The Basal Ganglia
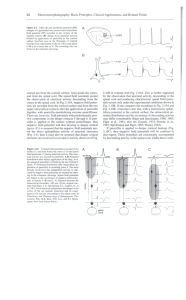
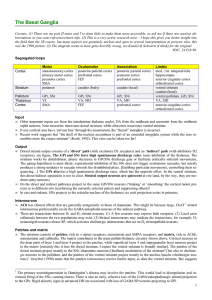
... • The “gain control” that the striatum seems to perform might provide fluctuating activity levels to scale movements in time and space… or as part of a program-selection mechanism. In this context, the competitive queuing models (Houghton & Hartley, 1995) seem particularly relevant. • The motor loop ...
... • The “gain control” that the striatum seems to perform might provide fluctuating activity levels to scale movements in time and space… or as part of a program-selection mechanism. In this context, the competitive queuing models (Houghton & Hartley, 1995) seem particularly relevant. • The motor loop ...
completion
... Neurotransmitter level is controlled by chemicals in presynaptic terminals known as ______________________ (MAO) and transporters that recycle them for further use. ANS: monoamine oxidases ...
... Neurotransmitter level is controlled by chemicals in presynaptic terminals known as ______________________ (MAO) and transporters that recycle them for further use. ANS: monoamine oxidases ...
Receptores Monoaminérgicos en Corteza Prefrontal: Mecanismo de Acción de Fármacos Antipsicóticos
... antagonist phencyclidine (PCP) on PFC function to understand the cellular and network elements involved in its schizomimeitc actions. PCP induces a marked disruption of the activity of the PFC in the rat, increasing and decreasing the activity of 45% and 33% of the pyramidal neurons recorded, respec ...
... antagonist phencyclidine (PCP) on PFC function to understand the cellular and network elements involved in its schizomimeitc actions. PCP induces a marked disruption of the activity of the PFC in the rat, increasing and decreasing the activity of 45% and 33% of the pyramidal neurons recorded, respec ...
Pathophysiology of Paresthesia
... layers (laminae I–II) of the dorsal horn; wide dynamic range neurons lie in deeper laminae (most of lamina V neurons are wide dynamic neurons). Nociceptive-specific neurons respond selectively to noxious stimuli conveyed by Aδ- and C-fibers. Wide dynamic range neurons excited both by noxious and non ...
... layers (laminae I–II) of the dorsal horn; wide dynamic range neurons lie in deeper laminae (most of lamina V neurons are wide dynamic neurons). Nociceptive-specific neurons respond selectively to noxious stimuli conveyed by Aδ- and C-fibers. Wide dynamic range neurons excited both by noxious and non ...
The Nervous System
... 5. Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane 6. The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration This action requires ATP ...
... 5. Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane 6. The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration This action requires ATP ...
glial versus neuronal uptake of glutamate
... high-affinity uptake into pre-synaptic neurones and glia, a model well established for monoaminergic systems. GABA, for instance, is taken up at high affinity by glia and GABAergic neurones, and the two uptake systems have been distinguished by the use of competitive analogues in vivo and in vitro. ...
... high-affinity uptake into pre-synaptic neurones and glia, a model well established for monoaminergic systems. GABA, for instance, is taken up at high affinity by glia and GABAergic neurones, and the two uptake systems have been distinguished by the use of competitive analogues in vivo and in vitro. ...
Building Production Systems with Realistic Spiking Neurons Terrence C. Stewart ()
... brain. Furthermore, if a neural level of description is desired, then it is unclear as to whether we should require a molecular, atomic, or quantum level of description. Below a certain level, there may be no advantage to going deeper, as the lower level implementation does not significantly affect ...
... brain. Furthermore, if a neural level of description is desired, then it is unclear as to whether we should require a molecular, atomic, or quantum level of description. Below a certain level, there may be no advantage to going deeper, as the lower level implementation does not significantly affect ...
LESSON 5.2 WORKBOOK How do drugs alter synaptic transmis-
... that even trained mental health professionals cannot distinguish between them unless he or she knows about the person’s history of drug abuse. These effects disappear once people stop taking the drug. As mentioned previously, cocaine use increases alertness, energy, motor activity and feelings of we ...
... that even trained mental health professionals cannot distinguish between them unless he or she knows about the person’s history of drug abuse. These effects disappear once people stop taking the drug. As mentioned previously, cocaine use increases alertness, energy, motor activity and feelings of we ...
