Central nervous system
... • If the action potential (nerve impulse) starts, it is propagated over the entire axon • Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in • Sodium and potassium are actively transported back to their original positions = repolarization • Membrane is at rest again Copyright © 2003 Pea ...
... • If the action potential (nerve impulse) starts, it is propagated over the entire axon • Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in • Sodium and potassium are actively transported back to their original positions = repolarization • Membrane is at rest again Copyright © 2003 Pea ...
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Methods of study: Voltage-clamp and Current-clamp, recording of single ion channels (patch-clamp). Ligandregulated channels and voltage-regulated channels. Regulation of membrane ionic permeability. Creation and maintenance of ion gradients by ion pumps. Modulation of ion channels. Combinations of i ...
... Methods of study: Voltage-clamp and Current-clamp, recording of single ion channels (patch-clamp). Ligandregulated channels and voltage-regulated channels. Regulation of membrane ionic permeability. Creation and maintenance of ion gradients by ion pumps. Modulation of ion channels. Combinations of i ...
Exercise 5: Synaptic Integration - הפקולטה למדעי הבריאות
... The EPSP occuring first will now be closest to the cell soma. Will this sequence of EPSPs cause an action potential to initiate? ...
... The EPSP occuring first will now be closest to the cell soma. Will this sequence of EPSPs cause an action potential to initiate? ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... – Transmits neural information that arises in the brainstem with axons descending into the spinal cord with many of fibers not crossing over to the opposite side of the body – Chiefly found in the reticular formation of the pons and medulla. – Primarily associated with postural control and muscle ...
... – Transmits neural information that arises in the brainstem with axons descending into the spinal cord with many of fibers not crossing over to the opposite side of the body – Chiefly found in the reticular formation of the pons and medulla. – Primarily associated with postural control and muscle ...
Nervous System
... An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated by the axon of another neuron or by the environment. Na+ pores open and the flood of Na+ ions makes the inside positive. This reversal of charges, from negative to positive is called a nerve impulse, or an action potential. ...
... An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated by the axon of another neuron or by the environment. Na+ pores open and the flood of Na+ ions makes the inside positive. This reversal of charges, from negative to positive is called a nerve impulse, or an action potential. ...
nervous system 2 notes - Hicksville Public Schools
... travel to the spinal cord and back to muscles. Movement occurs without the use of the brain. The brain gets the message a split second after the response. ...
... travel to the spinal cord and back to muscles. Movement occurs without the use of the brain. The brain gets the message a split second after the response. ...
Lecture 2 Powerpoint file
... • Action Potential occurs when voltagegated channels open • Voltage-Gated channels are clustered where axon and cell body meet (axon hillock) and along the axon ...
... • Action Potential occurs when voltagegated channels open • Voltage-Gated channels are clustered where axon and cell body meet (axon hillock) and along the axon ...
primary motor Cortex
... stimulus dependent, action potentials are always the same size. If a stimulus is strong enough to depolarize the membrane to a critical level referred to as threshold , then the membrane continues to depolarize on its own, independent of the stimulus. Typically, threshold is approximately 20 mV less ...
... stimulus dependent, action potentials are always the same size. If a stimulus is strong enough to depolarize the membrane to a critical level referred to as threshold , then the membrane continues to depolarize on its own, independent of the stimulus. Typically, threshold is approximately 20 mV less ...
Hearing and Equilibrium Human Ear Major questions Anatomy of
... membrane--> stereocilia flex back and forth in or against tectorial membrane • Mechanical opening of ion channels ...
... membrane--> stereocilia flex back and forth in or against tectorial membrane • Mechanical opening of ion channels ...
Control_Systems11
... small space between the two neurons is called the Synaptic Cleft Neurotransmitters: chemical signals that transmit an impulse across the synapse to another cell ...
... small space between the two neurons is called the Synaptic Cleft Neurotransmitters: chemical signals that transmit an impulse across the synapse to another cell ...
Unit 1 – Nervous and Endocrine System
... Motor Neuron – relay info to effectors (muscles, glands); cell body located in CNS; axons in PNS Sensory Neuron – relay info about environment to CNS (brain) Interneuron – connect neurons; only found in CNS ...
