Photosynthesis Notes
... 1 molecule of glucose stores 90 times more chemical energy than ATP Cells can make ATP from ADP as needed by using the energy in foods like glucose ...
... 1 molecule of glucose stores 90 times more chemical energy than ATP Cells can make ATP from ADP as needed by using the energy in foods like glucose ...
Cellular Respiration Lecture Notes
... products during the first 2 stages 3. Passes electrons from one molecule to another 4. electrons combined with hydrogen ions 5. molecular oxygen to form water 6. energy released at each step of the chain is stored in mitochondria to make ATP ii. Substrate level phosphorylation 1. Forms smaller amoun ...
... products during the first 2 stages 3. Passes electrons from one molecule to another 4. electrons combined with hydrogen ions 5. molecular oxygen to form water 6. energy released at each step of the chain is stored in mitochondria to make ATP ii. Substrate level phosphorylation 1. Forms smaller amoun ...
Slide 1
... the matrix side • A nuclear coded protein could insert from the space between the membrane ...
... the matrix side • A nuclear coded protein could insert from the space between the membrane ...
Cell Transport
... across a membrane AGAINST its concentration gradient and requires energy. • We eat food containing nutrients for energy, glucose being one of them. – Recall: glucose cannot be stored inside body as it is water-soluble, so it must be converted into glycogen. This conversion MAKES energy in the form o ...
... across a membrane AGAINST its concentration gradient and requires energy. • We eat food containing nutrients for energy, glucose being one of them. – Recall: glucose cannot be stored inside body as it is water-soluble, so it must be converted into glycogen. This conversion MAKES energy in the form o ...
February 5 AP Biology - John D. O`Bryant School of Math & Science
... Try This! The presence of only Photosystem I, not Photosystem II, in the bundle sheath cells of C4 plants has an effect on O2 concentration. What is that effect, and how might that benefit the plant? Without PS II, no O2 is generated in the bundle-sheath cells! This avoids the problem of O2 c ...
... Try This! The presence of only Photosystem I, not Photosystem II, in the bundle sheath cells of C4 plants has an effect on O2 concentration. What is that effect, and how might that benefit the plant? Without PS II, no O2 is generated in the bundle-sheath cells! This avoids the problem of O2 c ...
MEMBRANE MODEL: The Bubble Lab
... MEMBRANE MODEL: The Bubble Lab The cell’s plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with protein molecules imbedded in it. The protein molecules transport other molecules through the membrane and into or out of the cell. All of the membranes in the cell (nuclear envelop, endoplasmic reticulum, membr ...
... MEMBRANE MODEL: The Bubble Lab The cell’s plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with protein molecules imbedded in it. The protein molecules transport other molecules through the membrane and into or out of the cell. All of the membranes in the cell (nuclear envelop, endoplasmic reticulum, membr ...
cis - Biology Courses Server
... From results of experiments such as these, Dobberstein and Blobel proposed a hypothesis 1. The signal for translocation of a secretory protein into the ER resides in the nascent polypeptide, in the form of a leader “pre-” sequence or “signal peptide;” 2. Translocation of the polypeptide across the E ...
... From results of experiments such as these, Dobberstein and Blobel proposed a hypothesis 1. The signal for translocation of a secretory protein into the ER resides in the nascent polypeptide, in the form of a leader “pre-” sequence or “signal peptide;” 2. Translocation of the polypeptide across the E ...
AP Biology Question Set
... 48. The conversion of ATP to ADP and Pi releases approxi mately 7.3 kcal/mol of energy. This energy release fuels (endergonic) reactions in the cell. Equilibrium of the reaction is far to the right and favors the formation of ADP. In the converse, the formation of ATP from ADP and Pi is energy inten ...
... 48. The conversion of ATP to ADP and Pi releases approxi mately 7.3 kcal/mol of energy. This energy release fuels (endergonic) reactions in the cell. Equilibrium of the reaction is far to the right and favors the formation of ADP. In the converse, the formation of ATP from ADP and Pi is energy inten ...
Name: Date - cloudfront.net
... 16. Why does the cell membrane arrange into a BILAYER (double layer) of phospholipids, with the heads facing the outside and inside of the cell and the tails facing each other? [HINT: Think about which parts are “water-loving” and which parts are “water-hating?”] ____________________________________ ...
... 16. Why does the cell membrane arrange into a BILAYER (double layer) of phospholipids, with the heads facing the outside and inside of the cell and the tails facing each other? [HINT: Think about which parts are “water-loving” and which parts are “water-hating?”] ____________________________________ ...
Slide 1
... light energy and convert it to chemical energy • Chloroplast, like the nucleus, has a double membrane • It is within these inner thylakoid membranes that the energy from sunlight is trapped ...
... light energy and convert it to chemical energy • Chloroplast, like the nucleus, has a double membrane • It is within these inner thylakoid membranes that the energy from sunlight is trapped ...
131110 COS ATP - Community of Reason
... Energy is defined as the capacity to do work, i.e. to move matter. Cells, tissues and organisms need energy for a variety of processes ...
... Energy is defined as the capacity to do work, i.e. to move matter. Cells, tissues and organisms need energy for a variety of processes ...
Photosynthesis
... Temperature- as you increase temperature, enzyme action will increase until an opitmum temperature of 37 degrees Celsius is reached Enzyme-Substrate Concentration1. High levels of enzyme + low levels of substrate = an increase in enzyme action 2. Low levels of enzyme + high levels of substrate = a d ...
... Temperature- as you increase temperature, enzyme action will increase until an opitmum temperature of 37 degrees Celsius is reached Enzyme-Substrate Concentration1. High levels of enzyme + low levels of substrate = an increase in enzyme action 2. Low levels of enzyme + high levels of substrate = a d ...
