Chapter 34
... Neurotransmitter: type of signaling molecule that is synthesized in neurons only Plasma membrane has many gated channels for calcium ions In between action potentials, more calcium ions outside than inside (gate are shut) ...
... Neurotransmitter: type of signaling molecule that is synthesized in neurons only Plasma membrane has many gated channels for calcium ions In between action potentials, more calcium ions outside than inside (gate are shut) ...
Action potential - Solon City Schools
... – Pushing information through axon is based on process of positive and negative charges of electrical atoms (ions) • Potassium (K+), Sodium (Na+), Chloride (Cl-) ...
... – Pushing information through axon is based on process of positive and negative charges of electrical atoms (ions) • Potassium (K+), Sodium (Na+), Chloride (Cl-) ...
Neurons - WordPress.com
... well as nutrients) • Cover neurons with myelin • Clean up debris • “Housewives” • Regulate external environment (ions, etc.) • Most abundant glial cells are the ASTROCYTES ...
... well as nutrients) • Cover neurons with myelin • Clean up debris • “Housewives” • Regulate external environment (ions, etc.) • Most abundant glial cells are the ASTROCYTES ...
Synapses and neuronal signalling
... • Different types of information are conveyed using similar signals carried by distinct pathways • Gene expression creates diversity and change in neuronal function ...
... • Different types of information are conveyed using similar signals carried by distinct pathways • Gene expression creates diversity and change in neuronal function ...
Topic 5
... than those with chemical synapses. Typically the channel created by the grouping of proteins is called a connexon. However, as shown here, the term connexon can also be applied to the aggregate cluster of proteins. ...
... than those with chemical synapses. Typically the channel created by the grouping of proteins is called a connexon. However, as shown here, the term connexon can also be applied to the aggregate cluster of proteins. ...
Membrane potential
... • Voltage change causes voltage-gated channels in the membrane to open • As a result of ion flow through these channels, the inside of neuron briefly ...
... • Voltage change causes voltage-gated channels in the membrane to open • As a result of ion flow through these channels, the inside of neuron briefly ...
Chapter 10: Sensory Physiology
... Sensory Receptors Overview are transducers → convert stimuli into graded potential (receptor potential) are of various complexity ...
... Sensory Receptors Overview are transducers → convert stimuli into graded potential (receptor potential) are of various complexity ...
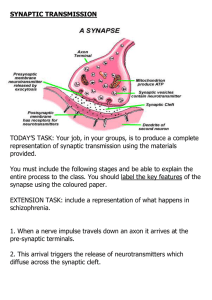
SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION
... serotonin. These can all influence the post-synaptic neuron to respond in an inhibitory way (decreases the firing of a cell) or an excitatory way (increases the firing of a cell). Schizophrenia, for example, is a mental disorder thought to be the result of excessive activity of the neurotransmitte ...
... serotonin. These can all influence the post-synaptic neuron to respond in an inhibitory way (decreases the firing of a cell) or an excitatory way (increases the firing of a cell). Schizophrenia, for example, is a mental disorder thought to be the result of excessive activity of the neurotransmitte ...
File
... The change in voltage A stimulus can trigger the voltage-activated channels. Voltage-activated channels are responsible for the sudden change of voltage. There is a specific voltage-activated channel for every ion that pass through the membrane of a neuron. But the potassium and sodium ions voltage ...
... The change in voltage A stimulus can trigger the voltage-activated channels. Voltage-activated channels are responsible for the sudden change of voltage. There is a specific voltage-activated channel for every ion that pass through the membrane of a neuron. But the potassium and sodium ions voltage ...
Brain`s Building Blocks
... Alcohol affects the brain by imitating a naturally occurring neurotransmitter, GABA GABA Neurons ◦ GABA neurons have chemical locks that can be opened by chemical keys in the form of the neurotransmitter GABA ...
... Alcohol affects the brain by imitating a naturally occurring neurotransmitter, GABA GABA Neurons ◦ GABA neurons have chemical locks that can be opened by chemical keys in the form of the neurotransmitter GABA ...
Dynamic Equilibrium Review 1. Describe the structure and function
... How does this important to a neuron? The outside of the cell is more positive, relative to the inside. This assists in ion exchange (Na+ in, K+ out) that is the process of neuron firing. 3. How is both passive and active transport part of the function of a neuron? Sodium will rush in once the ion ch ...
