28. Nervous Systems
... formation to cortex makes us alert and aware • EEG measures electrical activity in the brain during arousal and sleep – In REM sleep, brain waves are similar to the awake state; most dreams occur Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... formation to cortex makes us alert and aware • EEG measures electrical activity in the brain during arousal and sleep – In REM sleep, brain waves are similar to the awake state; most dreams occur Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Chapter 13 - tanabe homepage
... • Interior of axon regains negative charge (-65mV) • Wave of depolarization/repolarization travels down the axon ...
... • Interior of axon regains negative charge (-65mV) • Wave of depolarization/repolarization travels down the axon ...
Schwann cells
... contraction, gland secretion, or transfer of information • Resting potential • Transmembrane potential of a cell at rest • All neural activities begin with a change from resting potential ...
... contraction, gland secretion, or transfer of information • Resting potential • Transmembrane potential of a cell at rest • All neural activities begin with a change from resting potential ...
Stable propagation of synchronous spiking in cortical neural networks
... animals were young adult gerbils. A gerbil was deeply anaesthetized and its left cochlea was exposed. Tones from a loudspeaker were delivered to the ear via a tube ®tted to the left ear canal. The level of the tones was calibrated in the ear canal at the beginning of each experiment. Basal scala tym ...
... animals were young adult gerbils. A gerbil was deeply anaesthetized and its left cochlea was exposed. Tones from a loudspeaker were delivered to the ear via a tube ®tted to the left ear canal. The level of the tones was calibrated in the ear canal at the beginning of each experiment. Basal scala tym ...
Mechanism for propagation of rate signals through a 10
... can exhibit coherence resonance in response to noise only.[8] Here, the mean firing rate of layer 2, f2 is a single-peaked function of τsyn , with a maximum at τsyn = 3 ms. Accordingly, the output rate is also peaked at τsyn = 3 ms, suggesting that the propagation of rate signals can be modulated by ...
... can exhibit coherence resonance in response to noise only.[8] Here, the mean firing rate of layer 2, f2 is a single-peaked function of τsyn , with a maximum at τsyn = 3 ms. Accordingly, the output rate is also peaked at τsyn = 3 ms, suggesting that the propagation of rate signals can be modulated by ...
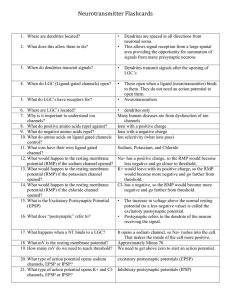
Neurotransmitter Flashcards
... 145. When a person is detoxing from alcohol abuse, what medicine is given, what symptom does it prevent, and how does the medicine work (what is its mechanism of action)? 146. What two neurotransmitters are inhibitory? 147. Alcohol stimulates what 2 neurotransmitters? 148. What effect does alcohol h ...
... 145. When a person is detoxing from alcohol abuse, what medicine is given, what symptom does it prevent, and how does the medicine work (what is its mechanism of action)? 146. What two neurotransmitters are inhibitory? 147. Alcohol stimulates what 2 neurotransmitters? 148. What effect does alcohol h ...
ROLE OF EARLY ACOUSTIC EXPERIENCE IN DEVELOPMENT OF THE RAT by
... termination of the sensory restriction (Cynader, Berman, & Hein, 1976; Wiesel & Hubel, 1965). 1.2 Critical Periods in Development Most experience-dependent neocortical changes occur during specific temporal periods when the functional and structural properties of neurons are particularly susceptible ...
... termination of the sensory restriction (Cynader, Berman, & Hein, 1976; Wiesel & Hubel, 1965). 1.2 Critical Periods in Development Most experience-dependent neocortical changes occur during specific temporal periods when the functional and structural properties of neurons are particularly susceptible ...
EXCITABLE TISSUES
... 5. Un‐myelinated fibres Currents flow around the depolarised area. These flow through the next bit of the membrane and alter its permeability to Na+ ions. The next bit of membrane depolarises. Every tiny increment of the membrane must be depolarised, and depolarisation is ...