2. Cell Transport Mechanisms
... molecules that are manufactured in the cell are released through the cell membrane. ...
... molecules that are manufactured in the cell are released through the cell membrane. ...
Prof. Des R. Richardson
... Interestingly, stressors in the tumor microenvironment trigger endocytosis for cell signaling to assist cell survival. Hence, we examined how glucose variation-induced stress regulated early endosome and lysosome formation via endocytosis of the plasma membrane. Furthermore, the impact of glucose va ...
... Interestingly, stressors in the tumor microenvironment trigger endocytosis for cell signaling to assist cell survival. Hence, we examined how glucose variation-induced stress regulated early endosome and lysosome formation via endocytosis of the plasma membrane. Furthermore, the impact of glucose va ...
Ass4 - The University of Sydney
... during folding Proteins destined for export from the cell have a localization signal contained in the mRNA sequence at the 5’ untranslated region which enables a SRP to bind and direct translation into the ER Proteins destined for export are ferried to the inner face of the cell membrane in vesicles ...
... during folding Proteins destined for export from the cell have a localization signal contained in the mRNA sequence at the 5’ untranslated region which enables a SRP to bind and direct translation into the ER Proteins destined for export are ferried to the inner face of the cell membrane in vesicles ...
1 Old Exam I Questions Choose an answer of A,B, C, or D for each
... 44) Briefly (< 1 page) explain how proton translocation through the Fo base of ATP synthase stimulates the ATP synthesizing activity of the F1 head. Include in your description: 1) names and activities of all relevant subunits (6 pt), 2) location of the enzyme in the mitochondria and direction of H+ ...
... 44) Briefly (< 1 page) explain how proton translocation through the Fo base of ATP synthase stimulates the ATP synthesizing activity of the F1 head. Include in your description: 1) names and activities of all relevant subunits (6 pt), 2) location of the enzyme in the mitochondria and direction of H+ ...
Photosynthesis and alternate pathways
... That energy is captured (partly) in the formation of an ATP molecule from ADP (called photophosphorylation). The electron is eventually passed to an oxidized P700 of photosystem I. When P700 was itself excited by light, it was oxidized, and passed an electron through a series of acceptors, with the ...
... That energy is captured (partly) in the formation of an ATP molecule from ADP (called photophosphorylation). The electron is eventually passed to an oxidized P700 of photosystem I. When P700 was itself excited by light, it was oxidized, and passed an electron through a series of acceptors, with the ...
Celltransport3
... • Maintenance of a membrane potential in all cells – Na+- K+ pump keeps inside of membrane negative, outside of membrane positive ...
... • Maintenance of a membrane potential in all cells – Na+- K+ pump keeps inside of membrane negative, outside of membrane positive ...
Resting potential - Neurons in Action
... Answer all underlined questions. You can answer them directly on this worksheet. Plots should be drawn on separate sheets of paper. In the Panel and Graph Manager window, press the button that says “K conductance only”. This will set the conductance to zero for all ions but potassium. In this simula ...
... Answer all underlined questions. You can answer them directly on this worksheet. Plots should be drawn on separate sheets of paper. In the Panel and Graph Manager window, press the button that says “K conductance only”. This will set the conductance to zero for all ions but potassium. In this simula ...
Title - Iowa State University
... 2. Glycolysis involves breaking down glucose to make two molecules of ________. This also creates ___ molecules of ATP and ___ molecules of NADH. Glycolysis requires Oxygen, which is termed ________ respiration. Glycolysis occurs in ___ steps or ___ phases. 3. Pyruvate then enters the mitochondr ...
... 2. Glycolysis involves breaking down glucose to make two molecules of ________. This also creates ___ molecules of ATP and ___ molecules of NADH. Glycolysis requires Oxygen, which is termed ________ respiration. Glycolysis occurs in ___ steps or ___ phases. 3. Pyruvate then enters the mitochondr ...
The Endomembrane System
... Prevalent in cells synthesizing & breaking down lipids (e.g. liver cells: produce bile salts from cholesterol & break down ...
... Prevalent in cells synthesizing & breaking down lipids (e.g. liver cells: produce bile salts from cholesterol & break down ...
Addition of the following reactions responsible for the synthesis of
... a. phosphatidate, old: C1836H3398O400P50, new: C1682H3116O413P50 b. phosphatidylglycerol, old: C1986H3748O500P50, new: C1832H3466O513P50 c. phosphatidylserine, old: C1986H3698N50O500P50, new: C1832H3416N50O513P50 d. CDP-diacylglycerol, old: C2286H3998N150O750P100, new: C2132H3716N150O763P100 e. card ...
... a. phosphatidate, old: C1836H3398O400P50, new: C1682H3116O413P50 b. phosphatidylglycerol, old: C1986H3748O500P50, new: C1832H3466O513P50 c. phosphatidylserine, old: C1986H3698N50O500P50, new: C1832H3416N50O513P50 d. CDP-diacylglycerol, old: C2286H3998N150O750P100, new: C2132H3716N150O763P100 e. card ...
The Three Major Parts of the Cell
... there is H2O surrounding your cells…. • Extracellular fluid outside each cell and • The cytoplasm (made of water and various molecules) in each cell • How do the phospholipid molecules line up? ...
... there is H2O surrounding your cells…. • Extracellular fluid outside each cell and • The cytoplasm (made of water and various molecules) in each cell • How do the phospholipid molecules line up? ...
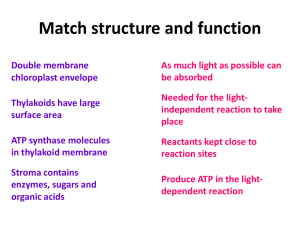
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.