November 2000 Volume 3 Number Supp pp 1184
... cognitive aspects of working memory tasks. Models have been developed on different levels of abstraction, including highly abstract connectionist models, which neglect the temporal and spatial dynamics of neurons and synapses, firing rate models incorporating some biophysically meaningful time const ...
... cognitive aspects of working memory tasks. Models have been developed on different levels of abstraction, including highly abstract connectionist models, which neglect the temporal and spatial dynamics of neurons and synapses, firing rate models incorporating some biophysically meaningful time const ...
Electroencephalography: Basic Principles, Clinical Applications, and
... field potentials (7) during interictal activity. The interictal activity was elicited by penicillin. A,B: Potential distribution after surface application of the drug. In A, the spread of penicillin is limited by the use of penicillinase. C: Potential distribution after intracortical application of ...
... field potentials (7) during interictal activity. The interictal activity was elicited by penicillin. A,B: Potential distribution after surface application of the drug. In A, the spread of penicillin is limited by the use of penicillinase. C: Potential distribution after intracortical application of ...
Motor functions
... patellar,etc) are diminished or absenthyporeflexia or areflexia. • Superficial reflexes are normal. The term superficial reflexes is given to muscle responses evoked by cutaneous stimuli Those in common clinical use include the abdomunal and cremasteric reflexes. ...
... patellar,etc) are diminished or absenthyporeflexia or areflexia. • Superficial reflexes are normal. The term superficial reflexes is given to muscle responses evoked by cutaneous stimuli Those in common clinical use include the abdomunal and cremasteric reflexes. ...
Plasticity in gray and white: neuroimaging changes in brain structure
... they are interconnected to distant neuronal populations; and on properties of non-neuronal cells, such as glia. Neuroimaging evidence, reviewed below, shows both differences in structural features among individuals and the relevant functions that these structures subserve, and changes in structural ...
... they are interconnected to distant neuronal populations; and on properties of non-neuronal cells, such as glia. Neuroimaging evidence, reviewed below, shows both differences in structural features among individuals and the relevant functions that these structures subserve, and changes in structural ...
Chapters 9 and 10 Lipids and Membranes Lipids
... These are channels in the membrane that permit the rapid movement of specific molecules across the membrane. The tertiary and quaternary structure of integral membrane proteins create an aqueous hole in the membrane. The movement of solute through a channel is always from higher to lower concentrati ...
... These are channels in the membrane that permit the rapid movement of specific molecules across the membrane. The tertiary and quaternary structure of integral membrane proteins create an aqueous hole in the membrane. The movement of solute through a channel is always from higher to lower concentrati ...
THE SPINAL CORD Development of the Spinal Nerves (Fig.2) The
... of the muscle and tendon. Each tendon organ is related to a single group Ib sensory axon (the Ib axons are slightly smaller than the Ia axons that innervate the muscle spindles). In contrast to the parallel arrangement of extrafusal muscle fibers and spindles, Golgi tendon organs are in series with ...
... of the muscle and tendon. Each tendon organ is related to a single group Ib sensory axon (the Ib axons are slightly smaller than the Ia axons that innervate the muscle spindles). In contrast to the parallel arrangement of extrafusal muscle fibers and spindles, Golgi tendon organs are in series with ...
Cell-Type Specific Properties of Pyramidal
... To understand sensory representation in cortex, it is crucial to identify its constituent cellular components based on cell-type--specific criteria. With the identification of cell types, an important question can be addressed: to what degree does the cellular properties of neurons depend on cortica ...
... To understand sensory representation in cortex, it is crucial to identify its constituent cellular components based on cell-type--specific criteria. With the identification of cell types, an important question can be addressed: to what degree does the cellular properties of neurons depend on cortica ...
Development of the Spinal Nerves
... of the muscle and tendon. Each tendon organ is related to a single group Ib sensory axon (the Ib axons are slightly smaller than the Ia axons that innervate the muscle spindles). In contrast to the parallel arrangement of extrafusal muscle fibers and spindles, Golgi tendon organs are in series with ...
... of the muscle and tendon. Each tendon organ is related to a single group Ib sensory axon (the Ib axons are slightly smaller than the Ia axons that innervate the muscle spindles). In contrast to the parallel arrangement of extrafusal muscle fibers and spindles, Golgi tendon organs are in series with ...
