Intracellular Redox Compartmentation and ROS
... environment. ROS-related redox signaling is tightly wedded to compartmentation. Because membranes function as barriers, highly redox-active powerhouses such as chloroplasts, peroxisomes, and mitochondria may elicit specific signaling responses. However, transporter functions allow membranes also to a ...
... environment. ROS-related redox signaling is tightly wedded to compartmentation. Because membranes function as barriers, highly redox-active powerhouses such as chloroplasts, peroxisomes, and mitochondria may elicit specific signaling responses. However, transporter functions allow membranes also to a ...
Scavenging of 14-3-3 proteins reveals their involvement in the cell
... of KATP channels (Yuan et al., 2003) implies that steric masking by the other subunit is not sufficient to explain inactivation of all the Arg-based signals present in the complex. Previous studies using soluble protein-A fusion proteins and reporter membrane proteins have shown that the C-terminal ...
... of KATP channels (Yuan et al., 2003) implies that steric masking by the other subunit is not sufficient to explain inactivation of all the Arg-based signals present in the complex. Previous studies using soluble protein-A fusion proteins and reporter membrane proteins have shown that the C-terminal ...
Membrane traffic and fusion at post-Golgi compartments
... appear to reach their destination along the secretory pathway according to the length of their hydrophobic region: proteins with a shorter membrane span are held back in the Golgi stack whereas those with a longer membrane span are trafficked to the PM (Brandizzi et al., 2002). The situation might be ...
... appear to reach their destination along the secretory pathway according to the length of their hydrophobic region: proteins with a shorter membrane span are held back in the Golgi stack whereas those with a longer membrane span are trafficked to the PM (Brandizzi et al., 2002). The situation might be ...
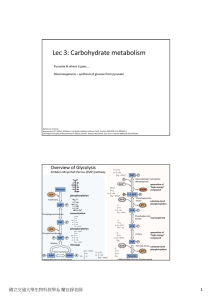
Lec 3: Carbohydrate metabolism
... use glucose as their sole or primary energy source, but they lack the enzymatic machinery to synthesize it. Liver and kidney cortex are the primary gluconeogenic tissues. ...
... use glucose as their sole or primary energy source, but they lack the enzymatic machinery to synthesize it. Liver and kidney cortex are the primary gluconeogenic tissues. ...
Chapter 6 Identifying and Measuring Transmembrane Helix–Helix
... aspect of cell biology and physiology (1). Consequently, proper functioning of these proteins is vital to health, and specific defects are associated with many known human diseases (2, 3). Most are anchored to the cellular membrane through one or several transmembrane (TM) domains that predominantly ...
... aspect of cell biology and physiology (1). Consequently, proper functioning of these proteins is vital to health, and specific defects are associated with many known human diseases (2, 3). Most are anchored to the cellular membrane through one or several transmembrane (TM) domains that predominantly ...
CONDUCTION INTRODUCTION
... nodes (due to greatly decreased time constant for conduction) and pauses to regenerate itself only at the nodes of Ranvier. The nodes of Ranvier occur about every mm which is a good deal less than the length constant of the cell, which is greatly increased due to the myelination. This assures that t ...
... nodes (due to greatly decreased time constant for conduction) and pauses to regenerate itself only at the nodes of Ranvier. The nodes of Ranvier occur about every mm which is a good deal less than the length constant of the cell, which is greatly increased due to the myelination. This assures that t ...
On the natural selection and evolution of the
... Other curious attributes that are characteristic of APB are a high carotenoid content, and the fact that even low intensities of continuous illumination greatly inhibit BChl synthesis and the formation of the photosynthetic apparatus (Shimada 1995; Yurkov and Beatty 1998). This pronounced light inhi ...
... Other curious attributes that are characteristic of APB are a high carotenoid content, and the fact that even low intensities of continuous illumination greatly inhibit BChl synthesis and the formation of the photosynthetic apparatus (Shimada 1995; Yurkov and Beatty 1998). This pronounced light inhi ...
Chapter 2
... function. This chapter and Chapter 3 extend the study of structurefunction relationships to polypeptides, which catalyze specific reactions, transport materials within a cell or across a membrane, protect cells from foreign invaders, regulate specific biological processes, and support various struct ...
