Chapter 11: Nervous System
... Axodendritic – synapses between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another Axosomatic – synapses between the axon of one neuron and the soma of another Other types of synapses include: Axoaxonic (axon to axon) Dendrodendritic (dendrite to dendrite) Dendrosomatic (dendrites to som ...
... Axodendritic – synapses between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another Axosomatic – synapses between the axon of one neuron and the soma of another Other types of synapses include: Axoaxonic (axon to axon) Dendrodendritic (dendrite to dendrite) Dendrosomatic (dendrites to som ...
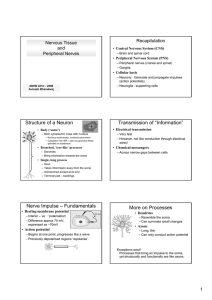
Structure of a Neuron Transmission of “Information” Nerve Impulse
... – Can summate small changes ...
... – Can summate small changes ...
Neural Tissue
... – Action potentials allow communication over both short and long distances within the body ...
... – Action potentials allow communication over both short and long distances within the body ...
SUMMARY
... new, tumor-specific targets for therapy have to be explored. The main focus of this thesis was therefore to identify new treatment targets, based on laboratory data, for potential translation into in vivo studies and, ultimately, clinical trials. Chapter 2 describes the role of AMPA-type glutamate r ...
... new, tumor-specific targets for therapy have to be explored. The main focus of this thesis was therefore to identify new treatment targets, based on laboratory data, for potential translation into in vivo studies and, ultimately, clinical trials. Chapter 2 describes the role of AMPA-type glutamate r ...
Lecture Outline ()
... • Local disturbances in membrane potential – occur when neuron is stimulated by chemicals, light, heat or mechanical disturbance – depolarization decreases potential across cell membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels • Na+ rushes in down concentration and electrical gradients • Na+ diffuses f ...
... • Local disturbances in membrane potential – occur when neuron is stimulated by chemicals, light, heat or mechanical disturbance – depolarization decreases potential across cell membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels • Na+ rushes in down concentration and electrical gradients • Na+ diffuses f ...
Electrical Stimulation of the Brain
... At rest, the inside of the neuron negative relative due to a higher concentration of positively charged ions outside the neuron. When stimulated, sodium channels open and positively charged sodium ions rush into the axon, depolarization a small region within the axon. The region of depolarization c ...
... At rest, the inside of the neuron negative relative due to a higher concentration of positively charged ions outside the neuron. When stimulated, sodium channels open and positively charged sodium ions rush into the axon, depolarization a small region within the axon. The region of depolarization c ...
Chapter 3
... neuron Dendrites receive information from adjacent neurons; process incoming chemicals and propel info to the nucleus The axon is the neural fiber that transmits info from the soma to the other end of the neuron; encased by myelin, a fatty substance that protects info stored inside the axon Th ...
... neuron Dendrites receive information from adjacent neurons; process incoming chemicals and propel info to the nucleus The axon is the neural fiber that transmits info from the soma to the other end of the neuron; encased by myelin, a fatty substance that protects info stored inside the axon Th ...
Synaptic transmission
... • Though there are two types( chemical and electrical), but, since almost all the synapses un CNS are chemical synapses, so these are discussed in detail. • In these, the first neuron secretes at its nerve ending synapse a chemical substance called a neurotransmitter (or often called simply transmit ...
... • Though there are two types( chemical and electrical), but, since almost all the synapses un CNS are chemical synapses, so these are discussed in detail. • In these, the first neuron secretes at its nerve ending synapse a chemical substance called a neurotransmitter (or often called simply transmit ...
1. Intro to Nervous System WEB
... hillock & travel along the axon to the axon terminal • Arrival of action potential causes the release of neurotransmitters across a synapse to the dentrites of the next neuron • Neurotransmitters can excite or inhibit the next neuron ...
... hillock & travel along the axon to the axon terminal • Arrival of action potential causes the release of neurotransmitters across a synapse to the dentrites of the next neuron • Neurotransmitters can excite or inhibit the next neuron ...
Nervous System
... *Production of both types of potentials depend upon the existence of a resting membrane potential (RMP) and the presence of certain types of ion channel. *The RMP is an electrical voltage across the membrane at rest. When Na+ enters from the outside to inside the cell, it causes depolarization. ...
... *Production of both types of potentials depend upon the existence of a resting membrane potential (RMP) and the presence of certain types of ion channel. *The RMP is an electrical voltage across the membrane at rest. When Na+ enters from the outside to inside the cell, it causes depolarization. ...
I. Functions and Divisions of the Nervous System A. The nervous
... 2. The neuron cell body, also called the perikaryon or soma, is the major biosynthetic center containing the usual organelles except for centrioles. 3. Neurons have armlike processes that extend from the cell body. a. Dendrites are cell processes that are the receptive regions of the cell and provid ...
