Neurons and Nervous System
... potential when they open and close. The membrane is depolarized when Na+ enters the cell and the inside of the neuron becomes less negative than when at rest. If gated K+ channels open and K+ leaves, the cell becomes more negative inside and the membrane is ...
... potential when they open and close. The membrane is depolarized when Na+ enters the cell and the inside of the neuron becomes less negative than when at rest. If gated K+ channels open and K+ leaves, the cell becomes more negative inside and the membrane is ...
File
... prioritize information and to focus on many different things at once. • People with low levels of GABA neurotransmitters can suffer from certain anxiety disorders, panic disorders, and Parkinson’s disease. • Certain drugs, like caffeine, inhibits the release of GABA causing your brain to become ‘mor ...
... prioritize information and to focus on many different things at once. • People with low levels of GABA neurotransmitters can suffer from certain anxiety disorders, panic disorders, and Parkinson’s disease. • Certain drugs, like caffeine, inhibits the release of GABA causing your brain to become ‘mor ...
Nervous System Cells - Dr. M`s Classes Rock
... Neurotransmitters: means by which neurons communicate with one another; more than 30 compounds are known to be neurotransmitters, and dozens of others are suspected Common classification of neurotransmitters: o Function: determined by the postsynaptic receptor; two major functional classificatio ...
... Neurotransmitters: means by which neurons communicate with one another; more than 30 compounds are known to be neurotransmitters, and dozens of others are suspected Common classification of neurotransmitters: o Function: determined by the postsynaptic receptor; two major functional classificatio ...
0pt20pt [1.44]Spike Train Correlations Induced [1ex] [1.44]by
... Graphs with weighted or multiple edges ...
... Graphs with weighted or multiple edges ...
UNIT 4 – HOMEOSTASIS 8.1 – Human Body Systems and H
... miminum level of a stimulus required to produce a response (usually 50 mV) ...
... miminum level of a stimulus required to produce a response (usually 50 mV) ...
Questions and Answers
... 7. How specialised/general are the brain areas 8. What’s the ”frequency” of the brain? Starting from a ”typical” firing frequency for a neuron in inactive mode, if we knew the depth of the neural network (or some approximation of it) we could estimate the time required for one cycle and get some sor ...
... 7. How specialised/general are the brain areas 8. What’s the ”frequency” of the brain? Starting from a ”typical” firing frequency for a neuron in inactive mode, if we knew the depth of the neural network (or some approximation of it) we could estimate the time required for one cycle and get some sor ...
Slide ()
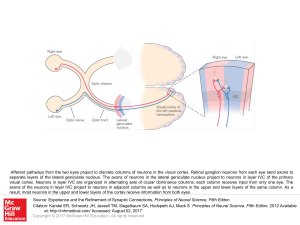
... visual cortex. Neurons in layer IVC are organized in alternating sets of ocular dominance columns; each column receives input from only one eye. The axons of the neurons in layer IVC project to neurons in adjacent columns as well as to neurons in the upper and lower layers of the same column. As a r ...
... visual cortex. Neurons in layer IVC are organized in alternating sets of ocular dominance columns; each column receives input from only one eye. The axons of the neurons in layer IVC project to neurons in adjacent columns as well as to neurons in the upper and lower layers of the same column. As a r ...
a study of axonal protein trafficking in neuronal networks via the
... Figure 3: Rat cortical neurons cultured 14 days in the microfluidic device (a) overview of the neuron growth, and (b) close view of axon region. plasmid encoding axonal proteins with green fluorescent protein tag. When chemicals inducing synapse activities was applied in either chamber, the traffick ...
... Figure 3: Rat cortical neurons cultured 14 days in the microfluidic device (a) overview of the neuron growth, and (b) close view of axon region. plasmid encoding axonal proteins with green fluorescent protein tag. When chemicals inducing synapse activities was applied in either chamber, the traffick ...
TEACHER`S GUIDE
... After viewing this video students should understand the following concepts: 1. The brain is a structure that controls many different functions; areas within the brain are highly specialized to control specific functions, but they are also interconnected. 2. Neurons send information to each other usi ...
