The S RNA segment of tomato spotted wilt virus has an ambisense
... corresponds to a protein of 465 amino acids and an Mr of 52.4K. The amino acid sequence of this putative protein does not contain hydropfiobic regions that might function as signal peptides or transmembrane domains, according to the hydropathy algorithms of Hopp & Woods (1981) and Kyte & Doolittle ( ...
... corresponds to a protein of 465 amino acids and an Mr of 52.4K. The amino acid sequence of this putative protein does not contain hydropfiobic regions that might function as signal peptides or transmembrane domains, according to the hydropathy algorithms of Hopp & Woods (1981) and Kyte & Doolittle ( ...
MIT 2006: Engineering bacteria to smell good
... Need: To specifically control who can read the DNA message Means: Riboregulation Some slides borrowed from the 2006 Berkeley Team ...
... Need: To specifically control who can read the DNA message Means: Riboregulation Some slides borrowed from the 2006 Berkeley Team ...
1. Introduction Organisms are made up of the sum of their genes and
... alternatively processed or modified through RNA editing. Furthermore, some human proteins are involved in various complexes, catalysing different reactions. Messenger RNA (mRNA) has been analysed for more than 40 years. The development of new methods to purify RNA and ribonucleoprotein particles (RN ...
... alternatively processed or modified through RNA editing. Furthermore, some human proteins are involved in various complexes, catalysing different reactions. Messenger RNA (mRNA) has been analysed for more than 40 years. The development of new methods to purify RNA and ribonucleoprotein particles (RN ...
The abundance and cell cycle dependent expression of the mRNA
... the relative amounts of the specific mRNAs in the samples studied. The results presented in Tablel indicate that HMG-17 mRNA is about 32-fold more abundant than actin mRNA and 15-fold more abundant than histone H4 or HMG-14 mRNA. The abundance of the HMG-17 mRNA is not due to non-specific binding of ...
... the relative amounts of the specific mRNAs in the samples studied. The results presented in Tablel indicate that HMG-17 mRNA is about 32-fold more abundant than actin mRNA and 15-fold more abundant than histone H4 or HMG-14 mRNA. The abundance of the HMG-17 mRNA is not due to non-specific binding of ...
HUA1, a Regulator of Stamen and Carpel Identities
... (such as ag-1) show stamen-to-petal transformation in the third whorl (Bowman et al., 1989), flowers of the weak ag-4 allele contain stamens in the third whorl (Sieburth et al., 1995). Recessive hua1-1 and hua2-1 mutations alter the identity of the third whorl organs in ag-4 flowers. ag-4 hua1-1 or ...
... (such as ag-1) show stamen-to-petal transformation in the third whorl (Bowman et al., 1989), flowers of the weak ag-4 allele contain stamens in the third whorl (Sieburth et al., 1995). Recessive hua1-1 and hua2-1 mutations alter the identity of the third whorl organs in ag-4 flowers. ag-4 hua1-1 or ...
Gene Section GLIS2 (GLIS family zinc finger 2) in Oncology and Haematology
... HGNC (Hugo): GLIS2 Location: 16p13.3 ...
... HGNC (Hugo): GLIS2 Location: 16p13.3 ...
Carcinoma Myelocytomatosis
... c-Myc works as part of a heterodimeric complex with the protein Max, which binds itself to the carboxy-terminal basic-helix-loop-helix-zipper (bHLHZ) domain of the c-Myc protein. This MycMax heterodimer is able to bind specific DNA sequences, such as the E-box sequence ‘CACGTG’. We also find two hig ...
... c-Myc works as part of a heterodimeric complex with the protein Max, which binds itself to the carboxy-terminal basic-helix-loop-helix-zipper (bHLHZ) domain of the c-Myc protein. This MycMax heterodimer is able to bind specific DNA sequences, such as the E-box sequence ‘CACGTG’. We also find two hig ...
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA
... do not contain introns. Fig. 11. Organization of genes for the 5S rRNA Eukaryotic tRNA molecules are also excised from large transcripts (called pre-tRNA), which may contain one or more tRNA sequences. During processing the introns and spacer sequences are removed, at the 3’ end a specific CCA seque ...
... do not contain introns. Fig. 11. Organization of genes for the 5S rRNA Eukaryotic tRNA molecules are also excised from large transcripts (called pre-tRNA), which may contain one or more tRNA sequences. During processing the introns and spacer sequences are removed, at the 3’ end a specific CCA seque ...
DNA vs. RNA
... Introns are sections of DNA not needed for a protein (it stays IN the nucleus) Exons are sections of DNA needed for a protein (when converted into RNA these exons EXIT the nucleus) ...
... Introns are sections of DNA not needed for a protein (it stays IN the nucleus) Exons are sections of DNA needed for a protein (when converted into RNA these exons EXIT the nucleus) ...
Other RNA Processing Events
... removing the last 2 nucleotides from RNA – RNase T is the major participant in removing very last nucleotide ...
... removing the last 2 nucleotides from RNA – RNase T is the major participant in removing very last nucleotide ...
CRS questions
... 3) It has been estimated that approximately half of human genes yield mRNAs of different sequences because the splicing of introns can vary among different tissues and cellular circumstances. Consider what would be the consequence of splicing RNAs in different ways; different proteins would be produ ...
... 3) It has been estimated that approximately half of human genes yield mRNAs of different sequences because the splicing of introns can vary among different tissues and cellular circumstances. Consider what would be the consequence of splicing RNAs in different ways; different proteins would be produ ...
Block 1: Genetics Dr. McKinney Test 1: Transcription (4) The order
... T/F: A major difference between mRNA/tRNA synthesis and rRNA synthesis is the fact that mRNA/tRNA synthesis occurs from genes located in the nucleolus, where many copies are present, and is carried out by RNA pol I. a. False: rRNA synthesis occurs in the nucleolar region where there are approximatel ...
