Peripheral Nervous System
... • If a neuron responds at all, it responds completely • A nerve impulse is conducted whenever a stimulus of threshold intensity or above is applied to an axon • All impulses carried on an axon are the same strength ...
... • If a neuron responds at all, it responds completely • A nerve impulse is conducted whenever a stimulus of threshold intensity or above is applied to an axon • All impulses carried on an axon are the same strength ...
Dynamic timescale
... the neocortex. This is achieved by filtering incoming nerve impulses according to the excitatory or inhibitory status of the synapses. Findings by Jack et al. (1981) inevitably imply an activation barrier, which hinders vesicular docking, opening, and releasing of transmitter molecules at the presyn ...
... the neocortex. This is achieved by filtering incoming nerve impulses according to the excitatory or inhibitory status of the synapses. Findings by Jack et al. (1981) inevitably imply an activation barrier, which hinders vesicular docking, opening, and releasing of transmitter molecules at the presyn ...
Drug Addiction - Perelman School of Medicine at the
... or neuron, that conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body or soma. ...
... or neuron, that conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body or soma. ...
Chapter 12 The Nervous System
... • The Schwann cells line the length of the axon in the PNS. • The myelin sheath is a fatty layer that formed by the Schwann cell that wraps around the axon. • The gap between each Schwann cell is called the node of Ranvier. The axon is exposed in this gap and allows the impulse to jump from one node ...
... • The Schwann cells line the length of the axon in the PNS. • The myelin sheath is a fatty layer that formed by the Schwann cell that wraps around the axon. • The gap between each Schwann cell is called the node of Ranvier. The axon is exposed in this gap and allows the impulse to jump from one node ...
315midterm - Rocky Mountain College
...The benefits of having the impulse travel down the axon the way it does are:
Once the impulse (signal) reaches the end of the axon, it:
...
- it cannot be seen or touched
- quicker and quieter
- quicker and uses less energy
- releases more vesicles which ‘open’ the + or - ...
Nervous System - Napa Valley College
... a great enough stimulation the channels won’t open. The level of the action potential is always the same. The direction is always one way down the axon. The sodium channels are inactivated for awhile after the action potential passes = refractory period. ...
... a great enough stimulation the channels won’t open. The level of the action potential is always the same. The direction is always one way down the axon. The sodium channels are inactivated for awhile after the action potential passes = refractory period. ...
Questions on Muscular System
... - muscle contraction is vital for maintaining normal body temperature - without nerve stimulation, no muscle contraction occur - once begun, the action potential is unstoppable - one nerve impulse produce only one contraction - muscle cell relaxes until stimulated by another round of ACh. - all-or-n ...
... - muscle contraction is vital for maintaining normal body temperature - without nerve stimulation, no muscle contraction occur - once begun, the action potential is unstoppable - one nerve impulse produce only one contraction - muscle cell relaxes until stimulated by another round of ACh. - all-or-n ...
Biological of Behavior
... The neuron that sends a signal across the gap is called the presynaptic neuron. The neuron that receives the signal is called the postsynaptic neuron. ...
... The neuron that sends a signal across the gap is called the presynaptic neuron. The neuron that receives the signal is called the postsynaptic neuron. ...
Chapters 11: Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous
... • _____ _______ – where a neuron meets its target cell (in this case another neuron) is called a neuronal synapse - electrical (gap junctions) – breathing, cardiac & SMC - ____________ – most synapses – can occur between an axon of one neuron and another part of another neuron (dendrite, soma, axon) ...
... • _____ _______ – where a neuron meets its target cell (in this case another neuron) is called a neuronal synapse - electrical (gap junctions) – breathing, cardiac & SMC - ____________ – most synapses – can occur between an axon of one neuron and another part of another neuron (dendrite, soma, axon) ...
Lecture notes - University of Sussex
... •A spike is generated when the membrane potential is greater than its threshold ...
... •A spike is generated when the membrane potential is greater than its threshold ...
Chapter 9 Senses - msubillings.edu
... it’s attachable state → it is then reattached to the opsin (this requires ATP). In the dark the rods have open ligandgated sodium (Na + ) channels (bound ligand is cyclic quanosine monophosphate (cGMP)) that allow a continual flow of sodium into the cell, at the same time the sodium-potassium-pump ( ...
... it’s attachable state → it is then reattached to the opsin (this requires ATP). In the dark the rods have open ligandgated sodium (Na + ) channels (bound ligand is cyclic quanosine monophosphate (cGMP)) that allow a continual flow of sodium into the cell, at the same time the sodium-potassium-pump ( ...
Our brain is made of so many neurons, which communicate each
... In this project, we will elucidate the regulatory mechanisms for synaptic transmission and clarify the etiology of neuropsychiatric disorders by analyzing 1) a novel epilepsy-related ligand/receptor, “LGI1/ADAMs”, and 2) important regulators of various cell functions, “palmitoylating enzymes”, both ...
... In this project, we will elucidate the regulatory mechanisms for synaptic transmission and clarify the etiology of neuropsychiatric disorders by analyzing 1) a novel epilepsy-related ligand/receptor, “LGI1/ADAMs”, and 2) important regulators of various cell functions, “palmitoylating enzymes”, both ...
Key - Cornell
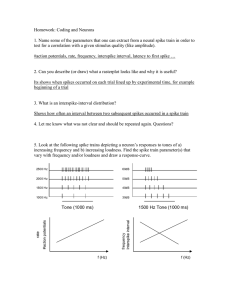
... 1. Name some of the parameters that one can extract from a neural spike train in order to test for a correlation with a given stimulus quality (like amplitude). #action potentials, rate, frequency, interspike interval, latency to first spike … ...