... After viewing this video students should understand the following concepts: 1. The brain is a structure that controls many different functions; areas within the brain are highly specialized to control specific functions, but they are also interconnected. 2. Neurons send information to each other usi ...
Chapter 12 - Membrane Transport . PPT - A
... An action potential in the axon of a neuron is called a nerve impulse and is the way neurons communicate. The AP is a brief reversal of membrane potential with a total amplitude of 100 mV (from -70mV to +30mV) APs do not decrease in strength with distance The depolarization phase is followed by a re ...
... An action potential in the axon of a neuron is called a nerve impulse and is the way neurons communicate. The AP is a brief reversal of membrane potential with a total amplitude of 100 mV (from -70mV to +30mV) APs do not decrease in strength with distance The depolarization phase is followed by a re ...
MEDIA REVIEW Neurons In Action: Computer Simulations with
... Neurons in Action was developed by Drs. John W. Moore and Ann E. Stuart. Dr. Moore is a co-author of NEURON, a powerful simulation environment that models neurons based on the equations that describe their behavior. Using NEURON, Moore and Stuart created the seventeen tutorials that make up Neurons ...
... Neurons in Action was developed by Drs. John W. Moore and Ann E. Stuart. Dr. Moore is a co-author of NEURON, a powerful simulation environment that models neurons based on the equations that describe their behavior. Using NEURON, Moore and Stuart created the seventeen tutorials that make up Neurons ...
ANSWERS TO CHAPTER 8
... 2. Somatic motor nervous system: voluntary, innervates skeletal muscle; Autonomic nervous system: involuntary, innervates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands. 3. Multipolar neurons: several dendrites and one axon, includes motor neurons; bipolar neurons: one dendrite and one axon, found in the ...
... 2. Somatic motor nervous system: voluntary, innervates skeletal muscle; Autonomic nervous system: involuntary, innervates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands. 3. Multipolar neurons: several dendrites and one axon, includes motor neurons; bipolar neurons: one dendrite and one axon, found in the ...
PAPER #3: EMBARGOED PRESS RELEASE STRICTLY UNDER
... and the hyperactive release of dopamine. Over time, increasing activation of a key part of the extended amygdala-the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis produces a long-lasting increase in signal transmission onto neurons that produce dopamine so that the rats became desensitized to the cocaine. Sin ...
... and the hyperactive release of dopamine. Over time, increasing activation of a key part of the extended amygdala-the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis produces a long-lasting increase in signal transmission onto neurons that produce dopamine so that the rats became desensitized to the cocaine. Sin ...
Chapter 2
... Parts of a Neuron Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches ...
... Parts of a Neuron Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches ...
Note 11.1 - The Nervous System
... The Structure and Organization of the Human Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) – is the body’s coordinating centre for mechanical and chemical actions; made up of the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – are all the parts of the nervous system, excluding the brain and s ...
... The Structure and Organization of the Human Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) – is the body’s coordinating centre for mechanical and chemical actions; made up of the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – are all the parts of the nervous system, excluding the brain and s ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... (e.g., incontinence) D. The sympathetic and parasympathetic branches demonstrate Cannon’s 4 properties of ______________ 1. Maintenance of the __________ environment 2. Up-down ______________ of target tissues 3. _______________ control – one branch excites some tissues, whereas the other inhibits t ...
... (e.g., incontinence) D. The sympathetic and parasympathetic branches demonstrate Cannon’s 4 properties of ______________ 1. Maintenance of the __________ environment 2. Up-down ______________ of target tissues 3. _______________ control – one branch excites some tissues, whereas the other inhibits t ...
nervous system development and histology
... tissue) in the periphery of the body all are multipolar• Association (interneurons) –• transmit information between neurons within the CNS; analyze inputs, • coordinate outputs are the most common type of neuron (20 billion)• are all multipolar• ...
