Operant Conditioning.notebook - Ms. K. Anthony Waterford Valley
... The following concepts are important to our understanding of the effect of cognitive processes and biological factors on conditioning. Cognitive Map: this is a mental image of ones surroundings. I.e.. Mice develop cognitive maps that represent a maze that they just ran through. Latent Learning: t ...
... The following concepts are important to our understanding of the effect of cognitive processes and biological factors on conditioning. Cognitive Map: this is a mental image of ones surroundings. I.e.. Mice develop cognitive maps that represent a maze that they just ran through. Latent Learning: t ...
Lesson 1 | The Nervous System
... 7. The central nervous system consists of the brain and (sensory system/spinal cord). 8. Thought processes are carried out in the (cerebrum/cerebellum). 9. The peripheral nervous system consists of the somatic and (central/autonomic) systems. 10. The most common cause of damage to the nervous system ...
... 7. The central nervous system consists of the brain and (sensory system/spinal cord). 8. Thought processes are carried out in the (cerebrum/cerebellum). 9. The peripheral nervous system consists of the somatic and (central/autonomic) systems. 10. The most common cause of damage to the nervous system ...
behavior - ScienceToGo
... Learning is the modification of behavior based on specific experiences ...
... Learning is the modification of behavior based on specific experiences ...
Target in Field Search: Distractor in Field - Smith
... Most neurons in the deeper layers of the SC show activity aligned with the visual input and the motor response in single-target tasks. Many of these same neurons show additional discharge that is correlated with higherlevel decision processes in more natural visual tasks. In the case of pop-out sear ...
... Most neurons in the deeper layers of the SC show activity aligned with the visual input and the motor response in single-target tasks. Many of these same neurons show additional discharge that is correlated with higherlevel decision processes in more natural visual tasks. In the case of pop-out sear ...
Slide ()
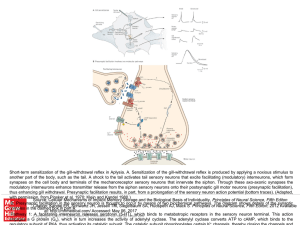
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
GTC Flyer - Graduate Training Centre of Neuroscience
... of higher brain functions that allow humans and animals to operate successfully in natural environments. Concrete topics include the neuronal basis of perception and its top-down control by attention, expectation and motivation. Furthermore, spatial orientation, planning and execution of movements, ...
... of higher brain functions that allow humans and animals to operate successfully in natural environments. Concrete topics include the neuronal basis of perception and its top-down control by attention, expectation and motivation. Furthermore, spatial orientation, planning and execution of movements, ...
Document
... 1993: Meeting on Neural Modeling and Functional Brain Imaging • Brought together modelers and functional brain imagers for the first time. • Tried to determine what research questions modelers could address • The four questions: – Relation between neural activity and imaging signals – Effective con ...
... 1993: Meeting on Neural Modeling and Functional Brain Imaging • Brought together modelers and functional brain imagers for the first time. • Tried to determine what research questions modelers could address • The four questions: – Relation between neural activity and imaging signals – Effective con ...
File
... ● Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. ● Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters (e.g., reuptake mechanisms, agonists, antagonists). ● Discuss the effect of the ...
... ● Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. ● Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters (e.g., reuptake mechanisms, agonists, antagonists). ● Discuss the effect of the ...
Nervous System
... • For example … you put your hand on a tac – Sensory neurons in your hand react to the pain by sending nerve impulses (signal) to the spinal cord – Interneurons relay the message to the motor neurons – Impulse travels to your arm which you lift quickly! ...
... • For example … you put your hand on a tac – Sensory neurons in your hand react to the pain by sending nerve impulses (signal) to the spinal cord – Interneurons relay the message to the motor neurons – Impulse travels to your arm which you lift quickly! ...
Unit 1 History and Approaches 2017
... = the view that knowledge originates in experience and that science should, therefore, rely on observation and experimentation. Lets make this easy….its SCIENCE ...
... = the view that knowledge originates in experience and that science should, therefore, rely on observation and experimentation. Lets make this easy….its SCIENCE ...
Brain and Behaviour
... Axon – passes information to other neurons Dendrites – receive information from other neurons For a neural impulse to “FIRE” the combined impulses that reach the dendrite must reach a certain level of intensity or THRESHOLD – this is an all of nothing response to neurons either reaching the th ...
... Axon – passes information to other neurons Dendrites – receive information from other neurons For a neural impulse to “FIRE” the combined impulses that reach the dendrite must reach a certain level of intensity or THRESHOLD – this is an all of nothing response to neurons either reaching the th ...
