Chapter 11 Efferent Division: Autonomic and Somatic Motor Control
... Neurotransmitter synthesis takes place in the axon varicosities Neurotransmitter release at the autonomic synapse is similar to that at a “model” synapse: • AP arrives at the varicosity • Voltage-gated Ca++ channels open • Ca++ enters the neuron • Neurotransmitter released into the synapse • Diffuse ...
... Neurotransmitter synthesis takes place in the axon varicosities Neurotransmitter release at the autonomic synapse is similar to that at a “model” synapse: • AP arrives at the varicosity • Voltage-gated Ca++ channels open • Ca++ enters the neuron • Neurotransmitter released into the synapse • Diffuse ...
neurotransmitters 101
... man winter. The same logic applies to neurotransmission. Without enough neurotransmitters in the system, whether excitatory or inhibitory, the system as a whole does not function properly. This creates a situation ripe for the onset of disease. Similarly, neurotransmitter-related conditions can mani ...
... man winter. The same logic applies to neurotransmission. Without enough neurotransmitters in the system, whether excitatory or inhibitory, the system as a whole does not function properly. This creates a situation ripe for the onset of disease. Similarly, neurotransmitter-related conditions can mani ...
Dopamine control of pyramidal neuron activity in the primary motor
... but not a D1 antagonist, in rats in vivo. Moreover, specific dopaminergic deafferentation of M1 impairs motor skill learning (Hosp et al., 2011) and is associated with decreased long term potentiation (LTP) that is mimicked by reversible blockade of D2 receptors (Molina-Luna et al., 2009). These dat ...
... but not a D1 antagonist, in rats in vivo. Moreover, specific dopaminergic deafferentation of M1 impairs motor skill learning (Hosp et al., 2011) and is associated with decreased long term potentiation (LTP) that is mimicked by reversible blockade of D2 receptors (Molina-Luna et al., 2009). These dat ...
Realistic synaptic inputs for model neural networks
... model neuron used throughout this discussion consists of an active soma and a single, passive dendritic tree. This arrangement is commonly known as the Rall model of the 11p"roo" [!& 1 q .nA_ i!. bar a long history in the literat13re p; 3, The somm k considered to be the site of the nonlinear proces ...
... model neuron used throughout this discussion consists of an active soma and a single, passive dendritic tree. This arrangement is commonly known as the Rall model of the 11p"roo" [!& 1 q .nA_ i!. bar a long history in the literat13re p; 3, The somm k considered to be the site of the nonlinear proces ...
Accurate reconstruction of neuronal morphology
... 6.3.1.2. Injection of biocytin When sharp intracellular electrodes are used, the pipette solution should contain 2-4% biocytin (Sigma) by weight in 1M potassium acetate. This is about the limit in the amount of biocytin that can be dissolved in 1M potassium acetate, and slight warming may be require ...
... 6.3.1.2. Injection of biocytin When sharp intracellular electrodes are used, the pipette solution should contain 2-4% biocytin (Sigma) by weight in 1M potassium acetate. This is about the limit in the amount of biocytin that can be dissolved in 1M potassium acetate, and slight warming may be require ...
Neural Network Dynamics
... potentials produce transient changes in the conductance of the postsynaptic neuron. This can be duplicated in an integrate-and-fire network. However, in the models we review a simplification is made: The postsynaptic effect of a presynaptic action potential is modeled as current injection into the neu ...
... potentials produce transient changes in the conductance of the postsynaptic neuron. This can be duplicated in an integrate-and-fire network. However, in the models we review a simplification is made: The postsynaptic effect of a presynaptic action potential is modeled as current injection into the neu ...
Hippocampus, 22, 1703-1719
... learning-dependent reductions in the amplitude and duration of calcium-dependent postburst afterhyperpolarizations (AHPs), accompanied by other increases in excitability (i.e., increased firing rate, or reduced spike-frequency accommodation) after trace eyeblink conditioning or spatial learning, wit ...