... T/F: A major difference between mRNA/tRNA synthesis and rRNA synthesis is the fact that mRNA/tRNA synthesis occurs from genes located in the nucleolus, where many copies are present, and is carried out by RNA pol I. a. False: rRNA synthesis occurs in the nucleolar region where there are approximatel ...
Ovation™ RNA Amplification System
... were plotted on the x-and y-axis, respectively. A high level of correlation (R2 = 0.97) was obtained. ...
... were plotted on the x-and y-axis, respectively. A high level of correlation (R2 = 0.97) was obtained. ...
Proteins – synthesis and roles in cells
... • There are several types of common gene splicing events. • Exon Skipping: This is the most common known gene splicing mechanism in which exon(s) are included or excluded from the final gene transcript leading to extended or shortened mRNA variants. The exons are the coding regions of a gene and are ...
... • There are several types of common gene splicing events. • Exon Skipping: This is the most common known gene splicing mechanism in which exon(s) are included or excluded from the final gene transcript leading to extended or shortened mRNA variants. The exons are the coding regions of a gene and are ...
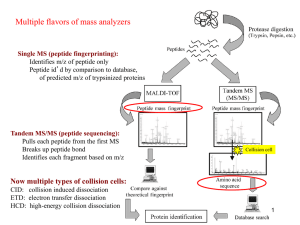
Proteomics2_2012
... Often focus on proteins identified by at least 2 different PSMs (or proteins with single PSMs of very high posterior probability) ...
... Often focus on proteins identified by at least 2 different PSMs (or proteins with single PSMs of very high posterior probability) ...
Document
... level of tryptophan? The leader region has a short coding sequence that could represent a leader peptide of 14 amino acids. Fig. 13.6: shows that it contains a ribosome binding site whose AUG codon is followed by a short coding region that contains two successive codons for tryptophan. When the ce ...
... level of tryptophan? The leader region has a short coding sequence that could represent a leader peptide of 14 amino acids. Fig. 13.6: shows that it contains a ribosome binding site whose AUG codon is followed by a short coding region that contains two successive codons for tryptophan. When the ce ...
Document
... CALR (40-500ng) were converted to radiolabeled oligonucleotide probes using [α32P]dATP and the Prime-a-gene labeling system (Promega). Probes generated from each reaction were purified ...
... CALR (40-500ng) were converted to radiolabeled oligonucleotide probes using [α32P]dATP and the Prime-a-gene labeling system (Promega). Probes generated from each reaction were purified ...
Translation
... → polypeptide chain is released from tRNA at the P site and it is bound by peptide bond to the amino acid carried by the tRNA at the A site → at the same time tRNA carrying prolonged polypeptide chain is shifted from the A site to the P site and now free tRNA is shifted from the P site to E site → t ...
... → polypeptide chain is released from tRNA at the P site and it is bound by peptide bond to the amino acid carried by the tRNA at the A site → at the same time tRNA carrying prolonged polypeptide chain is shifted from the A site to the P site and now free tRNA is shifted from the P site to E site → t ...
Translation
... → polypeptide chain is released from tRNA at the P site and it is bound by peptide bond to the amino acid carried by the tRNA at the A site → at the same time tRNA carrying prolonged polypeptide chain is shifted from the A site to the P site and now free tRNA is shifted from the P site to E site → t ...
... → polypeptide chain is released from tRNA at the P site and it is bound by peptide bond to the amino acid carried by the tRNA at the A site → at the same time tRNA carrying prolonged polypeptide chain is shifted from the A site to the P site and now free tRNA is shifted from the P site to E site → t ...
Translation
... → polypeptide chain is released from tRNA at the P site and it is bound by peptide bond to the amino acid carried by the tRNA at the A site → at the same time tRNA carrying prolonged polypeptide chain is shifted from the A site to the P site and now free tRNA is shifted from the P site to E site → t ...
... → polypeptide chain is released from tRNA at the P site and it is bound by peptide bond to the amino acid carried by the tRNA at the A site → at the same time tRNA carrying prolonged polypeptide chain is shifted from the A site to the P site and now free tRNA is shifted from the P site to E site → t ...
Mechanism of activation
... – Specific binding between activator or coactivator and the transcription complex – Mutations in target of binding should abolish activation – Find targets in suppressor screens ...
... – Specific binding between activator or coactivator and the transcription complex – Mutations in target of binding should abolish activation – Find targets in suppressor screens ...
Genes and RNA
... i.e., they are the same in most introns in most species. There is a GU at the 5’ splice site of the intron and an AG at the 3’ splice site in virtually all cases examined ("the GU-AG rule") Consensus sequences of 5’ and 3’ splice junctions in eukaryotic mRNAs. Almost all introns begin with GU and en ...
... i.e., they are the same in most introns in most species. There is a GU at the 5’ splice site of the intron and an AG at the 3’ splice site in virtually all cases examined ("the GU-AG rule") Consensus sequences of 5’ and 3’ splice junctions in eukaryotic mRNAs. Almost all introns begin with GU and en ...
Qβ replicase discriminates between legitimate and illegitimate
... thermodynamically more stable than are the intrastand secondary structures: If a mixture of complementary is annealed (melted and then slow cooled), they are completely converted into double helix. • Within the replicative complex, the template and the nascent strands are close to one another, which ...
... thermodynamically more stable than are the intrastand secondary structures: If a mixture of complementary is annealed (melted and then slow cooled), they are completely converted into double helix. • Within the replicative complex, the template and the nascent strands are close to one another, which ...