Os textos são da exclusiva responsabilidade dos autores
... Greater distress was associated with a more negative frontal slow wave and a larger late positive potential (LPP), with children of high and low levels of distress showing markedly different patterns of cortical neural activity. Source modeling with Geosouce software suggested that slow wave neural ...
... Greater distress was associated with a more negative frontal slow wave and a larger late positive potential (LPP), with children of high and low levels of distress showing markedly different patterns of cortical neural activity. Source modeling with Geosouce software suggested that slow wave neural ...
Nervous System Formative Study Guide File
... b. Sensory neurons Sensory neurons are nerve cells that transmit sensory information (sight, sound, feeling, etc.). They are activated by sensory input, and send projections to other elements of the nervous system, ultimately conveying sensory information to the brain or spinal cord. c. CNS The cent ...
... b. Sensory neurons Sensory neurons are nerve cells that transmit sensory information (sight, sound, feeling, etc.). They are activated by sensory input, and send projections to other elements of the nervous system, ultimately conveying sensory information to the brain or spinal cord. c. CNS The cent ...
Myers Module Four
... the muscles of our internal organs, influencing such functions as glandular activity, heartbeat, and digestion. It may be consciously overridden. The sympathetic nervous system arouses and expends energy. Heartrate, blood pressure, digestion, blood sugar, and perspiration are controlled by it. The p ...
... the muscles of our internal organs, influencing such functions as glandular activity, heartbeat, and digestion. It may be consciously overridden. The sympathetic nervous system arouses and expends energy. Heartrate, blood pressure, digestion, blood sugar, and perspiration are controlled by it. The p ...
A pheromone is a chemical emitted by an organism that is meant to
... A pheromone is a chemical emitted by an organism that is meant to affect the behavior of another organism. These chemicals are used for a wide variety of purposes—an ant will lay a trail of pheromones to guide his compatriots to food, for example, or a mamma rabbit will use the chemicals to signal h ...
... A pheromone is a chemical emitted by an organism that is meant to affect the behavior of another organism. These chemicals are used for a wide variety of purposes—an ant will lay a trail of pheromones to guide his compatriots to food, for example, or a mamma rabbit will use the chemicals to signal h ...
Module 24: Operant Conditioning, Summary Notes
... Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning was developed by B.F. Skinner and is a type of learning in which organisms learn to voluntarily respond in a certain way depending on the consequences (rewards or punishment). Operant Behavior is defined as the learned behavior that produces consequences. Fo ...
... Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning was developed by B.F. Skinner and is a type of learning in which organisms learn to voluntarily respond in a certain way depending on the consequences (rewards or punishment). Operant Behavior is defined as the learned behavior that produces consequences. Fo ...
MIT Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences Instructor: Professor Sebastian Seung
... Lateral inhibition amplifies ...
... Lateral inhibition amplifies ...
EQ2.5 - major divisions of the nervous system
... What are the major divisions of the nervous system, and what are their basic functions? The two major divisions of the nervous system are the central and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is divided in two parts : the brain and the spinal chord. The Peripheral nervous system ...
... What are the major divisions of the nervous system, and what are their basic functions? The two major divisions of the nervous system are the central and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is divided in two parts : the brain and the spinal chord. The Peripheral nervous system ...
Nervous Sys Learning targets
... 2. draw a concept map to show the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system 3. List the types of neuroglia and cite their functions ...
... 2. draw a concept map to show the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system 3. List the types of neuroglia and cite their functions ...
Neuroethology

Neuroethology is the evolutionary and comparative approach to the study of animal behavior and its underlying mechanistic control by the nervous system. This interdisciplinary branch of behavioral neuroscience endeavors to understand how the central nervous system translates biologically relevant stimuli into natural behavior. For example, many bats are capable of echolocation which is used for prey capture and navigation. The auditory system of bats is often cited as an example for how acoustic properties of sounds can be converted into a sensory map of behaviorally relevant features of sounds. Neuroethologists hope to uncover general principles of the nervous system from the study of animals with exaggerated or specialized behaviors.As its name implies, neuroethology is a multidisciplinary field composed of neurobiology (the study of the nervous system) and ethology (the study of behavior in natural conditions). A central theme of the field of neuroethology, delineating it from other branches of neuroscience, is this focus on natural behavior. Natural behaviors may be thought of as those behaviors generated through means of natural selection (i.e. finding mates, navigation, locomotion, predator avoidance) rather than behaviors in disease states, or behavioral tasks that are particular to the laboratory.