Introduction to the Clinically Oriented Anatomy
... regional and systemic approaches to studying anatomy and stresses clinical application. Clinical anatomy often involves inverting or reversing the thought process. For example, instead of thinking, “The . . . nerve provides innervation to this area of skin,” clinical anatomy asks, “Numbness in this ...
... regional and systemic approaches to studying anatomy and stresses clinical application. Clinical anatomy often involves inverting or reversing the thought process. For example, instead of thinking, “The . . . nerve provides innervation to this area of skin,” clinical anatomy asks, “Numbness in this ...
Nerve activates contraction
... in the human brain: 100 billion Average number of neurons in an octopus brain: 300 billion Rate of neuron growth during development of a fetus (in the womb): 250,000 neurons/minute Diameter of a neuron: 4 to 100 microns Longest axon of a neuron: around 15 feet (Giraffe primary afferent axon from toe ...
... in the human brain: 100 billion Average number of neurons in an octopus brain: 300 billion Rate of neuron growth during development of a fetus (in the womb): 250,000 neurons/minute Diameter of a neuron: 4 to 100 microns Longest axon of a neuron: around 15 feet (Giraffe primary afferent axon from toe ...
Chapter 39
... Neurons and glial cells are the cells of the nervous system A. Glial cells collectively make up the neuroglia and provide metabolic and structural support 1. Microglia are phagocytic and are involved in repairing injury or preventing further spread of infection 2. Astrocytes are phagocytic and may a ...
... Neurons and glial cells are the cells of the nervous system A. Glial cells collectively make up the neuroglia and provide metabolic and structural support 1. Microglia are phagocytic and are involved in repairing injury or preventing further spread of infection 2. Astrocytes are phagocytic and may a ...
Presentation Package - faculty.coe.unt.edu
... Neuromuscular Junctions • Neurons communicate with muscle cells at neuromuscular junctions, which function much like a neural synapse. • The refractory period is the time it takes the muscle fiber to repolarize before the fiber can respond to another stimulus. • Acetylcholine and epinephrine are the ...
... Neuromuscular Junctions • Neurons communicate with muscle cells at neuromuscular junctions, which function much like a neural synapse. • The refractory period is the time it takes the muscle fiber to repolarize before the fiber can respond to another stimulus. • Acetylcholine and epinephrine are the ...
Central Nervous System
... • Meningeal layer invaginates into fissures to form septa which anchor brain in ...
... • Meningeal layer invaginates into fissures to form septa which anchor brain in ...
Thinking, Learning and Intelligence: The Brain Imagine a 500 pound
... would cause us to drink instead of yell? To solve these problems, we need many nerve cells that are separate but still able to alternate signals from one circuit to another. Fortunately we have enough of them to do this. The Neuron Neurons are the basic unit of the nervous system through which signa ...
... would cause us to drink instead of yell? To solve these problems, we need many nerve cells that are separate but still able to alternate signals from one circuit to another. Fortunately we have enough of them to do this. The Neuron Neurons are the basic unit of the nervous system through which signa ...
The Brain Summary Notes
... a sense of balance, another is involved in coordinating muscular movements while another part is involved in learning simple motor tasks. ...
... a sense of balance, another is involved in coordinating muscular movements while another part is involved in learning simple motor tasks. ...
lecture #6
... -inactivated by an enzyme acetylcholinesterase -blockage of the ACh receptors by antibodies = myasthenia gravis autoimmune disease that destroys these receptors and progressively destroys the NMJ -anticholinesterase drugs (inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase) prevent the breakdown of ACh and raise th ...
... -inactivated by an enzyme acetylcholinesterase -blockage of the ACh receptors by antibodies = myasthenia gravis autoimmune disease that destroys these receptors and progressively destroys the NMJ -anticholinesterase drugs (inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase) prevent the breakdown of ACh and raise th ...
Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of the Neurovascular Link
... a shared-tight molecular regulation between the ...
... a shared-tight molecular regulation between the ...
Untitled 2
... • Amitotic - neurons cannot be replace if destroyed, lose their ability to divide as they assume role of communicating links of the nervous system • High metabolic rate - require continuous abundant supplies of oxygen and glucose; cannot survive for a few minutes without oxygen Neuron cell body Sphe ...
... • Amitotic - neurons cannot be replace if destroyed, lose their ability to divide as they assume role of communicating links of the nervous system • High metabolic rate - require continuous abundant supplies of oxygen and glucose; cannot survive for a few minutes without oxygen Neuron cell body Sphe ...
CH 8 Nervous System - Belle Vernon Area School District
... C. are important in planning, organizing and coordinating motor movements. D. are linked with the thalamus and cerebral cortex. E. have all of these characteristics. ...
... C. are important in planning, organizing and coordinating motor movements. D. are linked with the thalamus and cerebral cortex. E. have all of these characteristics. ...
Note 11
... - Hormones are produced by ductless gland (known as endocrine gland) and secreted into the blood capillary (its secretion will increase when there is a specific stimulation) - Blood carries the hormones around the body - Specific target organ(s) take(s) up the specific hormones, other organs are NOT ...
... - Hormones are produced by ductless gland (known as endocrine gland) and secreted into the blood capillary (its secretion will increase when there is a specific stimulation) - Blood carries the hormones around the body - Specific target organ(s) take(s) up the specific hormones, other organs are NOT ...
