SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Composed of somatic parts of CNS
... neuron of the paravertebral ganglion at that level 4. Pass through the sympathetic trunk without synapsing with anything and go through a splanchnic nerve to get to prevertebral ganglia o Splanchnics innervate the abdominopelvic viscera o PRESYNAPTIC SYMPATHETIC FIBERS that innervate head, neck, bod ...
... neuron of the paravertebral ganglion at that level 4. Pass through the sympathetic trunk without synapsing with anything and go through a splanchnic nerve to get to prevertebral ganglia o Splanchnics innervate the abdominopelvic viscera o PRESYNAPTIC SYMPATHETIC FIBERS that innervate head, neck, bod ...
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF NERVOUS SYSTEM DISEASES
... 1- high-frequency burst of action potentials, 2- hypersynchronization. ...
... 1- high-frequency burst of action potentials, 2- hypersynchronization. ...
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY (7th Edition in Modules) David Myers
... Action Potential Properties All-or-None Response: A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
... Action Potential Properties All-or-None Response: A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
Neurotransmitters
... Neurotransmitter release The release of a neurotransmitter is triggered by the arrival of a nerve impulse (or action potential) and occurs through an unusually rapid process of cellular secretion, also known as exocytosis: Within the presynaptic nerve terminal, vesicles containing neurotransmitter s ...
... Neurotransmitter release The release of a neurotransmitter is triggered by the arrival of a nerve impulse (or action potential) and occurs through an unusually rapid process of cellular secretion, also known as exocytosis: Within the presynaptic nerve terminal, vesicles containing neurotransmitter s ...
6 BIO Neurotransmitters - Appoquinimink High School
... neuron has a pre-set level of stimulation that needs to be met or exceeded in order for it to pass the received impulses on to the next neuron. This is called a neuron’s threshold. ...
... neuron has a pre-set level of stimulation that needs to be met or exceeded in order for it to pass the received impulses on to the next neuron. This is called a neuron’s threshold. ...
This Week in The Journal - Journal of Neuroscience
... The calcium-dependent exocytosis of synaptic vesicles requires assembly of the soluble N-ethyl maleimide sensitive factor adaptor protein receptor (SNARE) complex, consisting of the vesicular membrane-associated protein synaptobrevin, the plasma membrane-associated protein syntaxin, and synaptosomal ...
... The calcium-dependent exocytosis of synaptic vesicles requires assembly of the soluble N-ethyl maleimide sensitive factor adaptor protein receptor (SNARE) complex, consisting of the vesicular membrane-associated protein synaptobrevin, the plasma membrane-associated protein syntaxin, and synaptosomal ...
The Biological Perspective
... Curare a drug used on poison blow darts is just similar enough to fit into the receptor site without actually stimulating the cell This blocks acetylcholine from its receptor sites causing ...
... Curare a drug used on poison blow darts is just similar enough to fit into the receptor site without actually stimulating the cell This blocks acetylcholine from its receptor sites causing ...
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY (7th Edition in Modules) David Myers
... Action Potential Properties All-or-None Response: A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
... Action Potential Properties All-or-None Response: A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
Chapter 7
... The cochlea is part of the inner ear; it is filled with fluid, therefore sounds transferred through the air must be transferred into a liquid medium; the ossicles aid in this transmission The cochlea is divided into 3 sections: the scala vestibuli, scala media, and scala tympani The receptive organ, ...
... The cochlea is part of the inner ear; it is filled with fluid, therefore sounds transferred through the air must be transferred into a liquid medium; the ossicles aid in this transmission The cochlea is divided into 3 sections: the scala vestibuli, scala media, and scala tympani The receptive organ, ...
00216 - UROP
... Brain Slice Cultures Activation of group I metabotropic glutamate (mGlu) receptors causes the endocannabinoid system to induce both short- and long-term changes in synaptic strength in the striatum, the hippocampus, and other regions of the brain. Although current electrophysiological evidence sugge ...
... Brain Slice Cultures Activation of group I metabotropic glutamate (mGlu) receptors causes the endocannabinoid system to induce both short- and long-term changes in synaptic strength in the striatum, the hippocampus, and other regions of the brain. Although current electrophysiological evidence sugge ...
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT
... • Afferent fibers bring informa7on from sensory receptors from – Skeletal muscles (prime movers) – Nearby muscles (synergists, antagonists, fixators) – Tendons, joints and skin affected by the movement ...
... • Afferent fibers bring informa7on from sensory receptors from – Skeletal muscles (prime movers) – Nearby muscles (synergists, antagonists, fixators) – Tendons, joints and skin affected by the movement ...
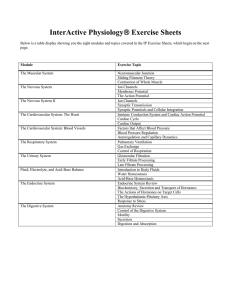
MS Word Version - Interactive Physiology
... a. The opening of voltage-gated K+ channels cause the membrane to _____________________. b. Does K+ move into or out of the cell? __________________ c. If the membrane potential becomes more negative than –70 mV, this is called _________. d. This potential is caused by what characteristic of K+ perm ...
... a. The opening of voltage-gated K+ channels cause the membrane to _____________________. b. Does K+ move into or out of the cell? __________________ c. If the membrane potential becomes more negative than –70 mV, this is called _________. d. This potential is caused by what characteristic of K+ perm ...
The Physics of the Brain
... • Postsynaptic receptors • Single channel transmission • Models of AMPA and NMDA receptors • Analysis of two state models • Realistic models ...
