PSB 4002 - Developmental Psychobiology Laboratory
... but it is still no larger than a dot, much much smaller that the period at the end of this sentence. • Over about 277 days of gestation, this one fertilized cell will become trillions of cells, all organized into the various glands, tissues, organs, etc. that constitute our brain/body system. ...
... but it is still no larger than a dot, much much smaller that the period at the end of this sentence. • Over about 277 days of gestation, this one fertilized cell will become trillions of cells, all organized into the various glands, tissues, organs, etc. that constitute our brain/body system. ...
Printable version
... 5. neurons can be classified by their structure a. multipolar - have 3+ processes; the most common type; some have no axon b. bipolar - have 2 processes; rare in adults, though found in the eye & nose c. unipolar - have 1 process 6. neurons can be classified by their function a. sensory (afferent) n ...
... 5. neurons can be classified by their structure a. multipolar - have 3+ processes; the most common type; some have no axon b. bipolar - have 2 processes; rare in adults, though found in the eye & nose c. unipolar - have 1 process 6. neurons can be classified by their function a. sensory (afferent) n ...
The Nervous System 2013
... The nervous system of the human being is responsible for sending, receiving, and processing nerve impulses throughout the body. All the organs and muscles inside your body rely upon these nerve impulses to function. It could be considered as the master control unit inside your body. Sense organs pro ...
... The nervous system of the human being is responsible for sending, receiving, and processing nerve impulses throughout the body. All the organs and muscles inside your body rely upon these nerve impulses to function. It could be considered as the master control unit inside your body. Sense organs pro ...
THERIGHTBRAINPOWERPOINT
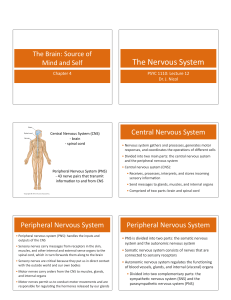
... parts of the nervous system are the Central Nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS). The CNS is the brain and the spinal cord. The PNS is the cranial and spinal nerves . The PNS contains both sensory and motor neurons. Motor neurons in the PNS are divided into two systems. T ...
... parts of the nervous system are the Central Nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS). The CNS is the brain and the spinal cord. The PNS is the cranial and spinal nerves . The PNS contains both sensory and motor neurons. Motor neurons in the PNS are divided into two systems. T ...
Supporting Cells of the Nervous System
... Schwann cells structure: • They do all this by making a myelin sheath around many of the neuron processes in the PNS. They wrap themselves very tightly around the process of a neuron. • The cytoplasm and nucleus is squeezed to the surface of the wrapping called the neurolemma. • The layer that lies ...
... Schwann cells structure: • They do all this by making a myelin sheath around many of the neuron processes in the PNS. They wrap themselves very tightly around the process of a neuron. • The cytoplasm and nucleus is squeezed to the surface of the wrapping called the neurolemma. • The layer that lies ...
The Nervous System
... • Peripheral nervous system (PNS): handles the inputs and outputs of the CNS • Sensory nerves carry messages from receptors in the skin, muscles, and other internal and external sense organs to the spina ...
... • Peripheral nervous system (PNS): handles the inputs and outputs of the CNS • Sensory nerves carry messages from receptors in the skin, muscles, and other internal and external sense organs to the spina ...
B- Parietal
... C- Between Neurons– 40 pts. (the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of another) ...
... C- Between Neurons– 40 pts. (the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of another) ...
The Brain - Science Leadership Academy
... • The cerebrum is responsible for 85% of the weight of the brain. ...
... • The cerebrum is responsible for 85% of the weight of the brain. ...
Reflex Arc - Cloudfront.net
... cord, nerves, and sense organs Allows communication between different parts of the body Allows you to sense (see, hear, etc.), comprehend, AND respond (usually muscle) to the environment ...
... cord, nerves, and sense organs Allows communication between different parts of the body Allows you to sense (see, hear, etc.), comprehend, AND respond (usually muscle) to the environment ...
the nervous system - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... processes that extend from opposite sides of the cell body and appear only in the inner ear, olfactory epithelium of the nose and the retina. Unipolar: one short process that emerges from the body and divides like an inverted T into two long branches. ...
... processes that extend from opposite sides of the cell body and appear only in the inner ear, olfactory epithelium of the nose and the retina. Unipolar: one short process that emerges from the body and divides like an inverted T into two long branches. ...
Biopsychology The Nervous System
... – while the mother always passes on an X chromosome to determine the gender of the fetus; if the father passes on an X chromosome the fetus is genetically female and if he passes on a Y chromosome the fetus is genetically male genetic disorders can also occur during development: – Down’s syndrom ...
