The Nervous System
... -K+ ions are mostly inside with large anions (proteins, sulfates, phosphates) -large anions can only cross the membrane through ion channels or using carrier proteins -K+ ions are pumped into the cell and Na+ ions are pumped out -K+ ions can diffuse out of the cell more easily than Na+ because they ...
... -K+ ions are mostly inside with large anions (proteins, sulfates, phosphates) -large anions can only cross the membrane through ion channels or using carrier proteins -K+ ions are pumped into the cell and Na+ ions are pumped out -K+ ions can diffuse out of the cell more easily than Na+ because they ...
Neuron Physiology Notes
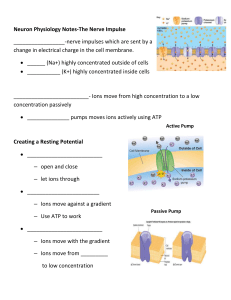
... _________________________- Ions move from high concentration to a low concentration passively ______________ pumps moves ions actively using ATP Active Pump ...
... _________________________- Ions move from high concentration to a low concentration passively ______________ pumps moves ions actively using ATP Active Pump ...
here - York University
... When an action potential invades an axonal terminal, voltage-gated calcium channels open causing an increase in calcium in the cytoplasm. Higher concentration of calcium will cause the neurotransmitter filled vesicles to fuse to the membrane, allowing the neurotransmitters to diffuse to the post-syn ...
... When an action potential invades an axonal terminal, voltage-gated calcium channels open causing an increase in calcium in the cytoplasm. Higher concentration of calcium will cause the neurotransmitter filled vesicles to fuse to the membrane, allowing the neurotransmitters to diffuse to the post-syn ...
BIOLOGICAL BASES OF BEHAVIOR
... • The speed at which an action potential travels the axon ranges from 2 to 250 mph. ...
... • The speed at which an action potential travels the axon ranges from 2 to 250 mph. ...
THE NEURON (Slides 4 to 14) • Based on the PowerPoint attached
... What happens to the membrane of the neuron when it is resting? When a neuron is resting, its membrane forms a partial barrier between the inside and the outside of the neuron – the solution contains electrically charged particles called ions. When the neuron is at rest – where are there more negativ ...
... What happens to the membrane of the neuron when it is resting? When a neuron is resting, its membrane forms a partial barrier between the inside and the outside of the neuron – the solution contains electrically charged particles called ions. When the neuron is at rest – where are there more negativ ...
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue
... come down the axon – no matter how strong it is. 9. The __________________ __________________ __________________ is the time immediately after the Na gates close and repolarization is still occurring that a exceptionally strong stimulus may cause depolarization. F. Impulses 1. Impulses travel at dif ...
... come down the axon – no matter how strong it is. 9. The __________________ __________________ __________________ is the time immediately after the Na gates close and repolarization is still occurring that a exceptionally strong stimulus may cause depolarization. F. Impulses 1. Impulses travel at dif ...
Forea Wang
... electrode succeeds in driving synaptic activity to the patched postsynaptic neuron. If activity is synaptic, we should be able to measure a constant Δt between stimulation and response. Meanwhile, other electrodes will be stimulated to elicit interplay of other synapses onto the same neuron. Once sy ...
... electrode succeeds in driving synaptic activity to the patched postsynaptic neuron. If activity is synaptic, we should be able to measure a constant Δt between stimulation and response. Meanwhile, other electrodes will be stimulated to elicit interplay of other synapses onto the same neuron. Once sy ...
Nervous System Lecture Notes Page
... Arriving Action Potential Depolarizes Synaptic Knob Ca++ Enters Cytoplasm of Presynaptic Neuron Exocytosis of Synaptic Vesicles, Releasing ...
... Arriving Action Potential Depolarizes Synaptic Knob Ca++ Enters Cytoplasm of Presynaptic Neuron Exocytosis of Synaptic Vesicles, Releasing ...
Nervous System Outline 1
... 1. This is the interpretation of the energy by the Central Nervous System (CNS). (Basically “thinking” about the stimulus.) 2. This interpretation of the stimulus leads to a determination of the appropriate response. C. Motor Output – Sending out of impulses from the brain or spinal cord to glands o ...
... 1. This is the interpretation of the energy by the Central Nervous System (CNS). (Basically “thinking” about the stimulus.) 2. This interpretation of the stimulus leads to a determination of the appropriate response. C. Motor Output – Sending out of impulses from the brain or spinal cord to glands o ...
Tutorial 10: Temporal and Spatial Summation Figure 10: Temporal
... separate points of the dendritic tree (Kogo & Ariel, 1999). Two distinct responses are distinguished based on the interval between the time of stimulation at each of the two sites of postsynaptic membrane. Surprisingly, a facilitation of response was never observed. This could be a unique characteri ...
... separate points of the dendritic tree (Kogo & Ariel, 1999). Two distinct responses are distinguished based on the interval between the time of stimulation at each of the two sites of postsynaptic membrane. Surprisingly, a facilitation of response was never observed. This could be a unique characteri ...
Theoretical neuroscience: Single neuron dynamics and computation
... • Dendritic spines contain a huge diversity of molecules (in particular protein kinases and phosphatases) whose interactions define complex networks ...
... • Dendritic spines contain a huge diversity of molecules (in particular protein kinases and phosphatases) whose interactions define complex networks ...