... 1. Name some of the parameters that one can extract from a neural spike train in order to test for a correlation with a given stimulus quality (like amplitude). #action potentials, rate, frequency, interspike interval, latency to first spike … ...
Biopsychology Revision
... • Synaptic connections can be excitatory or inhibitory – the difference lies in the action of the neurotransmitter at the postsynaptic receptor • Excitatory - they make it more likely the next neuron will fire (such as acetylcholine) • Inhibitory - they make it less likely the next neuron will fire ...
... • Synaptic connections can be excitatory or inhibitory – the difference lies in the action of the neurotransmitter at the postsynaptic receptor • Excitatory - they make it more likely the next neuron will fire (such as acetylcholine) • Inhibitory - they make it less likely the next neuron will fire ...
Nervous System ppt
... Comparing the results, what would you say about each situation? Why is this the case? Some signals are transmitted through a series of connected neurons, and some signals are transmitted through a really long neuron (long axon) Which animal would you think would need really long axons to transmit si ...
... Comparing the results, what would you say about each situation? Why is this the case? Some signals are transmitted through a series of connected neurons, and some signals are transmitted through a really long neuron (long axon) Which animal would you think would need really long axons to transmit si ...
Supplement to: Modulation of Intracortical Synaptic Potentials by
... distinct types: graded and action potential dependent. Graded transmission does not require the generation of action potentials, but rather operates through tonic synaptic vesicle release, the rate of which is modified by changes in the membrane potential of the presynaptic terminal (for review see5 ...
... distinct types: graded and action potential dependent. Graded transmission does not require the generation of action potentials, but rather operates through tonic synaptic vesicle release, the rate of which is modified by changes in the membrane potential of the presynaptic terminal (for review see5 ...
Reflex Arc - WordPress.com
... Reflexes are automatic - don’t have to think about them Message doesn’t have to go to brain for response to occur, sent directly to spinal cord Since there is no processing, reactions can be very quick ...
... Reflexes are automatic - don’t have to think about them Message doesn’t have to go to brain for response to occur, sent directly to spinal cord Since there is no processing, reactions can be very quick ...
IONIC BASES OF THE RESTING MEMBRANE POTENTIAL
... of something that may be intuitively obvious: namely, that solutions cannot be charged. Thus, both the intracellular and extracellular environments must be electrically neutral. Clearly, this contradicts something that we all take for granted, namely, that the resting membrane potential arises from ...
... of something that may be intuitively obvious: namely, that solutions cannot be charged. Thus, both the intracellular and extracellular environments must be electrically neutral. Clearly, this contradicts something that we all take for granted, namely, that the resting membrane potential arises from ...
Supplement: Modulation of Intracortical Synaptic Potentials by
... distinct types: graded and action potential dependent. Graded transmission does not require the generation of action potentials, but rather operates through tonic synaptic vesicle release, the rate of which is modified by changes in the membrane potential of the presynaptic terminal (for review see5 ...
... distinct types: graded and action potential dependent. Graded transmission does not require the generation of action potentials, but rather operates through tonic synaptic vesicle release, the rate of which is modified by changes in the membrane potential of the presynaptic terminal (for review see5 ...
Chater 2 - Study Guide
... chemical messenger that triggers muscle contractions. automatic response to sensory input. neural network. junction between a sending neuron and a receiving neuron. neural cable containing many axons. ...
... chemical messenger that triggers muscle contractions. automatic response to sensory input. neural network. junction between a sending neuron and a receiving neuron. neural cable containing many axons. ...
Nervous_System__Ch_7__S2015
... Autonomic system regulates the activity of cardiac and smooth muscles and glands. This system covers all motor output to all the organs and blood vessels of the body. Broken down to two divisions, both use two neurons and one ganglion. – Sympathetic division brings about “fight or flight” responses; ...
... Autonomic system regulates the activity of cardiac and smooth muscles and glands. This system covers all motor output to all the organs and blood vessels of the body. Broken down to two divisions, both use two neurons and one ganglion. – Sympathetic division brings about “fight or flight” responses; ...
Effects of Warm Up and Cool Down
... investigate and feed back to the group about the following bone conditions: – Osteoporosis and how this affects physical activity – Growth plate and how this affects physical activity – Osteoarthritis and how this affects physical ...
... investigate and feed back to the group about the following bone conditions: – Osteoporosis and how this affects physical activity – Growth plate and how this affects physical activity – Osteoarthritis and how this affects physical ...
1. A biological psychologist would be more likely to study
... chemical messenger that triggers muscle contractions. automatic response to sensory input. neural network. junction between a sending neuron and a receiving neuron. neural cable containing many axons. ...
... chemical messenger that triggers muscle contractions. automatic response to sensory input. neural network. junction between a sending neuron and a receiving neuron. neural cable containing many axons. ...
End-plate potential

End plate potentials (EPPs) are the depolarizations of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane in the neuromuscular junction. They are called ""end plates"" because the postsynaptic terminals of muscle fibers have a large, saucer-like appearance. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron, vesicles carrying neurotransmitters (mostly acetylcholine) are exocytosed and the contents are released into the neuromuscular junction. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and lead to its depolarization. In the absence of an action potential, acetylcholine vesicles spontaneously leak into the neuromuscular junction and cause very small depolarizations in the postsynaptic membrane. This small response (~0.5mV) is called a miniature end plate potential (MEPP) and is generated by one acetylcholine-containing vesicle. It represents the smallest possible depolarization which can be induced in a muscle.