intro to psych brain and behavior
... An action potential (nerve impulse) sweeps down the axon Ion channels open and sodium ions rush in ...
... An action potential (nerve impulse) sweeps down the axon Ion channels open and sodium ions rush in ...
Structure of a Neuron Transmission of “Information” Nerve Impulse
... – Peripheral nerves (cranial and spinal) – Ganglia ...
... – Peripheral nerves (cranial and spinal) – Ganglia ...
File
... information to the cell body. • Your arm represents the "axon" taking information away from the cell body. • Your jumper/shirt represents the myelin sheath that that facilitates the transmission of nerve ...
... information to the cell body. • Your arm represents the "axon" taking information away from the cell body. • Your jumper/shirt represents the myelin sheath that that facilitates the transmission of nerve ...
The Nervous System
... The Nervous System • Transmission of nerve impulse – Chemical changes across the membrane of neuron. – Membrane of a unstimulated neuron is polarized. • Difference in electrical charges between the outside and inside of the membrane. • Inside is negative; outside is positive. ...
... The Nervous System • Transmission of nerve impulse – Chemical changes across the membrane of neuron. – Membrane of a unstimulated neuron is polarized. • Difference in electrical charges between the outside and inside of the membrane. • Inside is negative; outside is positive. ...
Research Proposal: Nivedita Chatterjee
... glia-like cells. This work will also use existing mutant strains to study genes involved in neuron-glia interactions during nervous system development. So far, there exists little information as to how the activities of individual neurons might correlate with particular behavioral patterns. In colla ...
... glia-like cells. This work will also use existing mutant strains to study genes involved in neuron-glia interactions during nervous system development. So far, there exists little information as to how the activities of individual neurons might correlate with particular behavioral patterns. In colla ...
chapter38
... to a stimulus. A stimulus has to be of enough strength to cause an action potential to occur. The critical point at which a stimulus causes an action potential is called the threshold. ...
... to a stimulus. A stimulus has to be of enough strength to cause an action potential to occur. The critical point at which a stimulus causes an action potential is called the threshold. ...
The Nervous System and the Brain
... The somatic nervous system connects the CNS to sensory receptors and muscles. Neurons in the somatic nervous system transmit messages about sights, sounds, smell, temperature, and body position to the CNS. It also transmits information from the brain to produce purposeful motor movements. The autono ...
... The somatic nervous system connects the CNS to sensory receptors and muscles. Neurons in the somatic nervous system transmit messages about sights, sounds, smell, temperature, and body position to the CNS. It also transmits information from the brain to produce purposeful motor movements. The autono ...
2.2 Electrical Communication Study Guide by Hisrich
... 2.2.i How can biomedical professionals help treat, cure and improve the quality of life of those suffering from nervous system disorders? The main person that treats neurological disorders is a Neurologist (one who studies nerves). That’s a special kind of doctor that specializes in the nervous syst ...
... 2.2.i How can biomedical professionals help treat, cure and improve the quality of life of those suffering from nervous system disorders? The main person that treats neurological disorders is a Neurologist (one who studies nerves). That’s a special kind of doctor that specializes in the nervous syst ...
Chapter 10 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
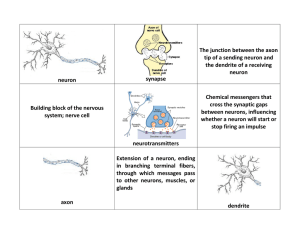
... them to the cell body • Axon – conducts impulses away from the nerve cell • Terminal end fibers – lead the nervous impulse away from the axon and toward the synapse. ...
... them to the cell body • Axon – conducts impulses away from the nerve cell • Terminal end fibers – lead the nervous impulse away from the axon and toward the synapse. ...
PSYC465 - neuroanatomy
... blood vessels. Cells in the walls of cerebral blood vessels are tightly packed. This provides a barrier for the passage of some large-molecules and proteins into the brain. Not all large molecules are impeded (e.g., glucose). Sex hormones readily pass through to certain brain areas where the BBB is ...
... blood vessels. Cells in the walls of cerebral blood vessels are tightly packed. This provides a barrier for the passage of some large-molecules and proteins into the brain. Not all large molecules are impeded (e.g., glucose). Sex hormones readily pass through to certain brain areas where the BBB is ...
