Document
... using synthetic division, and the quotient/remainder row of that division is all non-negative numbers, then r is an upper bound of the real zeros of P. • Case 2: If an< 0, Case 1 hold except the quotient/remainder row must be all nonpositive numbers. ...
... using synthetic division, and the quotient/remainder row of that division is all non-negative numbers, then r is an upper bound of the real zeros of P. • Case 2: If an< 0, Case 1 hold except the quotient/remainder row must be all nonpositive numbers. ...
The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
... introduce the field of complex or imaginary numbers in which it does have a solution. So how does this idea of a field apply to our investigation of the FTA? One thing to understand is that addition, subtraction, and multiplication hold true for the integers, even though the integers are not a field ...
... introduce the field of complex or imaginary numbers in which it does have a solution. So how does this idea of a field apply to our investigation of the FTA? One thing to understand is that addition, subtraction, and multiplication hold true for the integers, even though the integers are not a field ...
Algebra II (10) Semester 2 Exam Outline – May 2015 Unit 1
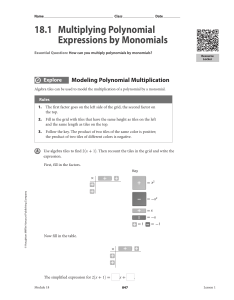
... Algebra II (10) Semester 2 Exam Outline – May 2015 Unit 1: Polynomial Functions Identify, evaluate, add and subtract polynomials. (6.1) Classify and graph polynomials. (6.1) Multiply polynomials, use binomial expansion to expand binomial expressions that are raised to positive integer powers. ...
... Algebra II (10) Semester 2 Exam Outline – May 2015 Unit 1: Polynomial Functions Identify, evaluate, add and subtract polynomials. (6.1) Classify and graph polynomials. (6.1) Multiply polynomials, use binomial expansion to expand binomial expressions that are raised to positive integer powers. ...
Here
... The second of these is easy — acb0 d0 = ab0 cd0 = a0 bcd0 = a0 bc0 d = a0 c0 bd. For the first, we have that adb0 d0 = ab0 dd0 = a0 bdd0 = a0 d0 bd, and bcb0 d0 = bb0 cd0 = bb0 c0 d = b0 c0 bd, and adding these gives the required equation. 17. State and prove the factor theorem for the polynomial r ...
... The second of these is easy — acb0 d0 = ab0 cd0 = a0 bcd0 = a0 bc0 d = a0 c0 bd. For the first, we have that adb0 d0 = ab0 dd0 = a0 bdd0 = a0 d0 bd, and bcb0 d0 = bb0 cd0 = bb0 c0 d = b0 c0 bd, and adding these gives the required equation. 17. State and prove the factor theorem for the polynomial r ...
Week7_1
... – For example, the reciprocal of an element. An element multiplying all other elements must result in different results if f(y) is irreducible. ...
... – For example, the reciprocal of an element. An element multiplying all other elements must result in different results if f(y) is irreducible. ...