... 5. Un‐myelinated fibres Currents flow around the depolarised area. These flow through the next bit of the membrane and alter its permeability to Na+ ions. The next bit of membrane depolarises. Every tiny increment of the membrane must be depolarised, and depolarisation is ...
Neural network
... spikes called action potentials. • Spike originates in cell body, travels down axon(轴突), and causes synaptic terminals to release neurotransmitters. • Chemical diffuses across synapse to dendrites of other neurons. • Neurotransmitters can be excititory or inhibitory. • If net input of neurotransmitt ...
... spikes called action potentials. • Spike originates in cell body, travels down axon(轴突), and causes synaptic terminals to release neurotransmitters. • Chemical diffuses across synapse to dendrites of other neurons. • Neurotransmitters can be excititory or inhibitory. • If net input of neurotransmitt ...
firing pattern modulation by oscillatory input in
... Abstract/Neocortical neurons in vivo receive periodic stimuli due to feedforward input from the periphery as well as local cellular and circuit properties. In order to understand how neurons process such information, the responses of neurons to periodic sine wave current stimuli of varying frequenci ...
... Abstract/Neocortical neurons in vivo receive periodic stimuli due to feedforward input from the periphery as well as local cellular and circuit properties. In order to understand how neurons process such information, the responses of neurons to periodic sine wave current stimuli of varying frequenci ...
download file
... input directs spatial and temporal plasticity in primary auditory cortex. J Neurophysiol 86: 326 –338, 2001. The cortical representation of the sensory environment is continuously modified by experience. Changes in spatial (receptive field) and temporal response properties of cortical neurons underl ...
... input directs spatial and temporal plasticity in primary auditory cortex. J Neurophysiol 86: 326 –338, 2001. The cortical representation of the sensory environment is continuously modified by experience. Changes in spatial (receptive field) and temporal response properties of cortical neurons underl ...
Olfactory network dynamics and the coding of multidimensional
... • In other words, it must be able to select against temporal summation and for spatial summation of (coincident) input; input synchronization and active shortening of the integration window, as found here, is a solution to this problem. ...
... • In other words, it must be able to select against temporal summation and for spatial summation of (coincident) input; input synchronization and active shortening of the integration window, as found here, is a solution to this problem. ...
This Week in The Journal - The Journal of Neuroscience
... during undirected singing than during female-directed singing, suggesting FoxP2 expression is associated with song stability. Indeed, when FoxP2 is knocked down in Area X in juvenile finches, the birds fail to accurately reproduce a tutor’s song and they sing more variable songs as adults. To furthe ...
... during undirected singing than during female-directed singing, suggesting FoxP2 expression is associated with song stability. Indeed, when FoxP2 is knocked down in Area X in juvenile finches, the birds fail to accurately reproduce a tutor’s song and they sing more variable songs as adults. To furthe ...
3._Biological_Basis_of_Behavior_objectives
... at any resources. Any additional material covered in your assigned reading and notes should also be reviewed. Study BEYOND RECOGNITION! 1. Be able to state the definition of biological psychology. 2. Identify various technology used to register brain activity and/or take images of the brain. 3. Defi ...
... at any resources. Any additional material covered in your assigned reading and notes should also be reviewed. Study BEYOND RECOGNITION! 1. Be able to state the definition of biological psychology. 2. Identify various technology used to register brain activity and/or take images of the brain. 3. Defi ...
Itch neurons play a role in managing pain
... "To our surprise, we found the spinal cord neurons receiving the peripheral pain and itch inputs are not separate. They can receive signals from itch fibers and also pain fibers," says study coauthor and neuroscientist at Johns Hopkins University Xinzhong Dong. These neurons, called the GRP neurons, ...
... "To our surprise, we found the spinal cord neurons receiving the peripheral pain and itch inputs are not separate. They can receive signals from itch fibers and also pain fibers," says study coauthor and neuroscientist at Johns Hopkins University Xinzhong Dong. These neurons, called the GRP neurons, ...
20150210_RAVI_Lecture
... and Biosensors, allow neurobiologists to better dissect neural circuits Tool development will require a multidisciplinary approach (bioengineers, microscopist, computer scientists, and biologist) ...