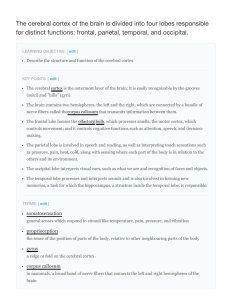
The cerebral cortex of the brain is divided into four lobes
... The occipital lobe is located at the back of the brain. It is primarily involved in vision: seeing, recognizing, and identifying the visual world. The temporal lobe is located at the base of the brain by the ears. It is primarily involved in processing and interpreting sounds. It also contains the h ...
... The occipital lobe is located at the back of the brain. It is primarily involved in vision: seeing, recognizing, and identifying the visual world. The temporal lobe is located at the base of the brain by the ears. It is primarily involved in processing and interpreting sounds. It also contains the h ...
The Mechanical Senses: Vestibular and Somatosensation
... For this course, don’t worry about the different pathways to the brain for the different types of sensory neurons, although I will show the pain pathways. ...
... For this course, don’t worry about the different pathways to the brain for the different types of sensory neurons, although I will show the pain pathways. ...
Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses
... Figure 2.11 (a) Shapes of some glia cells. Oligodendrocytes produce myelin sheaths that insulate certain vertebrate axons in the central nervous system; Schwann cells have a similar function in the periphery. The oligodendrocyte is shown here forming a segment of myelin sheath for two axons; in fac ...
... Figure 2.11 (a) Shapes of some glia cells. Oligodendrocytes produce myelin sheaths that insulate certain vertebrate axons in the central nervous system; Schwann cells have a similar function in the periphery. The oligodendrocyte is shown here forming a segment of myelin sheath for two axons; in fac ...
Phylum Platyhelminthesnotesfilledin - Spring
... Phylum Platyhelminthes: Acoelomated Animals General Characteristics Bilateral symmetry: body can be divided along one plane of symmetry to yield 2 mirrored halves (anterior, posterior, dorsal, ventral, left and right) Has 1 digestive cavity Acoelomates: lack a coelom (body cavity) Exhibit ce ...
... Phylum Platyhelminthes: Acoelomated Animals General Characteristics Bilateral symmetry: body can be divided along one plane of symmetry to yield 2 mirrored halves (anterior, posterior, dorsal, ventral, left and right) Has 1 digestive cavity Acoelomates: lack a coelom (body cavity) Exhibit ce ...
TRUTH Read
... HINkING ABOUT PSYCHOLOGY 1. How do messages travel from one neuron to another? 2. Identify the systems that make up the peripheral nervous system. 3. Critical Thinking In what way do the parasympathetic and the sympathetic ner vous systems work together? ...
... HINkING ABOUT PSYCHOLOGY 1. How do messages travel from one neuron to another? 2. Identify the systems that make up the peripheral nervous system. 3. Critical Thinking In what way do the parasympathetic and the sympathetic ner vous systems work together? ...
Biology 12 Name: Nervous System Practice Exam Types of Neurons
... Types of Neurons and Reflex Arcs 1. Identify the parts of the following motor neuron: dendrites, cell body, nucleus, axon, myelin, node of Ranvier, axon bulb (terminal) and draw an arrow to show the direction of nerve impulse. ...
... Types of Neurons and Reflex Arcs 1. Identify the parts of the following motor neuron: dendrites, cell body, nucleus, axon, myelin, node of Ranvier, axon bulb (terminal) and draw an arrow to show the direction of nerve impulse. ...
different types of dementia
... brain are gradually destroyed, and nerve cells die. Areas in the brain become smaller, and cavities within the brain containing fluid become enlarged. Vascular dementia is another type of dementia that is caused by a series of small strokes. These “mini-strokes” often go unnoticed but cause damage t ...
... brain are gradually destroyed, and nerve cells die. Areas in the brain become smaller, and cavities within the brain containing fluid become enlarged. Vascular dementia is another type of dementia that is caused by a series of small strokes. These “mini-strokes” often go unnoticed but cause damage t ...
reflexes_lesson
... Ask them how do these muscle know to move; what tells them? Hopefully they will say spinal cord and brain How does the brain and spinal chord tell these muscles what to do? Nerve cells!!! (like playing telephone) Today we are going to talk about the nervous system and how it relates to sports. What ...
... Ask them how do these muscle know to move; what tells them? Hopefully they will say spinal cord and brain How does the brain and spinal chord tell these muscles what to do? Nerve cells!!! (like playing telephone) Today we are going to talk about the nervous system and how it relates to sports. What ...
BIOL 218 F 2012 MTX 4 Q NS 121121
... Functions of the peripheral nervous system include A) providing sensory information to the CNS only. B) making higher order decisions to interpret sensory inputs. C) carrying motor commands to the peripheral tissues and systems only. D) carrying information up and down the spinal cord. E) providing ...
... Functions of the peripheral nervous system include A) providing sensory information to the CNS only. B) making higher order decisions to interpret sensory inputs. C) carrying motor commands to the peripheral tissues and systems only. D) carrying information up and down the spinal cord. E) providing ...
Document
... o They also help coordinate large-scale body movements, such as running or climbing. ...
... o They also help coordinate large-scale body movements, such as running or climbing. ...
Sensory organs and perception
... The retina, lining the back of the eye, consists of ten layers of cells containing photoreceptors (rods and cones) that convert the light waves to neural impulses through a photochemical reaction. Aside from the differences in shape suggested by their names, rod and cone cells contain different ligh ...
... The retina, lining the back of the eye, consists of ten layers of cells containing photoreceptors (rods and cones) that convert the light waves to neural impulses through a photochemical reaction. Aside from the differences in shape suggested by their names, rod and cone cells contain different ligh ...
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... the success of massage in pain relief). These sensations are lost with amputations and thus their inhibitory effect. ...
... the success of massage in pain relief). These sensations are lost with amputations and thus their inhibitory effect. ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.