301 Definitions – Revised Shannon Benson
... Neurons are the building-blocks of the body’s nervous system. They are specialized nerve cells that communicate electrical and chemical messages between the brain, through the spinal cord, and to other parts of the body. Expanded Definition: History: The term “neuron” was first introduced in an arti ...
... Neurons are the building-blocks of the body’s nervous system. They are specialized nerve cells that communicate electrical and chemical messages between the brain, through the spinal cord, and to other parts of the body. Expanded Definition: History: The term “neuron” was first introduced in an arti ...
Technical Definitions
... Neurons are the building-blocks of the body’s nervous system. They are specialized nerve cells that communicate electrical and chemical messages between the brain, through the spinal cord, and to other parts of the body. Expanded Definition: History: The term “neuron” was first introduced in an arti ...
... Neurons are the building-blocks of the body’s nervous system. They are specialized nerve cells that communicate electrical and chemical messages between the brain, through the spinal cord, and to other parts of the body. Expanded Definition: History: The term “neuron” was first introduced in an arti ...
Synapses and neuronal signalling
... • Glial function • The 4 functional domains within a neuron • Signalling networks underlie specific behaviours • Electrical nature of neuronal signalling • Different types of information are conveyed using similar signals carried by distinct pathways • Gene expression creates diversity and change in ...
... • Glial function • The 4 functional domains within a neuron • Signalling networks underlie specific behaviours • Electrical nature of neuronal signalling • Different types of information are conveyed using similar signals carried by distinct pathways • Gene expression creates diversity and change in ...
Drugs Hanson 4
... • Many drugs affect the activity of neurotransmitters by altering their synthesis, storage, release, or deactivation. • Neurotransmitters frequently altered by drugs of abuse: ...
... • Many drugs affect the activity of neurotransmitters by altering their synthesis, storage, release, or deactivation. • Neurotransmitters frequently altered by drugs of abuse: ...
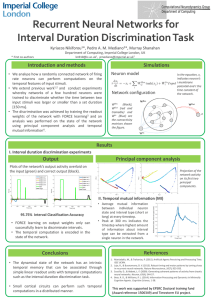
Recurrent Neural Networks for Interval Duration Discrimination Task
... rate neurons can perform computations on the temporal features of input stimuli. • We extend previous work1,2 and conduct experiments whereby networks of a few hundred neurons were trained to discriminate whether the time between two input stimuli was larger or smaller than a set duration [150 ms]. ...
... rate neurons can perform computations on the temporal features of input stimuli. • We extend previous work1,2 and conduct experiments whereby networks of a few hundred neurons were trained to discriminate whether the time between two input stimuli was larger or smaller than a set duration [150 ms]. ...
Note: This hypothesis is mainly concerned with peripheral neurons
... This problem has begun to be addressed by using conditional knockouts, or by crossing NT knockouts with mouse mutants lacking pro-apoptotic genes. Recent evidence from these kinds of experiments suggests that long distance peripheral sensory axon growth in vivo is NT-dependent. ...
... This problem has begun to be addressed by using conditional knockouts, or by crossing NT knockouts with mouse mutants lacking pro-apoptotic genes. Recent evidence from these kinds of experiments suggests that long distance peripheral sensory axon growth in vivo is NT-dependent. ...
A Gaussian Approach to Neural Nets with Multiple Memory Domains
... and the mathematical formalism is similar to behaviour of isolated and non-isolated neural that of isolated networks [4]. Neural nets are nets with chemical markers and high assumed to be constructed of discrete sets of connectivity, and the relationship between randomly interconnected neurons with ...
... and the mathematical formalism is similar to behaviour of isolated and non-isolated neural that of isolated networks [4]. Neural nets are nets with chemical markers and high assumed to be constructed of discrete sets of connectivity, and the relationship between randomly interconnected neurons with ...
Optogenetics and the Circuit Dynamics of Psychiatric
... TMS treatment in patients with depression, its mechanistic underpinning has been poorly understood and hence is likely far from optimal (in fact, relatively very few locations in the human brain have yet been explored with neurostimulation). For deep structures that TMS cannot currently reach, addit ...
... TMS treatment in patients with depression, its mechanistic underpinning has been poorly understood and hence is likely far from optimal (in fact, relatively very few locations in the human brain have yet been explored with neurostimulation). For deep structures that TMS cannot currently reach, addit ...
General_Psychology_files/Chapter Two Part One2014 - K-Dub
... • Hold the ruler near the end (highest number) and let it hang down. Have another person put his or her hand at the bottom of the ruler and have them ready to grab the ruler (however, they should not be touching the ruler). Tell the other person that you will drop the ruler sometime within the next ...