... tissue) in the periphery of the body all are multipolar• Association (interneurons) –• transmit information between neurons within the CNS; analyze inputs, • coordinate outputs are the most common type of neuron (20 billion)• are all multipolar• ...
Neuron
... Nerve cells, like other cells of the body, have an electric charge that can be measured across their outer cell membrane (resting potential). The resting membrane potential is the result of the differential separation of charged ions, especially Na+ and K+, across the membrane and the resting membra ...
... Nerve cells, like other cells of the body, have an electric charge that can be measured across their outer cell membrane (resting potential). The resting membrane potential is the result of the differential separation of charged ions, especially Na+ and K+, across the membrane and the resting membra ...
Action potential
... At the simplest level (individual neurons) Many dendrites receive neurotransmitter messages simultaneously Some excitatory, some inhibitory ...
... At the simplest level (individual neurons) Many dendrites receive neurotransmitter messages simultaneously Some excitatory, some inhibitory ...
Following the discussion about mirror neurons and imagery we want
... Ego activity producing not only psychological activities (imagery emotions etc) but giving hierarchical organization to all biological levels of the organism. So the ego is a psycho-physic unit continuously generated and generating. We started with a research (Ruggieri, Fiorenza, Sabatini, 1986) whe ...
... Ego activity producing not only psychological activities (imagery emotions etc) but giving hierarchical organization to all biological levels of the organism. So the ego is a psycho-physic unit continuously generated and generating. We started with a research (Ruggieri, Fiorenza, Sabatini, 1986) whe ...
Chapter 7: Structure of Nervous System
... Cable properties cause EPSPs to _____________ quickly over time and distance Spatial summation takes place when EPSPs from different synapses occur in postsynaptic cell at _____________ time Temporal Summation Temporal summation occurs because EPSPs that occur closely in time can sum before th ...
... Cable properties cause EPSPs to _____________ quickly over time and distance Spatial summation takes place when EPSPs from different synapses occur in postsynaptic cell at _____________ time Temporal Summation Temporal summation occurs because EPSPs that occur closely in time can sum before th ...
Changing Channels
... He wanted to identify the different neurons and deduce the contribution of each toward evoking hunger. The problem was that no tools were available to systematically probe brain wiring with the precision he needed. Neurons perform their assigned duties by firing or turning silent in response to chem ...
... He wanted to identify the different neurons and deduce the contribution of each toward evoking hunger. The problem was that no tools were available to systematically probe brain wiring with the precision he needed. Neurons perform their assigned duties by firing or turning silent in response to chem ...
Anatomy Review - Interactive Physiology
... a. acetyl choline, postsynaptic neuron b. neurotransmitter, synaptic cleft 36. (Page 8.) The neuron receiving the signal is called the postsynaptic neuron. When activated, receptors on the postsynaptic neuron open ____ _________. a. ion channels b. voltage-gated receptors c. passive channels 37. (Pa ...
... a. acetyl choline, postsynaptic neuron b. neurotransmitter, synaptic cleft 36. (Page 8.) The neuron receiving the signal is called the postsynaptic neuron. When activated, receptors on the postsynaptic neuron open ____ _________. a. ion channels b. voltage-gated receptors c. passive channels 37. (Pa ...
Brain(annotated)
... to the dendrites of a connected neuron (or some enervated tissue). In the cortex, a typical neuron will send signals to ~10,000 postsynaptic neurons. Synapses don’t transmit the spike with perfect efficiency. It will typically take tens of spikes in a short time to excite the postsynaptic neuron. Th ...
... to the dendrites of a connected neuron (or some enervated tissue). In the cortex, a typical neuron will send signals to ~10,000 postsynaptic neurons. Synapses don’t transmit the spike with perfect efficiency. It will typically take tens of spikes in a short time to excite the postsynaptic neuron. Th ...
Nonsynaptic plasticity
Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.


![0pt20pt [1.44]Spike Train Correlations Induced [1ex] [1.44]by](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014522750_1-d16804f4edee9aca177facbeaf42eec6-300x300.png)