Raven Ch
... The effects on the postsynaptic cell would be somewhat similar if TEA were applied to the presynaptic cell. The presynaptic cell would depolarize and would continue to release neurotransmitter until it had exhausted its store of synaptic vesicles. As a result, the postsynaptic cell would be bombarde ...
... The effects on the postsynaptic cell would be somewhat similar if TEA were applied to the presynaptic cell. The presynaptic cell would depolarize and would continue to release neurotransmitter until it had exhausted its store of synaptic vesicles. As a result, the postsynaptic cell would be bombarde ...
full text pdf
... more Why do neurons build synapses or neurites just to degrade them again later on during development? For one, neurons (many billions in the mammalian brain) must make many highly specific synaptic connections (often thousands for a mammalian neuron in the brain). Accordingly, many specificity path ...
... more Why do neurons build synapses or neurites just to degrade them again later on during development? For one, neurons (many billions in the mammalian brain) must make many highly specific synaptic connections (often thousands for a mammalian neuron in the brain). Accordingly, many specificity path ...
Copyright 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
... All rights reserved. Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted in section 117 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without express permission of the copyright owner is unlawful. Request for further information should be addressed to the Permission Department, John Wiley & Son ...
... All rights reserved. Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted in section 117 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without express permission of the copyright owner is unlawful. Request for further information should be addressed to the Permission Department, John Wiley & Son ...
REFLEX ARCS - Anatomy.tv
... A tendon reflex is initiated by a substantial amount of tension in a muscle tendon, and results in the reflex relaxation of the skeletal muscle attached to that tendon. It is less sensitive than the stretch reflex, but produces an opposite effect. 1. Golgi tendon organ The reflex begins when sensory ...
... A tendon reflex is initiated by a substantial amount of tension in a muscle tendon, and results in the reflex relaxation of the skeletal muscle attached to that tendon. It is less sensitive than the stretch reflex, but produces an opposite effect. 1. Golgi tendon organ The reflex begins when sensory ...
CHAPTER 3 Neuroscience and Behavior
... The electrical stimulation blocks abnormal nerve signals that produce the symptoms of Parkinson’s. Because DBS requires patients to be awake during the operation, Farkas was well aware of the procedure: “The surgeons numbed my skull and began drilling. When the anesthesia wore off, they were already ...
... The electrical stimulation blocks abnormal nerve signals that produce the symptoms of Parkinson’s. Because DBS requires patients to be awake during the operation, Farkas was well aware of the procedure: “The surgeons numbed my skull and began drilling. When the anesthesia wore off, they were already ...
doc Practice midterm
... c. Receive direct connections from axons in the right somatosensory of the cortex d. Project to the left nucleus VPL of the thalamus 3. Complete distruction of the left half of the spinak cird at the highest Lumbar level (L1) will interfere with which of the following : a. Stretch relexes in the ank ...
... c. Receive direct connections from axons in the right somatosensory of the cortex d. Project to the left nucleus VPL of the thalamus 3. Complete distruction of the left half of the spinak cird at the highest Lumbar level (L1) will interfere with which of the following : a. Stretch relexes in the ank ...
Answers to WHAT DID YOU LEARN questions
... pathways are: the spinal nerve pathway, the postganglionic sympathetic pathway, the splanchnic nerve pathway, and the adrenal medulla pathway. In the spinal nerve pathway, the preganglionic axon synapses in the sympathetic trunk, and the postganglionic axon leaves the trunk via a gray ramus communic ...
... pathways are: the spinal nerve pathway, the postganglionic sympathetic pathway, the splanchnic nerve pathway, and the adrenal medulla pathway. In the spinal nerve pathway, the preganglionic axon synapses in the sympathetic trunk, and the postganglionic axon leaves the trunk via a gray ramus communic ...
Olfaction
... sensory receptor cells: They are not mediated by any protective barrier and make direct contact with the brain § Contrast with visual receptors that are protected by cornea, hearing receptors protected by eardrum, taste buds are buried in papillae § Therefore, many drugs can be inhaled § OSN a ...
... sensory receptor cells: They are not mediated by any protective barrier and make direct contact with the brain § Contrast with visual receptors that are protected by cornea, hearing receptors protected by eardrum, taste buds are buried in papillae § Therefore, many drugs can be inhaled § OSN a ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.