Neurons` Short-Term Plasticity Amplifies Signals
... understanding the most basic level of this process: the short-term plasticity at hippocampal synapses that result from processing incoming signals resembling place-field responses. The researchers, Vitaly Klyachko and Charles Stevens, discovered a novel short-term plasticity mechanism by which excita ...
... understanding the most basic level of this process: the short-term plasticity at hippocampal synapses that result from processing incoming signals resembling place-field responses. The researchers, Vitaly Klyachko and Charles Stevens, discovered a novel short-term plasticity mechanism by which excita ...
2014 nervous system ppt
... Another multiple guess for your CNS! 9. Action potentials are usually propagated in only one direction along an axon because: A. The node of Ranvier conducts in one direction B. The brief refractory period prevents opening of voltage gated Na+ channels C. The axon hillock has a higher membrane pote ...
... Another multiple guess for your CNS! 9. Action potentials are usually propagated in only one direction along an axon because: A. The node of Ranvier conducts in one direction B. The brief refractory period prevents opening of voltage gated Na+ channels C. The axon hillock has a higher membrane pote ...
Brain and Behaviour
... reach the dendrite must reach a certain level of intensity or THRESHOLD – this is an all of nothing response to neurons either reaching the threshold or they don’t . If the Threshold is reached then the neuron transmits an electrical impulse down the axon and this impulse that runs down the axon i ...
... reach the dendrite must reach a certain level of intensity or THRESHOLD – this is an all of nothing response to neurons either reaching the threshold or they don’t . If the Threshold is reached then the neuron transmits an electrical impulse down the axon and this impulse that runs down the axon i ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM - Coast Colleges Home Page
... Arriving Action Potential Depolarizes Synaptic Knob Ca++ Enters Cytoplasm of Presynaptic Neuron Exocytosis of Synaptic Vesicles, Releasing ...
... Arriving Action Potential Depolarizes Synaptic Knob Ca++ Enters Cytoplasm of Presynaptic Neuron Exocytosis of Synaptic Vesicles, Releasing ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
... Arriving Action Potential Depolarizes Synaptic Knob Ca++ Enters Cytoplasm of Presynaptic Neuron Exocytosis of Synaptic Vesicles, Releasing ...
... Arriving Action Potential Depolarizes Synaptic Knob Ca++ Enters Cytoplasm of Presynaptic Neuron Exocytosis of Synaptic Vesicles, Releasing ...
File
... urgently. For example, if you burn your fingers it is important that your brain gets the message to withdraw your hand very quickly. ...
... urgently. For example, if you burn your fingers it is important that your brain gets the message to withdraw your hand very quickly. ...
A.1 Neural Development
... Single nerve myriad of synapses to neighboring nerve cells best fit wins, others die off Strengthening communication in that single connection Controlled by IgCAM (neural adhesion molecule) ...
... Single nerve myriad of synapses to neighboring nerve cells best fit wins, others die off Strengthening communication in that single connection Controlled by IgCAM (neural adhesion molecule) ...
3/26
... while the brain integrates the incoming signals to determine an appropriate response. CB 48.3 ...
... while the brain integrates the incoming signals to determine an appropriate response. CB 48.3 ...
Neuron Notes Neuron- Cells that carry messages throughout the
... 1. cell body: largest part, contains nucleus and most of cytoplasm – most metabolic activity of cell occurs here 2. dendrites: spread out from cell body; short, branched extensions; carry impulses toward the cell body 3. axons: (transmit/send signals) long fiber that carries impulses away from cell ...
... 1. cell body: largest part, contains nucleus and most of cytoplasm – most metabolic activity of cell occurs here 2. dendrites: spread out from cell body; short, branched extensions; carry impulses toward the cell body 3. axons: (transmit/send signals) long fiber that carries impulses away from cell ...
Assignment: Sensing mechanical changes in firing neurons
... Volts/meter. When an action potential travels down the axon, deviations from this resting potential in the order of 100 milliVolts occur, causing a strong change in electrical field strength over this membrane. It is our hypothesis that this change in electrical field causes small mechanical deforma ...
... Volts/meter. When an action potential travels down the axon, deviations from this resting potential in the order of 100 milliVolts occur, causing a strong change in electrical field strength over this membrane. It is our hypothesis that this change in electrical field causes small mechanical deforma ...
Nervous and Immune Systems
... Taste, smell, solute concentration (osmoreceptors), glucose, oxygen, carbon dioxide Photoreceptors: receptors that respond to different wavelengths of light ...
... Taste, smell, solute concentration (osmoreceptors), glucose, oxygen, carbon dioxide Photoreceptors: receptors that respond to different wavelengths of light ...
Chapter 3 Notes (part 1) 1. Basic Elements of the Nervous System (a
... C. The charge rises to +35 or +40mv, at which point this “extra” charge propagates down the axon toward the axon terminal (this is the action potential) D. The “all or nothing” principle states that neurons are either active or inactive. EITHER the charge reaches the stimulus threshold, causing an a ...
... C. The charge rises to +35 or +40mv, at which point this “extra” charge propagates down the axon toward the axon terminal (this is the action potential) D. The “all or nothing” principle states that neurons are either active or inactive. EITHER the charge reaches the stimulus threshold, causing an a ...
Nonsynaptic plasticity
Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.