The retinal toxicity of an antiepileptic drug blocking the GABA
... an anti-epileptic drug. Indeed, this drug blocks the GABA-transaminase and thus increases up to 5 fold the retinal GABA concentration. In patients, it was found to generate an irreversible constriction of the visual field. Despite this major secondary effect, the damaging consequences of seizures an ...
... an anti-epileptic drug. Indeed, this drug blocks the GABA-transaminase and thus increases up to 5 fold the retinal GABA concentration. In patients, it was found to generate an irreversible constriction of the visual field. Despite this major secondary effect, the damaging consequences of seizures an ...
Review Senses and Nervous System Test
... Review Senses and Nervous System Test *(This is only an outline there is much more you should look over) CH 8 SENSES 1. What are the functions of the parts of eye? 2. What is blind spot, photoreceptors, rods, cones? 3. Read p 258, 262 4. What is colorblindness, cataracts, pink eye, glaucoma 5. What ...
... Review Senses and Nervous System Test *(This is only an outline there is much more you should look over) CH 8 SENSES 1. What are the functions of the parts of eye? 2. What is blind spot, photoreceptors, rods, cones? 3. Read p 258, 262 4. What is colorblindness, cataracts, pink eye, glaucoma 5. What ...
Ling 8700: Lecture Notes 1 A Model of Neural Activation
... • dendrites: ‘roots’ near other neurons to receive chemical signals • an axon: a ‘trunk’ along which the neuron propagates electric potential • axon terminals: ‘branches’ near other neurons to send chemical signals • synapses: gaps betw. terminals and dendrites that permit thresholding • neurotransm ...
... • dendrites: ‘roots’ near other neurons to receive chemical signals • an axon: a ‘trunk’ along which the neuron propagates electric potential • axon terminals: ‘branches’ near other neurons to send chemical signals • synapses: gaps betw. terminals and dendrites that permit thresholding • neurotransm ...
Nervous System:
... Ion pumps in the cell membranes of neurons release three positively charged sodium ions, while taking in only two positively charged potassium ions which creates a negative charge inside the cell. The space inside the neuron now has a resting potential, which is a kind of membrane potential, because ...
... Ion pumps in the cell membranes of neurons release three positively charged sodium ions, while taking in only two positively charged potassium ions which creates a negative charge inside the cell. The space inside the neuron now has a resting potential, which is a kind of membrane potential, because ...
Neuroanatomy- anatomy of nerve cell (neuron)
... Terminal Buttons of axon (aka end buttons, terminal branches, synaptic knobs))- branched end of the axon that contains neurotransmitters ...
... Terminal Buttons of axon (aka end buttons, terminal branches, synaptic knobs))- branched end of the axon that contains neurotransmitters ...
Slide ()
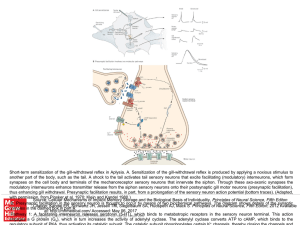
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
File
... synaptic cleft where they can bind with receptor sites on the postsynaptic ending to influence the electrical response in the postsynaptic neuron ...
... synaptic cleft where they can bind with receptor sites on the postsynaptic ending to influence the electrical response in the postsynaptic neuron ...
The Nervous System - Riverside Preparatory High School
... m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List the following in order: A. K+ channels open and K+ floods out of cell B. Membrane is polarized (resting potential) C. Neurotransmitters are released from vesicles into synaptic cleft D. Na+ channels open and Na+ ...
... m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List the following in order: A. K+ channels open and K+ floods out of cell B. Membrane is polarized (resting potential) C. Neurotransmitters are released from vesicles into synaptic cleft D. Na+ channels open and Na+ ...
Unit 3A: Neural Processing and the Endocrine System Introduction
... 3. Axons are long “arms” that send info away from the cell body to other neurons or body parts. 1. Axons are insulated by the myelin sheath. This insulation helps control the impulses and speeds their travel. 2. Messages travel along neurons at between 2 and 200 mph (depending on the type of neuron) ...