... • Hold the ruler near the end (highest number) and let it hang down. Have another person put his or her hand at the bottom of the ruler and have them ready to grab the ruler (however, they should not be touching the ruler). Tell the other person that you will drop the ruler sometime within the next ...
Psychiatry`s age of enlightenment
... Since its inception in 2005,1 the field of optogenetics has been responsible for the rapid progress in our understanding of the intricate neural circuit elements driving emotive behaviours relevant to psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, anxiety, depression and bipolar disorder. By using li ...
... Since its inception in 2005,1 the field of optogenetics has been responsible for the rapid progress in our understanding of the intricate neural circuit elements driving emotive behaviours relevant to psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, anxiety, depression and bipolar disorder. By using li ...
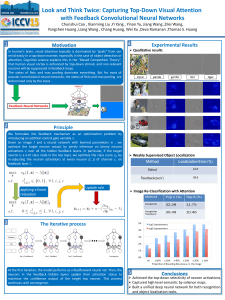
feedback-poster
... In human’s brain, visual attention typically is dominated by “goals” from our mind easily in a top-down manner, especially in the case of object detection or attention. Cognitive science explains this in the “Biased Competition Theory”, that human visual cortex is enhanced by top-down stimuli, and n ...
... In human’s brain, visual attention typically is dominated by “goals” from our mind easily in a top-down manner, especially in the case of object detection or attention. Cognitive science explains this in the “Biased Competition Theory”, that human visual cortex is enhanced by top-down stimuli, and n ...
Chapter Two Part One - K-Dub
... • Hold the ruler near the end (highest number) and let it hang down. Have another person put his or her hand at the bottom of the ruler and have them ready to grab the ruler (however, they should not be touching the ruler). Tell the other person that you will drop the ruler sometime within the next ...
... • Hold the ruler near the end (highest number) and let it hang down. Have another person put his or her hand at the bottom of the ruler and have them ready to grab the ruler (however, they should not be touching the ruler). Tell the other person that you will drop the ruler sometime within the next ...
Chapter Two Part One PPT - K-Dub
... • Hold the ruler near the end (highest number) and let it hang down. Have another person put his or her hand at the bottom of the ruler and have them ready to grab the ruler (however, they should not be touching the ruler). Tell the other person that you will drop the ruler sometime within the next ...
... • Hold the ruler near the end (highest number) and let it hang down. Have another person put his or her hand at the bottom of the ruler and have them ready to grab the ruler (however, they should not be touching the ruler). Tell the other person that you will drop the ruler sometime within the next ...
Avello_1.4_The_Believer_s_Brain
... The Paradox of Nietzschean Atheism Jason Wakefield, University of Cambridge, England. Review: The Believer's Brain (2014) R.S Donda & K.M Heilman. Psychology Press. Heilman was raised in Brooklyn, New York. He graduated from the University of Virginia School of Medicine in 1963 before studying neuro ...
... The Paradox of Nietzschean Atheism Jason Wakefield, University of Cambridge, England. Review: The Believer's Brain (2014) R.S Donda & K.M Heilman. Psychology Press. Heilman was raised in Brooklyn, New York. He graduated from the University of Virginia School of Medicine in 1963 before studying neuro ...
Modeling working memory and decision making using generic
... It can emulate any dynamical system, in particular any analog computer Induces multiple co-existing “partial-attractor” states in the circuit dynamics ...
... It can emulate any dynamical system, in particular any analog computer Induces multiple co-existing “partial-attractor” states in the circuit dynamics ...
BehNeuro11#2 (2) - Biology Courses Server
... What primary roles do the PV and LH play in regulating body weight i.e., what do they do? ...
... What primary roles do the PV and LH play in regulating body weight i.e., what do they do? ...
The relationship between the activity of neurons recorded
... Accurate decoding of the neural activity in the primary motor cortex (M1) could be very useful for brain machine interface applications such as computer displays or prosthetic limbs. In this study we examined information coding in M1 neurons to elucidate the relationship between the activity of M1 n ...
... Accurate decoding of the neural activity in the primary motor cortex (M1) could be very useful for brain machine interface applications such as computer displays or prosthetic limbs. In this study we examined information coding in M1 neurons to elucidate the relationship between the activity of M1 n ...
Slide 1
... Advantages: Spikes of biological neurons are well localized in time and not very frequent. Thus low number of events (sparse coding). Disadvantages: We need a mathematical expression (or method) to calculate the value of each state variable after an arbitrary time (the time of the next event). ...
