcasts, and in global navigation satellite systems such as GPS.The principle of operation of an atomic clock is not based on nuclear physics, but rather on atomic physics; it uses the microwave signal that electrons in atoms emit when they change energy levels. Early atomic clocks were based on masers at room temperature. Currently, the most accurate atomic clocks first cool the atoms to near absolute zero temperature by slowing them with lasers and probing them in atomic fountains in a microwave-filled cavity. An example of this is the NIST-F1 atomic clock, one of the U.S.'s national primary time and frequency standards.The accuracy of an atomic clock depends on two factors. The first factor is temperature of the sample atoms—colder atoms move much more slowly, allowing longer probe times. The second factor is the frequency and intrinsic width of the electronic transition. Higher frequencies and narrow lines increase the precision.National standards agencies in many countries maintain a network of atomic clocks which are intercompared and kept synchronized to an accuracy of 10−9 seconds per day (approximately 1 part in 1014). These clocks collectively define a continuous and stable time scale, International Atomic Time (TAI). For civil time, another time scale is disseminated, Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). UTC is derived from TAI, but approximately synchronised, by using leap seconds, to UT1, which is based on actual rotation of the Earth with respect to the solar time.