... Motor Neuron – relay info to effectors (muscles, glands); cell body located in CNS; axons in PNS Sensory Neuron – relay info about environment to CNS (brain) Interneuron – connect neurons; only found in CNS ...
Biology 621 - Chapter 12 Midterm Exam Review
... 29. Within the spinal cord, motor and sensory neurons are connected byinterneurons 30. The 2 divisions of the autonomic nervous system sympathetic ¶sympathetic 31 The above two divisions have a(n) antagonistic effects on the organs they control. 32What two ions are moved across a neuron’s membra ...
... 29. Within the spinal cord, motor and sensory neurons are connected byinterneurons 30. The 2 divisions of the autonomic nervous system sympathetic ¶sympathetic 31 The above two divisions have a(n) antagonistic effects on the organs they control. 32What two ions are moved across a neuron’s membra ...
Review 3 ____ 1. The cells that provide structural support and
... 10. Leonard's mother became dehydrated during a recent illness, and the levels of sodium in her body were significantly reduced. If enough sodium was lost you might expect that a. her nervous system would become highly activated and action potentials would be generated continuously b. fewer action p ...
... 10. Leonard's mother became dehydrated during a recent illness, and the levels of sodium in her body were significantly reduced. If enough sodium was lost you might expect that a. her nervous system would become highly activated and action potentials would be generated continuously b. fewer action p ...
TABLE OF CONTENTS - Test Bank, Manual Solution, Solution Manual
... reversal of the usual membrane polarization. Occurs when depolarization meets or goes beyond the threshold of excitation. The Molecular Basis of the Action Potential a. Principles of action potential: At the start, sodium ions are mostly outside the neuron and potassium ions are mostly inside. When ...
... reversal of the usual membrane polarization. Occurs when depolarization meets or goes beyond the threshold of excitation. The Molecular Basis of the Action Potential a. Principles of action potential: At the start, sodium ions are mostly outside the neuron and potassium ions are mostly inside. When ...
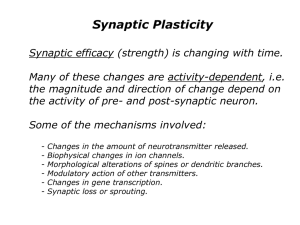
LTP
... Synaptic efficacy (strength) is changing with time. Many of these changes are activity-dependent, i.e. the magnitude and direction of change depend on the activity of pre- and post-synaptic neuron. Some of the mechanisms involved: ...
... Synaptic efficacy (strength) is changing with time. Many of these changes are activity-dependent, i.e. the magnitude and direction of change depend on the activity of pre- and post-synaptic neuron. Some of the mechanisms involved: ...
2013 Action Potential Modeling in PYTHON
... a result, the diffusion force will eventually be opposed and balanced by an electrical force[1]. At electrochemical equilibrium, this is called the resting membrane potential of the cell. This membrane potential represents a form of stored energy, and can be used to do work. Excitable cells such as ...
... a result, the diffusion force will eventually be opposed and balanced by an electrical force[1]. At electrochemical equilibrium, this is called the resting membrane potential of the cell. This membrane potential represents a form of stored energy, and can be used to do work. Excitable cells such as ...
Neurotransmission: “Muscle Messages”
... • Ask students “How can these neurons send messages to each other and to the muscle cell?” • Let students hypothesize as to what structures might be involved in neurotransmission, which is the process of communication between nerve cells and other cells in the body. Explore (10 minutes) Neurotransmi ...
... • Ask students “How can these neurons send messages to each other and to the muscle cell?” • Let students hypothesize as to what structures might be involved in neurotransmission, which is the process of communication between nerve cells and other cells in the body. Explore (10 minutes) Neurotransmi ...
unit 2 – nervous system / senses - Greater Atlanta Christian Schools
... -“polarized” b/c of electrical charge difference that exists on each side of the cell membrane - inside cell: -ve ; high amt. of K+ - outside cell: +ve; high amt of Na+ - cell membrane permeability K+ > Na+ - Na+/ K+ exchange pump maintains RMP 3. Stimulated Neuron (action potential) a. nerve (e ...