... Advantages: Spikes of biological neurons are well localized in time and not very frequent. Thus low number of events (sparse coding). Disadvantages: We need a mathematical expression (or method) to calculate the value of each state variable after an arbitrary time (the time of the next event). ...
Scientific priorities for the BRAIN Initiative
... to develop less invasive devices that allow longer recording with higher spatial and temporal resolution with minimal disruption. We must also invest heavily in optical neurophysiology to generate more and better genetically encoded probes, both for stimulating neurons and for recording calcium and ...
... to develop less invasive devices that allow longer recording with higher spatial and temporal resolution with minimal disruption. We must also invest heavily in optical neurophysiology to generate more and better genetically encoded probes, both for stimulating neurons and for recording calcium and ...
abstract - ELSC at
... potential generators can even lead to a temporally irregular circuit dynamics that is not chaotic but stable. This phenomenon can be understood from the bandwidth of population encoding in an ensemble of uncoupled noise-driven neurons. At fixed rate of AP firing, spike trains generated by model neur ...
... potential generators can even lead to a temporally irregular circuit dynamics that is not chaotic but stable. This phenomenon can be understood from the bandwidth of population encoding in an ensemble of uncoupled noise-driven neurons. At fixed rate of AP firing, spike trains generated by model neur ...
Project Self-Discovery
... • 1 sand grain-sized piece of brain can have 100,000 neurons and 1 MILLION synapses (small space between neurons across which messages are sent) • Types Different kinds for different messages and functions • motor (efferent)—send outgoing messages from brain to move muscles • sensory (afferent)—rece ...
... • 1 sand grain-sized piece of brain can have 100,000 neurons and 1 MILLION synapses (small space between neurons across which messages are sent) • Types Different kinds for different messages and functions • motor (efferent)—send outgoing messages from brain to move muscles • sensory (afferent)—rece ...
Supplementary Figure Legends
... well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma with compressed hepatic parenchyma (left). A representative liver section from an animal with BEP neuronal transplants shows almost normal liver morphology with mild fibrosis septae (right). ...
... well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma with compressed hepatic parenchyma (left). A representative liver section from an animal with BEP neuronal transplants shows almost normal liver morphology with mild fibrosis septae (right). ...
Systems Neuroscience - College of William and Mary
... We aim to provide new knowledge about how the neurons, synapses and networks of the brain stem assemble the rhythm-generating systems that drive breathing movements and control respiratory physiology. Breathing is an especially advantageous model system for this type of analysis because it is a beha ...
... We aim to provide new knowledge about how the neurons, synapses and networks of the brain stem assemble the rhythm-generating systems that drive breathing movements and control respiratory physiology. Breathing is an especially advantageous model system for this type of analysis because it is a beha ...
Quiz 1 - Suraj @ LUMS
... parameters that may be adapted during learning. A neural network is said to learn if its free parameters are adapted in response to experience in order to improve performance at learning an input-output mapping. The free parameters can be: weights Activation function parameters Architectural p ...
... parameters that may be adapted during learning. A neural network is said to learn if its free parameters are adapted in response to experience in order to improve performance at learning an input-output mapping. The free parameters can be: weights Activation function parameters Architectural p ...
Neural oscillation

Neural oscillation is rhythmic or repetitive neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by interactions between neurons. In individual neurons, oscillations can appear either as oscillations in membrane potential or as rhythmic patterns of action potentials, which then produce oscillatory activation of post-synaptic neurons. At the level of neural ensembles, synchronized activity of large numbers of neurons can give rise to macroscopic oscillations, which can be observed in the electroencephalogram (EEG). Oscillatory activity in groups of neurons generally arises from feedback connections between the neurons that result in the synchronization of their firing patterns. The interaction between neurons can give rise to oscillations at a different frequency than the firing frequency of individual neurons. A well-known example of macroscopic neural oscillations is alpha activity.Neural oscillations were observed by researchers as early as 1924 (by Hans Berger). More than 50 years later, intrinsic oscillatory behavior was encountered in vertebrate neurons, but its functional role is still not fully understood. The possible roles of neural oscillations include feature binding, information transfer mechanisms and the generation of rhythmic motor output. Over the last decades more insight has been gained, especially with advances in brain imaging. A major area of research in neuroscience involves determining how oscillations are generated and what their roles are. Oscillatory activity in the brain is widely observed at different levels of observation and is thought to play a key role in processing neural information. Numerous experimental studies support a functional role of neural oscillations; a unified interpretation, however, is still lacking.