... 2. The neuron cell body, also called the perikaryon or soma, is the major biosynthetic center containing the usual organelles except for centrioles. 3. Neurons have armlike processes that extend from the cell body. a. Dendrites are cell processes that are the receptive regions of the cell and provid ...
Chapter 14 - The Nervous System: Organization
... • Axon -conducts impulses away from the cell body • Axon Terminals - Neurotransmitters are manufactured in the cell body but released from axon terminals. The neurotransmitters stimulate other neurons. ...
... • Axon -conducts impulses away from the cell body • Axon Terminals - Neurotransmitters are manufactured in the cell body but released from axon terminals. The neurotransmitters stimulate other neurons. ...
Lecture nerve
... • Saltatory conduction -depolarization happens only at Nodes of Ranvier - areas along the axon that are unmyelinated and where there is a high density of voltage-gated ion channels -action potential “jumps” from node to node ...
... • Saltatory conduction -depolarization happens only at Nodes of Ranvier - areas along the axon that are unmyelinated and where there is a high density of voltage-gated ion channels -action potential “jumps” from node to node ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
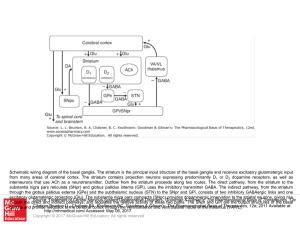
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Previously in Bio308
... Continuing from last time: Receptors 2 types of acetylcholine receptors: same ligand different response ...
... Continuing from last time: Receptors 2 types of acetylcholine receptors: same ligand different response ...
Neurons - World of Teaching
... abundance of + charges compared to inside. The inside of the membrane is negative compared to the outside. This is helped by the (-) proteins etc. The “sodium-potassium” pump pulls 2 K+ ions in for 3 Na+ ions sent out. This further creates a charge difference!! ...
... abundance of + charges compared to inside. The inside of the membrane is negative compared to the outside. This is helped by the (-) proteins etc. The “sodium-potassium” pump pulls 2 K+ ions in for 3 Na+ ions sent out. This further creates a charge difference!! ...
Sensory Systems
... The hair cells are vulnerable. Repeated exposure to loud noises can destroy them. Usually, the hair cells do not ________________, resulting in hearing loss. ...
... The hair cells are vulnerable. Repeated exposure to loud noises can destroy them. Usually, the hair cells do not ________________, resulting in hearing loss. ...
12-1 Chapter 12 Lecture Outline See PowerPoint Image Slides for
... • Local disturbances in membrane potential – occur when neuron is stimulated by chemicals, light, heat or mechanical disturbance – depolarization decreases potential across cell membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels • Na+ rushes in down concentration and electrical gradients • Na+ diffuses f ...
... • Local disturbances in membrane potential – occur when neuron is stimulated by chemicals, light, heat or mechanical disturbance – depolarization decreases potential across cell membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels • Na+ rushes in down concentration and electrical gradients • Na+ diffuses f ...
Chapter 12
... • Local disturbances in membrane potential – occur when neuron is stimulated by chemicals, light, heat or mechanical disturbance – depolarization decreases potential across cell membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels • Na+ rushes in down concentration and electrical gradients • Na+ diffuses f ...
... • Local disturbances in membrane potential – occur when neuron is stimulated by chemicals, light, heat or mechanical disturbance – depolarization decreases potential across cell membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels • Na+ rushes in down concentration and electrical gradients • Na+ diffuses f ...
Neurons: What They`re Made Of and How They
... images that are altered or edited after download could result in misinformation that may harm companion animals, aquatic life, or native species. ...
... images that are altered or edited after download could result in misinformation that may harm companion animals, aquatic life, or native species. ...
Levetiracetam in the Treatment of Epilepsy
... An abnormal synchronous and sustained activity (overexcitation) in a group of nerve cells This group of nerve cells = epileptogenic focus Abnormal interictal activity ...
... An abnormal synchronous and sustained activity (overexcitation) in a group of nerve cells This group of nerve cells = epileptogenic focus Abnormal interictal activity ...
Biology 3201 - s3.amazonaws.com
... abundance of + charges compared to inside. The inside of the membrane is negative compared to the outside. This is helped by the (-) proteins etc. The “sodium-potassium” pump pulls 2 K+ ions in for 3 Na+ ions sent out. This further creates a charge difference!! ...
... abundance of + charges compared to inside. The inside of the membrane is negative compared to the outside. This is helped by the (-) proteins etc. The “sodium-potassium” pump pulls 2 K+ ions in for 3 Na+ ions sent out. This further creates a charge difference!! ...
Lecture 08
... If the neurotranmitter interacts with receptor/ion channels that cause hyper-polarization of the postsynaptic membrane towwards more negative values – then we speak about inhibition. The major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain is γaminobutyric acid (GABA). COSC422 ...
... If the neurotranmitter interacts with receptor/ion channels that cause hyper-polarization of the postsynaptic membrane towwards more negative values – then we speak about inhibition. The major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain is γaminobutyric acid (GABA). COSC422 ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.