... -“polarized” b/c of electrical charge difference that exists on each side of the cell membrane - inside cell: -ve ; high amt. of K+ - outside cell: +ve; high amt of Na+ - cell membrane permeability K+ > Na+ - Na+/ K+ exchange pump maintains RMP 3. Stimulated Neuron (action potential) a. nerve (e ...
to get the file
... There are electrical (rare) and chemical synapses (very common) At an electrical synapse we have direct electrical coupling (e.g., heart muscle cells). At a chemical synapse a chemical substance (transmitter) is used to transport the signal. Electrical synapses operate bi-directional and are extreme ...
... There are electrical (rare) and chemical synapses (very common) At an electrical synapse we have direct electrical coupling (e.g., heart muscle cells). At a chemical synapse a chemical substance (transmitter) is used to transport the signal. Electrical synapses operate bi-directional and are extreme ...
NOB Ch 6 Answers - MCC Year 12 Biology
... What is the response to the message received? When a fall in blood pressure is detected, the message from pressure receptors in the arterial walls is conveyed to the central nervous system (CNS). The response is an increase in autonomic nerve impulses from the CNS that lead to the contraction of inv ...
... What is the response to the message received? When a fall in blood pressure is detected, the message from pressure receptors in the arterial walls is conveyed to the central nervous system (CNS). The response is an increase in autonomic nerve impulses from the CNS that lead to the contraction of inv ...
Nervous System Intro
... aggregations of myelinated axons from many neurons. • The lipid part of myelin imparts the white appearance. ...
... aggregations of myelinated axons from many neurons. • The lipid part of myelin imparts the white appearance. ...
Biology 621 - Chapter 12 Midterm Exam Review
... called the involuntary nervous system. ___ 24. ____ neurons carry impulses from receptors to the spinal cord. 25. What are the two major division of the peripheral nervous system? ____&___ 26 Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the brain and spinal cord.____ 27.The __ is the basic functio ...
... called the involuntary nervous system. ___ 24. ____ neurons carry impulses from receptors to the spinal cord. 25. What are the two major division of the peripheral nervous system? ____&___ 26 Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the brain and spinal cord.____ 27.The __ is the basic functio ...
Origin of Long- Term Memory - Neuromarketing Business Association
... It’s important to remember, that LTP is not a mechanism, but a outcome of the increased activity in two neurons, that result of a increase of APMA receptors, strengthen the synaptic connection, which allows the low frequent action potential a greater depolarization potential - This is the foundation ...
... It’s important to remember, that LTP is not a mechanism, but a outcome of the increased activity in two neurons, that result of a increase of APMA receptors, strengthen the synaptic connection, which allows the low frequent action potential a greater depolarization potential - This is the foundation ...
W7 Lecture
... Panel 4: A and B are stimulated enough to cause a suprathreshold graded depolarization, so an action potential results. Panel 5: Neuron C causes a graded hyperpolarization; A and C effects add, cancel each other out. ...
... Panel 4: A and B are stimulated enough to cause a suprathreshold graded depolarization, so an action potential results. Panel 5: Neuron C causes a graded hyperpolarization; A and C effects add, cancel each other out. ...
Nervous System - WordPress.com
... c) declines in amplitude as it moves along the axon d) results in transient reversal of the concentration (?electrical) gradient of Na+ across the cell membrane e) is not associated with any net movement of Na+ of K+ across the cell membrane ...
... c) declines in amplitude as it moves along the axon d) results in transient reversal of the concentration (?electrical) gradient of Na+ across the cell membrane e) is not associated with any net movement of Na+ of K+ across the cell membrane ...
End-plate potential

End plate potentials (EPPs) are the depolarizations of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane in the neuromuscular junction. They are called ""end plates"" because the postsynaptic terminals of muscle fibers have a large, saucer-like appearance. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron, vesicles carrying neurotransmitters (mostly acetylcholine) are exocytosed and the contents are released into the neuromuscular junction. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and lead to its depolarization. In the absence of an action potential, acetylcholine vesicles spontaneously leak into the neuromuscular junction and cause very small depolarizations in the postsynaptic membrane. This small response (~0.5mV) is called a miniature end plate potential (MEPP) and is generated by one acetylcholine-containing vesicle. It represents the smallest possible depolarization which can be induced in a muscle.