... – while the mother always passes on an X chromosome to determine the gender of the fetus; if the father passes on an X chromosome the fetus is genetically female and if he passes on a Y chromosome the fetus is genetically male genetic disorders can also occur during development: – Down’s syndrom ...
Unit10 Nervous Wk 1
... There are two main control systems (communication systems) in your body. 1. Nervous system – a system of electrical impulses organized into 2 main sections 2. Endocrine system – a system of glands that release signalling chemicals, or hormones ...
... There are two main control systems (communication systems) in your body. 1. Nervous system – a system of electrical impulses organized into 2 main sections 2. Endocrine system – a system of glands that release signalling chemicals, or hormones ...
Biology of the Mind Powerpoint
... The Nerves Nerves consist of neural “cables” containing many axons. They are part of the peripheral nervous system and connect muscles, glands, and sense organs to the central nervous system. ...
... The Nerves Nerves consist of neural “cables” containing many axons. They are part of the peripheral nervous system and connect muscles, glands, and sense organs to the central nervous system. ...
Biology of Mind
... The Nerves Nerves consist of neural “cables” containing many axons. They are part of the peripheral nervous system and connect muscles, glands, and sense organs to the central nervous system. ...
... The Nerves Nerves consist of neural “cables” containing many axons. They are part of the peripheral nervous system and connect muscles, glands, and sense organs to the central nervous system. ...
Activity Overview - Teacher Enrichment Initiatives
... The brain, like all organs of the body, is made up of cells. The brain is made of many types of cells. In Activity 1C, students learned about three types of cells found in the nervous system. These cells are – neurons, glial cells, and microglial cells (a specialized type of macrophage cell). In thi ...
... The brain, like all organs of the body, is made up of cells. The brain is made of many types of cells. In Activity 1C, students learned about three types of cells found in the nervous system. These cells are – neurons, glial cells, and microglial cells (a specialized type of macrophage cell). In thi ...
Guided Notes for the Nervous System-
... 9. Neurons, also called nerve cells, are highly specialized to transmit messages (nerve impulses) from one part of the body to another. ...
... 9. Neurons, also called nerve cells, are highly specialized to transmit messages (nerve impulses) from one part of the body to another. ...
Introduction to Neural Networks
... • Connectionism refers to a computer modeling approach to computation that is loosely based upon the architecture of the brain. • Many different models: – Multiple, individual “nodes” or “units” that operate at the same time (in parallel) – A network that connects the nodes together – Information is ...
... • Connectionism refers to a computer modeling approach to computation that is loosely based upon the architecture of the brain. • Many different models: – Multiple, individual “nodes” or “units” that operate at the same time (in parallel) – A network that connects the nodes together – Information is ...
STUDY GUIDE: UNIT III – BIOLOGICAL BASES OF BEHAVIOR AP
... 13-1: What do split brains reveal about functions of our two brain hemispheres? Corpus callosum & split brains Right-left differences in the intact brain 13-2: The biology of Consciousness Cognitive neuroscience Dual processing ...
... 13-1: What do split brains reveal about functions of our two brain hemispheres? Corpus callosum & split brains Right-left differences in the intact brain 13-2: The biology of Consciousness Cognitive neuroscience Dual processing ...
The Nervous System
... Neuron: a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system. Sensory neurons: neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord. Interneurons: neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory ...
... Neuron: a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system. Sensory neurons: neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord. Interneurons: neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory ...
Nervous System Disorders and Homeostatic Imbalances
... • A syndrome marked by muscular weakness and atrophy with spasticity and hyperflexion due to degeneration of the motor neurons of the spinal cord, medulla, and cortex • A degenerative disease • No known cure ...
... • A syndrome marked by muscular weakness and atrophy with spasticity and hyperflexion due to degeneration of the motor neurons of the spinal cord, medulla, and cortex • A degenerative disease • No known cure ...
PET (positron emission tomography): measures the different levels
... Neuron: a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system. Sensory neurons: neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord. Interneurons: neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory ...
... Neuron: a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system. Sensory neurons: neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord. Interneurons: neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory ...
White blood cells play important roles in protecting us from infections
... 4. Anticipated effects and future applications of research ...
... 4. Anticipated effects and future applications of research ...
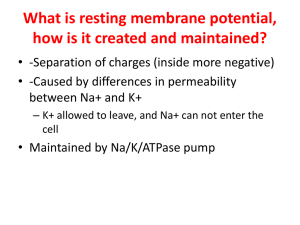
What is resting membrane potential, how is it created and maintained?
... action potentials are only generated at the nodes of Ranvier, rather than every adjacent part of the axon. • Occurs because myelin insulates the current and does not allow it to leak out ...
... action potentials are only generated at the nodes of Ranvier, rather than every adjacent part of the axon. • Occurs because myelin insulates the current and does not allow it to leak out ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.