... function. This chapter and Chapter 3 extend the study of structurefunction relationships to polypeptides, which catalyze specific reactions, transport materials within a cell or across a membrane, protect cells from foreign invaders, regulate specific biological processes, and support various struct ...
ppt
... •Our 6-carbon sugar is split into TWO 3-carbon products [Step 5] *Ultimately, all of the dihydroxyacetone phosphate will be converted into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, so each step is actually x 2 from here (because each of the two molecules will proceed through ...
... •Our 6-carbon sugar is split into TWO 3-carbon products [Step 5] *Ultimately, all of the dihydroxyacetone phosphate will be converted into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, so each step is actually x 2 from here (because each of the two molecules will proceed through ...
video slide
... Most of the chain’s components are proteins The carriers alternate reduced and oxidized states as they accept and donate electrons Electrons drop in free energy as they go down the chain and are finally passed to O2, forming H2O ...
... Most of the chain’s components are proteins The carriers alternate reduced and oxidized states as they accept and donate electrons Electrons drop in free energy as they go down the chain and are finally passed to O2, forming H2O ...
Chapter 9 powerpoint - Red Hook Central Schools
... • The electron transport chain generates no ATP • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from food to O2 into smaller steps that release energy in manageable amounts. Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... • The electron transport chain generates no ATP • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from food to O2 into smaller steps that release energy in manageable amounts. Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
The proteome of the infectious bronchitis virus Beau
... RNA and transcribing viral mRNA within an infected cell (Ziebuhr et al., 2000). Little is known about the structure or function of the other virally encoded proteins such as the lineage-specific accessory proteins of IBV – 3a, 3b, 5a, 5b and the putative ORF4 (Bentley et al., 2013; Casais et al., 20 ...
... RNA and transcribing viral mRNA within an infected cell (Ziebuhr et al., 2000). Little is known about the structure or function of the other virally encoded proteins such as the lineage-specific accessory proteins of IBV – 3a, 3b, 5a, 5b and the putative ORF4 (Bentley et al., 2013; Casais et al., 20 ...
Lecture 9 – Cellular Respiration
... • NAD+ accepts electrons and becomes NADH • NAD+ is reduced into NADH • NADH is a reducing agent, and is recycled back to NAD+ through oxidation Each NADH (the reduced form of NAD+) represents stored energy that is tapped to synthesize ATP. Each NADH produces 3 ATPs in the e- transport chain NSCC BI ...
... • NAD+ accepts electrons and becomes NADH • NAD+ is reduced into NADH • NADH is a reducing agent, and is recycled back to NAD+ through oxidation Each NADH (the reduced form of NAD+) represents stored energy that is tapped to synthesize ATP. Each NADH produces 3 ATPs in the e- transport chain NSCC BI ...
Protein Detection Methods in Proteomics Research
... In general, silver staining detects the proteins mainly on the gel surface. This is also the reason why further analysis of silver stained proteins is still possible. Silver staining is a multistep procedure. Because it is not an endpoint procedure, the staining intensities can vary from gel to gel. ...
... In general, silver staining detects the proteins mainly on the gel surface. This is also the reason why further analysis of silver stained proteins is still possible. Silver staining is a multistep procedure. Because it is not an endpoint procedure, the staining intensities can vary from gel to gel. ...
cellular respiration
... Put the following steps in the correct order. (Use Figure 9-13 p. 158 for help.) ______ Water forms ______ NADH oxidized ______ Flavoprotein oxidized ______ Fe-S protein oxidized ______ Flavoprotein reduced ______ Fe-S protein reduced ______ Ubiquinone reduced ______ Oxygen reduced ______ cyt a3 pas ...
... Put the following steps in the correct order. (Use Figure 9-13 p. 158 for help.) ______ Water forms ______ NADH oxidized ______ Flavoprotein oxidized ______ Fe-S protein oxidized ______ Flavoprotein reduced ______ Fe-S protein reduced ______ Ubiquinone reduced ______ Oxygen reduced ______ cyt a3 pas ...