Brain Powerpoint
... called norepinephrine – One of its major functions is to stimulate the adrenal glands to release a hormone called epinephrine – The resulting hormone rush is more commonly known as adrenaline ...
... called norepinephrine – One of its major functions is to stimulate the adrenal glands to release a hormone called epinephrine – The resulting hormone rush is more commonly known as adrenaline ...
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY (7th Edition in Modules) David Myers
... trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
... trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
The Nervous System - Marshall Middle
... responsible for the body functions which are not under conscious control like the heartbeat or the digestive system. The smooth operation of the peripheral nervous system is achieved by dividing it into sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. These are opposing actions and check on each other to pr ...
... responsible for the body functions which are not under conscious control like the heartbeat or the digestive system. The smooth operation of the peripheral nervous system is achieved by dividing it into sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. These are opposing actions and check on each other to pr ...
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending
... determine whether we should emotionally react to sensory stimuli, especially with rage or fear; processes emotional memories ...
... determine whether we should emotionally react to sensory stimuli, especially with rage or fear; processes emotional memories ...
14.1-NervousMusculo-Skeletal-System
... The gap between the neurons is called the synapse. This is where an electrical signal is passed from an axon of one neuron to a dendrite of another neuron. The signals are passed via neurotransmitters (serotonin, for example), which once released into the synapse, they stimulate a new electrical sig ...
... The gap between the neurons is called the synapse. This is where an electrical signal is passed from an axon of one neuron to a dendrite of another neuron. The signals are passed via neurotransmitters (serotonin, for example), which once released into the synapse, they stimulate a new electrical sig ...
Biological Psychology Modules 3 & 4
... • visual info – Auditory cortex • auditory info – Somatosensory cortex • info from skin • Association cortex – involved in complex cognitive tasks associating words with images • Broca’s area (aphasia) • Wernicke’s area (aphasia) ...
... • visual info – Auditory cortex • auditory info – Somatosensory cortex • info from skin • Association cortex – involved in complex cognitive tasks associating words with images • Broca’s area (aphasia) • Wernicke’s area (aphasia) ...
Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
... medial epicondyle of the humerus will produce strong tingling sensations along the forearm and hand. (a) Radial (b) Median (c) Phrenic (d) Femoral (e) Ulnar ...
... medial epicondyle of the humerus will produce strong tingling sensations along the forearm and hand. (a) Radial (b) Median (c) Phrenic (d) Femoral (e) Ulnar ...
the nervous system - Miss Gleason`s Science
... Zoloft is part of a class of drugs called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, or SSRIs for short. SSRIs act on a specific chemical within the brain known as serotonin. This is one of several chemicals used to send messages from one nerve cell to another. ...
... Zoloft is part of a class of drugs called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, or SSRIs for short. SSRIs act on a specific chemical within the brain known as serotonin. This is one of several chemicals used to send messages from one nerve cell to another. ...
Document
... cause cells to lose the ability to respond to it -This process is called habituation -The cell decreases the number of receptors because there is an abundance of neurotransmitters ...
... cause cells to lose the ability to respond to it -This process is called habituation -The cell decreases the number of receptors because there is an abundance of neurotransmitters ...
3.E.2 Nervous System - kromko
... Nervous System (PNS). The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord. The PNS consists of all nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord. ...
... Nervous System (PNS). The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord. The PNS consists of all nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord. ...
Endocrine System
... – Outer layer of the forebrain; gives you the ability to learn and store complex and abstract information. ...
... – Outer layer of the forebrain; gives you the ability to learn and store complex and abstract information. ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... A subcortical structure that regulates body temperature, hunger, thirst and sexual behavior Pituitary Gland The “master gland”. Secretes stimulating hormones to all but two of the endocrine glands. Without stimulating hormones the rest of the endocrine system could not function. Limbic System A grou ...
... A subcortical structure that regulates body temperature, hunger, thirst and sexual behavior Pituitary Gland The “master gland”. Secretes stimulating hormones to all but two of the endocrine glands. Without stimulating hormones the rest of the endocrine system could not function. Limbic System A grou ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.