... and Biosensors, allow neurobiologists to better dissect neural circuits Tool development will require a multidisciplinary approach (bioengineers, microscopist, computer scientists, and biologist) ...
Large-scale recording of neuronal ensembles
... exceeds a certain threshold, analogous to recording of action potentials (spikes) emitted by single neurons in the brain. By monitoring different but single musical instruments of the same or even different orchestras over many successive performances and pooling the measurements as if they were rec ...
... exceeds a certain threshold, analogous to recording of action potentials (spikes) emitted by single neurons in the brain. By monitoring different but single musical instruments of the same or even different orchestras over many successive performances and pooling the measurements as if they were rec ...
How to get on the right track
... cycle, they must migrate to their appropriate location and send out processes to make functional connections with their target cells. A crucial step is determining which process will become the signal-conducting component, the axon, and which processes will become the input components, the dendrites ...
... cycle, they must migrate to their appropriate location and send out processes to make functional connections with their target cells. A crucial step is determining which process will become the signal-conducting component, the axon, and which processes will become the input components, the dendrites ...
PDF file
... emergent) models are analogical and scruffy. The logic capabilities of emergent networks are still unclear, categorically. Neuroanatomical studies, surveyed by so far probably the most extensive and detailed review by Felleman & Van Essen [4] reported that in the brain the motor areas feed its signa ...
... emergent) models are analogical and scruffy. The logic capabilities of emergent networks are still unclear, categorically. Neuroanatomical studies, surveyed by so far probably the most extensive and detailed review by Felleman & Van Essen [4] reported that in the brain the motor areas feed its signa ...
Review. Glial cells in neuronal network function
... potential neuromodulatory roles (for a review see Perea et al. 2009). In the olfactory bulb, astrocytes have been shown to release GABA and glutamate, leading to a target cell-specific modulation of neuronal activity, because astrocytic GABA inhibits mitral and granule cells, whereas astrocytic glut ...
... potential neuromodulatory roles (for a review see Perea et al. 2009). In the olfactory bulb, astrocytes have been shown to release GABA and glutamate, leading to a target cell-specific modulation of neuronal activity, because astrocytic GABA inhibits mitral and granule cells, whereas astrocytic glut ...
Bio 103 Nervous System
... - can amplify an impulse - impulse from a single neuron in CNS may be amplified to activate enough motor units needed for muscle ...
... - can amplify an impulse - impulse from a single neuron in CNS may be amplified to activate enough motor units needed for muscle ...
Activity-dependent editing of neuromuscular synaptic connections
... Collectively, the available data on competition at neuromuscular and most other synapses support an activity-dependent positive feedback mechanism in which gradual changes in synaptic strength and synaptic area contribute to an input’s long-term viability. These events are summarized in cartoon form ...
... Collectively, the available data on competition at neuromuscular and most other synapses support an activity-dependent positive feedback mechanism in which gradual changes in synaptic strength and synaptic area contribute to an input’s long-term viability. These events are summarized in cartoon form ...
November 2000 Volume 3 Number Supp pp 1184
... Synaptic basis of persistent activity Firing rate models provide insight into many aspects of attractor networks but generally ignore the wide range of biophysical time scales in cortical neurons, the consequences of single spikes for dynamics, and the specific contributions of voltage-gated and syn ...
... Synaptic basis of persistent activity Firing rate models provide insight into many aspects of attractor networks but generally ignore the wide range of biophysical time scales in cortical neurons, the consequences of single spikes for dynamics, and the specific contributions of voltage-gated and syn ...
Drugs and the Synapse
... The Concept of the Synapse • This led to the idea of inhibitory postsynaptic potential or the temporary hyperpolarization of a membrane. • An ISPS occurs when synaptic input selectively opens the gates for positively charged potassium ions to leave the cell or negatively charged chloride ions to e ...
... The Concept of the Synapse • This led to the idea of inhibitory postsynaptic potential or the temporary hyperpolarization of a membrane. • An ISPS occurs when synaptic input selectively opens the gates for positively charged potassium ions to leave the cell or negatively charged chloride ions to e ...
Nonsynaptic plasticity
Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.