... learning-dependent reductions in the amplitude and duration of calcium-dependent postburst afterhyperpolarizations (AHPs), accompanied by other increases in excitability (i.e., increased firing rate, or reduced spike-frequency accommodation) after trace eyeblink conditioning or spatial learning, wit ...
Artificial Neural Networks Introduction to connectionism
... Knowledge refers to stored information or models used by a person or machine to interpret, predict and appropriately respond to the outside world. (Fischler & Firschein, 1987) ...
... Knowledge refers to stored information or models used by a person or machine to interpret, predict and appropriately respond to the outside world. (Fischler & Firschein, 1987) ...
Time constants
... spontaneous background activity, since this affects the membrane resistance (and recall τ = RC). For a typical spontaneous firing rate of about 5-10 Hz (Koch 1999, p. 412), the membrane time constant may be a small as 1-3 ms (Koch 1999, p. 413), while for zero background activity, it may exceed 100 ...
... spontaneous background activity, since this affects the membrane resistance (and recall τ = RC). For a typical spontaneous firing rate of about 5-10 Hz (Koch 1999, p. 412), the membrane time constant may be a small as 1-3 ms (Koch 1999, p. 413), while for zero background activity, it may exceed 100 ...
Synaptic Plasticity and Connectivity Requirements to
... measure the distribution of selectivity across cells before and after training. When comparing multiple networks, we use the mean of the stimulus-pair selectivity across cells. In order to determine whether or not the information about stimulus-pairs within a given associative network is sufficient ...
... measure the distribution of selectivity across cells before and after training. When comparing multiple networks, we use the mean of the stimulus-pair selectivity across cells. In order to determine whether or not the information about stimulus-pairs within a given associative network is sufficient ...
Chapter 02: Neurons and Glia
... The Prototypical Neuron—(cont.) • Dendrites – “Antennae” of neurons – Dendritic tree – Synapse—receptors – Dendritic spines • Postsynaptic (receives signals from axon terminal) ...
... The Prototypical Neuron—(cont.) • Dendrites – “Antennae” of neurons – Dendritic tree – Synapse—receptors – Dendritic spines • Postsynaptic (receives signals from axon terminal) ...
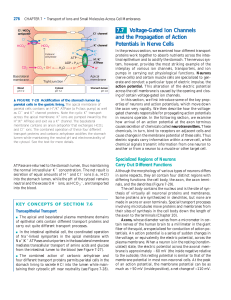
Voltage-Gated Ion Channels and the Propagation of Action
... It takes about 0.5 millisecond (ms) for neurotransmitters to diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to a receptor on the postsynaptic cells. Binding of neurotransmitter triggers opening or closing of specific ion channels in the plasma membrane of postsynaptic cells, leading to changes in the me ...
... It takes about 0.5 millisecond (ms) for neurotransmitters to diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to a receptor on the postsynaptic cells. Binding of neurotransmitter triggers opening or closing of specific ion channels in the plasma membrane of postsynaptic cells, leading to changes in the me ...
Gee JNeuro 2012 - Stanford University
... Surprisingly, this afterdepolarization is masked in quiescent brain slices, but is readily unmasked by physiologic levels of synaptic input which activate NMDA receptors, possibly explaining why this phenomenon has not been reported previously. Notably, we could still elicit this afterdepolarization ...
... Surprisingly, this afterdepolarization is masked in quiescent brain slices, but is readily unmasked by physiologic levels of synaptic input which activate NMDA receptors, possibly explaining why this phenomenon has not been reported previously. Notably, we could still elicit this afterdepolarization ...
DECODING NEURONAL FIRING AND MODELING NEURAL
... information that can be obtained about connections in large neural networks. However, a great deal of information is available about how synaptic strengths can change ...
... information that can be obtained about connections in large neural networks. However, a great deal of information is available about how synaptic strengths can change ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... – Limbic System: responsible for autonomic responses during emotional states (blushing, pallor, fainting, sweating, racing heart rate) ...