1. Describe the steps of the scientific method. 2. Define the terms
... Polar molecules like water have partially charged atoms at their ends Hydrogen bonds form when partial opposite charges in different molecules attract each other The partially positive hydrogens of one water molecule are attracted to the partially negative oxygen on another ...
... Polar molecules like water have partially charged atoms at their ends Hydrogen bonds form when partial opposite charges in different molecules attract each other The partially positive hydrogens of one water molecule are attracted to the partially negative oxygen on another ...
video slide
... the knob also spins, activating catalytic sites in the knob. Three catalytic sites in the stationary knob join inorganic Phosphate to ADP to make ATP. ...
... the knob also spins, activating catalytic sites in the knob. Three catalytic sites in the stationary knob join inorganic Phosphate to ADP to make ATP. ...
How Cells Release Chemical Energy
... Active transport forms a H+ concentration gradient in the outer mitochondrial compartment H+ follows its gradient through ATP synthase, which attaches a phosphate to ADP Finally, oxygen accepts electrons and combines with H+, forming water ...
... Active transport forms a H+ concentration gradient in the outer mitochondrial compartment H+ follows its gradient through ATP synthase, which attaches a phosphate to ADP Finally, oxygen accepts electrons and combines with H+, forming water ...
Prediction of mitochondrial proteins of malaria parasite
... analyzed the amino acid composition of mitochondrial proteins of PF and observed unique composition pattern, which is significantly different than composition pattern of eukaryotic proteins. Based on these observations, they developed a method PlasMit (Bender et al. 2003) for predicting mitochondria ...
... analyzed the amino acid composition of mitochondrial proteins of PF and observed unique composition pattern, which is significantly different than composition pattern of eukaryotic proteins. Based on these observations, they developed a method PlasMit (Bender et al. 2003) for predicting mitochondria ...
Document
... Active transport forms a H+ concentration gradient in the outer mitochondrial compartment H+ follows its gradient through ATP synthase, which attaches a phosphate to ADP Finally, oxygen accepts electrons and combines with H+, forming water ...
... Active transport forms a H+ concentration gradient in the outer mitochondrial compartment H+ follows its gradient through ATP synthase, which attaches a phosphate to ADP Finally, oxygen accepts electrons and combines with H+, forming water ...
Medical Biochemistry Review #2 By
... oxaloacetate (OAA) to malate while oxidizing NADH to NAD+. – Malate then enters the mitochondria where the reverse reaction is carried out by mitochondrial MDH – mitochondrial OAA goes to the cytoplasm to maintain this cycle ; must be transaminated to aspartate (Asp) with the amino group being donat ...
... oxaloacetate (OAA) to malate while oxidizing NADH to NAD+. – Malate then enters the mitochondria where the reverse reaction is carried out by mitochondrial MDH – mitochondrial OAA goes to the cytoplasm to maintain this cycle ; must be transaminated to aspartate (Asp) with the amino group being donat ...
Document
... Glycolysis: Energy-Production In reactions 6-10 of glycolysis, energy is generated as • sugar phosphates are cleaved to triose phosphates. • four ATP molecules are produced. ...
... Glycolysis: Energy-Production In reactions 6-10 of glycolysis, energy is generated as • sugar phosphates are cleaved to triose phosphates. • four ATP molecules are produced. ...
Adherence of Pathogenic Mycoplasmas to Host Cells
... percentage of genes in the minute mycoplasmal genomes is devoted to adhesion. Some of these genes code for membrane proteins, exposed at least partially on the membrane surface, acting as adhesins. Both M. pneumoniae and M. genitalium and ...
... percentage of genes in the minute mycoplasmal genomes is devoted to adhesion. Some of these genes code for membrane proteins, exposed at least partially on the membrane surface, acting as adhesins. Both M. pneumoniae and M. genitalium and ...
Chapter 6
... synthase to rotate. – The spinning rod causes a conformational change in the knob region, activating catalytic sites where ADP and inorganic phosphate combine to make ATP. ...
... synthase to rotate. – The spinning rod causes a conformational change in the knob region, activating catalytic sites where ADP and inorganic phosphate combine to make ATP. ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.