... • Postsynaptic receptors • Single channel transmission • Models of AMPA and NMDA receptors • Analysis of two state models • Realistic models ...
Option E Neurobiology and Behaviour
... • Carries nerve impulses from the sensory to the motor neuron; • Links up with other relay neurons to carry information up and down the spinal cord, eg to the memory centres of the brain. ...
... • Carries nerve impulses from the sensory to the motor neuron; • Links up with other relay neurons to carry information up and down the spinal cord, eg to the memory centres of the brain. ...
Report
... sensitize primary nociceptive neurons. This links methylglyoxal (a glycation agent overproduced in diabetes) to neuropathy and pain, but the actual mechanisms are unknown. To test the possible effect of methylglyoxal on K2P channels, we performed wholecell patch clamp recordings on rat and human TRE ...
... sensitize primary nociceptive neurons. This links methylglyoxal (a glycation agent overproduced in diabetes) to neuropathy and pain, but the actual mechanisms are unknown. To test the possible effect of methylglyoxal on K2P channels, we performed wholecell patch clamp recordings on rat and human TRE ...
Document
... Axons of ganglion cells form optic nerves Optic nerves meet at the optic chiasm (base of the cerebral cortex) Visions from the right visual field go to the left side of the brain and vise versa ...
... Axons of ganglion cells form optic nerves Optic nerves meet at the optic chiasm (base of the cerebral cortex) Visions from the right visual field go to the left side of the brain and vise versa ...
Nervous System Overview
... • Reciprocal inhibition prevents muscles from working against each other – When the biceps contracts which muscle is inhibited? ...
... • Reciprocal inhibition prevents muscles from working against each other – When the biceps contracts which muscle is inhibited? ...
Inquiry into Life, Eleventh Edition
... » More sodium outside than inside » More potassium inside than outside » Presence of nondiffusable ions inside • Resting potential is maintained by – Unequal permeability of membrane » More permeable to potassium than sodium at rest » Membrane tends to “leak” positive charges – Sodium-potassium pump ...
... » More sodium outside than inside » More potassium inside than outside » Presence of nondiffusable ions inside • Resting potential is maintained by – Unequal permeability of membrane » More permeable to potassium than sodium at rest » Membrane tends to “leak” positive charges – Sodium-potassium pump ...
Toxicology of the Nervous System
... Consuming large species such as tuna and swordfish even once a week may be linked to fatigue, headaches, inability to concentrate and hair loss, all symptoms of low-level mercury poisoning. In a study of 123 fish-loving subjects, the researchers found that 89% had blood levels of methylmercury that ...
... Consuming large species such as tuna and swordfish even once a week may be linked to fatigue, headaches, inability to concentrate and hair loss, all symptoms of low-level mercury poisoning. In a study of 123 fish-loving subjects, the researchers found that 89% had blood levels of methylmercury that ...
molecular targets for drug action
... G PROTEIN - trimer, alpha, beta, gamma subunits alpha subunit: GTPase aktivity: GDPGTP, stimulation (Gs) , inhibition (GI) of the effector ability to bind to and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). ...
... G PROTEIN - trimer, alpha, beta, gamma subunits alpha subunit: GTPase aktivity: GDPGTP, stimulation (Gs) , inhibition (GI) of the effector ability to bind to and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). ...
Autonomic Nervous System (Ch. 14)
... 1) Released by all preganglionic axons and all parasympathetic postganglionic axons 2) Cholinergic fibers - ACh-releasing fibers ii. Norepinephrine (NE) 1) Adrenergic fibers: Sympathetic postganglionic axons that release NE 2) Neurotransmitter effects: Excitatory or Inhibitory depending upon recepto ...
... 1) Released by all preganglionic axons and all parasympathetic postganglionic axons 2) Cholinergic fibers - ACh-releasing fibers ii. Norepinephrine (NE) 1) Adrenergic fibers: Sympathetic postganglionic axons that release NE 2) Neurotransmitter effects: Excitatory or Inhibitory depending upon recepto ...
Nervous system and neurons
... transmission is limited and lacks detail. There are inaccuracies. Specialist terminology is either absent or inappropriately used. ...
... transmission is limited and lacks detail. There are inaccuracies. Specialist terminology is either absent or inappropriately used. ...
Particle Size of Beta Amyloid Peptide Aggregates Using Dynamic
... amyloid peptide 1-42 to embryonic chick ciliary ganglion (CG) neurons inhibits potassium-evoked ACh release. The A? aggregates (at a concentration of 10 um) have to be preincubated (aging) for at least 72 hours at 37 C after solubilizing lyophilized peptide monomers in water. This requirement may be ...
... amyloid peptide 1-42 to embryonic chick ciliary ganglion (CG) neurons inhibits potassium-evoked ACh release. The A? aggregates (at a concentration of 10 um) have to be preincubated (aging) for at least 72 hours at 37 C after solubilizing lyophilized peptide monomers in water. This requirement may be ...
End-plate potential

End plate potentials (EPPs) are the depolarizations of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane in the neuromuscular junction. They are called ""end plates"" because the postsynaptic terminals of muscle fibers have a large, saucer-like appearance. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron, vesicles carrying neurotransmitters (mostly acetylcholine) are exocytosed and the contents are released into the neuromuscular junction. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and lead to its depolarization. In the absence of an action potential, acetylcholine vesicles spontaneously leak into the neuromuscular junction and cause very small depolarizations in the postsynaptic membrane. This small response (~0.5mV) is called a miniature end plate potential (MEPP) and is generated by one acetylcholine-containing vesicle. It represents the smallest possible depolarization which can be induced in a muscle.