... – Limbic System: responsible for autonomic responses during emotional states (blushing, pallor, fainting, sweating, racing heart rate) ...
Study guide (Word Document)
... The format of the lab exam is about 3/4 multiple-choice, 1/4 free response. ...
... The format of the lab exam is about 3/4 multiple-choice, 1/4 free response. ...
Noise in Neurons and Other Constraints
... How can we know what constitutes noise when recording signals from the brain? For instance, neuronal membrane potential shows small variations even at rest, even if synaptic inputs are pharmacologically blocked. Synpatic or electrode inputs near action potential threshold, a neuron may or may not fi ...
... How can we know what constitutes noise when recording signals from the brain? For instance, neuronal membrane potential shows small variations even at rest, even if synaptic inputs are pharmacologically blocked. Synpatic or electrode inputs near action potential threshold, a neuron may or may not fi ...
Systems memory consolidation in Drosophila
... acquisition and shortly afterwards, but not during retrieval [24,25]. a0 /b0 neurons play a key role in encoding the memory trace and in its early stabilization, but are not the site of storage because transmission is dispensable during retrieval. By contrast, output from the combination of a/b and ...
... acquisition and shortly afterwards, but not during retrieval [24,25]. a0 /b0 neurons play a key role in encoding the memory trace and in its early stabilization, but are not the site of storage because transmission is dispensable during retrieval. By contrast, output from the combination of a/b and ...
bio520_JANSEN_r4 - Cal State LA
... Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) indicates cell viablity: released only when membrane is disrupted. (n=3 exp, 3 cultures each, +/- SD) (Skaper et al, 2006) ...
... Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) indicates cell viablity: released only when membrane is disrupted. (n=3 exp, 3 cultures each, +/- SD) (Skaper et al, 2006) ...
Gnostic cells in the 21st century
... grandmother) cells, that means, single neurons firing to individual concepts? To address this question we should first consider possible definitions of what these cells are (Quian Quiroga and Kreiman 2010a,b). The first, extreme version of grandmother cell coding is that one and only one neuron enco ...
... grandmother) cells, that means, single neurons firing to individual concepts? To address this question we should first consider possible definitions of what these cells are (Quian Quiroga and Kreiman 2010a,b). The first, extreme version of grandmother cell coding is that one and only one neuron enco ...
Testing upper motor neuron function in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
... contrast is potentially very effective for exploring neuronal interconnection dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, but still needs more investigation; and novel neuroinflammatory and inhibitory positron emission tomography ligands might have utility in the future (Turner, 2012). However, ex ...
... contrast is potentially very effective for exploring neuronal interconnection dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, but still needs more investigation; and novel neuroinflammatory and inhibitory positron emission tomography ligands might have utility in the future (Turner, 2012). However, ex ...
The projection of the lateral geniculate nucleus to area 17 of the rat
... (At) axon terminals. The dendrite has a smooth outline and its cytoplasm contains microtubules (m), polyribosomes (r), and a cistern of endoplasmic reticulum (ER). One mitochondrion (mit) shows a dilatation of its outer membrane. The degenerating axon terminal is surrounded by astrocytic processes ( ...
... (At) axon terminals. The dendrite has a smooth outline and its cytoplasm contains microtubules (m), polyribosomes (r), and a cistern of endoplasmic reticulum (ER). One mitochondrion (mit) shows a dilatation of its outer membrane. The degenerating axon terminal is surrounded by astrocytic processes ( ...
Choline Esters
... Release of transmitter occurs when voltagesensitive calcium channels in the terminal membrane are opened, allowing an influx of calcium. The resulting increase in intracellular calcium causes fusion of vesicles with the surface membrane and exocytotic expulsion of acetylcholine and cotransmitters in ...
... Release of transmitter occurs when voltagesensitive calcium channels in the terminal membrane are opened, allowing an influx of calcium. The resulting increase in intracellular calcium causes fusion of vesicles with the surface membrane and exocytotic expulsion of acetylcholine and cotransmitters in ...
Nonsynaptic plasticity
Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.