... How does this important to a neuron? The outside of the cell is more positive, relative to the inside. This assists in ion exchange (Na+ in, K+ out) that is the process of neuron firing. 3. How is both passive and active transport part of the function of a neuron? Sodium will rush in once the ion ch ...
The Neuron - Austin Community College
... Threshold Voltage – membrane is depolarized by ~ 15 mV stimulus (from -70 to -55mV) The AP is a brief reversal of membrane potential with a total amplitude of 100 mV (from -70mV to ...
... Threshold Voltage – membrane is depolarized by ~ 15 mV stimulus (from -70 to -55mV) The AP is a brief reversal of membrane potential with a total amplitude of 100 mV (from -70mV to ...
Receptor families2015-10-30 14:065.9 MB
... • Comprise of three subunits (γ), subunits possess GTPase activity • Receptors in this family respond to agonists – by promoting the binding of GTP to the G protein alpha ( α ) subunit. – GTP activates the G protein and allows it, in turn, to activate the effector protein. – The G protein remain ...
... • Comprise of three subunits (γ), subunits possess GTPase activity • Receptors in this family respond to agonists – by promoting the binding of GTP to the G protein alpha ( α ) subunit. – GTP activates the G protein and allows it, in turn, to activate the effector protein. – The G protein remain ...
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue
... neurotransmitter. 3. Postsynaptic neuron – neuron conducting impulses away from the synapse a. The end of the dendrite has a receptor membrane. b. The membrane bears neurotransmitter receptors . 4. Synaptic Cleft – space between the synaptic knob & the receptor membrane. 30 – 50 nm wide B. Synaptic ...
... neurotransmitter. 3. Postsynaptic neuron – neuron conducting impulses away from the synapse a. The end of the dendrite has a receptor membrane. b. The membrane bears neurotransmitter receptors . 4. Synaptic Cleft – space between the synaptic knob & the receptor membrane. 30 – 50 nm wide B. Synaptic ...
Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... Neurotransmitters: Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons. When released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron’s dendrites, thereby influencing whether that neuron will generate a neural impulse ...
... Neurotransmitters: Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons. When released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron’s dendrites, thereby influencing whether that neuron will generate a neural impulse ...
Neural Modeling
... • Cells that have the ability to transmit action potentials are called ‘excitable cells’. • The action potentials are initiated by inputs from the dendrites arriving at the axon hillock, where the axon meets the soma. • Then they travel down the axon to terminal branches which have synapses to the n ...
... • Cells that have the ability to transmit action potentials are called ‘excitable cells’. • The action potentials are initiated by inputs from the dendrites arriving at the axon hillock, where the axon meets the soma. • Then they travel down the axon to terminal branches which have synapses to the n ...
Peripheral nervous system
... ◦ Form myelin sheaths around nerve fibers ◦ MS (multiple sclerosis) attacks myelin sheaths, converts them to hard covers that can’t conduct electrical impulses slurred speech, loss of balance, impaired vision, etc ...
... ◦ Form myelin sheaths around nerve fibers ◦ MS (multiple sclerosis) attacks myelin sheaths, converts them to hard covers that can’t conduct electrical impulses slurred speech, loss of balance, impaired vision, etc ...
Final Review
... Underlying molecular mechanisms • LTP (in area CA1) depends on certain changes at glutamate synapses • LTP requires some sort of additive effect of highfrequency stimulation, •Activation of synapses and depolarization of the postsynaptic neuron must occur at the same time •Types of glutamate recept ...
... Underlying molecular mechanisms • LTP (in area CA1) depends on certain changes at glutamate synapses • LTP requires some sort of additive effect of highfrequency stimulation, •Activation of synapses and depolarization of the postsynaptic neuron must occur at the same time •Types of glutamate recept ...
Chapter 11: Nervous System
... Axodendritic – synapses between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another Axosomatic – synapses between the axon of one neuron and the soma of another Other types of synapses include: Axoaxonic (axon to axon) Dendrodendritic (dendrite to dendrite) Dendrosomatic (dendrites to som ...
... Axodendritic – synapses between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another Axosomatic – synapses between the axon of one neuron and the soma of another Other types of synapses include: Axoaxonic (axon to axon) Dendrodendritic (dendrite to dendrite) Dendrosomatic (dendrites to som ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.