... 3. Axons are long “arms” that send info away from the cell body to other neurons or body parts. 1. Axons are insulated by the myelin sheath. This insulation helps control the impulses and speeds their travel. 2. Messages travel along neurons at between 2 and 200 mph (depending on the type of neuron) ...
01 - Fort Bend ISD
... 8. When a neuron is activated, a protein called the ____________________ uses energy to move sodium ions out of the cell and bring potassium ions into the cell. 9. A(n) _____________________ is an electrical impulse that results from a change in the distribution of charges across the cell membrane o ...
... 8. When a neuron is activated, a protein called the ____________________ uses energy to move sodium ions out of the cell and bring potassium ions into the cell. 9. A(n) _____________________ is an electrical impulse that results from a change in the distribution of charges across the cell membrane o ...
Unit 3A Notes
... 3. Axons are long “arms” that send info away from the cell body to other neurons or body parts. 1. Axons are insulated by the myelin sheath. This insulation helps control the impulses and speeds their travel. 2. Messages travel along neurons at between 2 and 200 mph (depending on the type of neuron) ...
... 3. Axons are long “arms” that send info away from the cell body to other neurons or body parts. 1. Axons are insulated by the myelin sheath. This insulation helps control the impulses and speeds their travel. 2. Messages travel along neurons at between 2 and 200 mph (depending on the type of neuron) ...
Document
... • Myelin sheath – speeds up transmission • Terminal Button – end of axon; secretes neurotransmitters • Neurotransmitters – chemical messengers • Synapse – point at which neurons interconnect ...
... • Myelin sheath – speeds up transmission • Terminal Button – end of axon; secretes neurotransmitters • Neurotransmitters – chemical messengers • Synapse – point at which neurons interconnect ...
Chapter 2 (The Brain) Study Guide 1. What is a neuron? What are
... Chapter 2 (The Brain) Study Guide 1. What is a neuron? What are the three basic types of neurons? What is the difference between a neuron with myelin compared to a neuron that is not myelinated? 2. What is stimulus threshold? All-or-none principle? (domino example in class) 3. What is a synapse? 4. ...
... Chapter 2 (The Brain) Study Guide 1. What is a neuron? What are the three basic types of neurons? What is the difference between a neuron with myelin compared to a neuron that is not myelinated? 2. What is stimulus threshold? All-or-none principle? (domino example in class) 3. What is a synapse? 4. ...
Neuron Functioning
... neurons. • There are many different neurotransmitters. – Examples: • Acetylcholine – activates muscles • Serotonin – involved in regulating moods • Dopamine – related to schizophrenia and Parkinson’s ...
... neurons. • There are many different neurotransmitters. – Examples: • Acetylcholine – activates muscles • Serotonin – involved in regulating moods • Dopamine – related to schizophrenia and Parkinson’s ...
Nervous System powerpoint new
... – On top of protection, the myelin sheath allows for faster conduction of impulses and greater power of regeneration ...
... – On top of protection, the myelin sheath allows for faster conduction of impulses and greater power of regeneration ...
Nervous System
... – Increase diameter of axon; reduces resistance to current flow; found primarily in invertebrates – Axon is myelinated; impulse jumps from node to node (Nodes of Ranvier – the only site of action potentials) = saltatory conduction – one action potential still serves as stimulus for the next one, but ...
... – Increase diameter of axon; reduces resistance to current flow; found primarily in invertebrates – Axon is myelinated; impulse jumps from node to node (Nodes of Ranvier – the only site of action potentials) = saltatory conduction – one action potential still serves as stimulus for the next one, but ...
3/26
... while the brain integrates the incoming signals to determine an appropriate response. CB 48.3 ...
... while the brain integrates the incoming signals to determine an appropriate response. CB 48.3 ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 7
... 10. A self-propagating wave of electrical negativity that travels along the surface of the neuron membrane is called a/an _______________________. 11. Indentations between the Schwann cells/myelin sheaths are called the _________ of ______________. 12. Nerve cells are also known as _________________ ...
... 10. A self-propagating wave of electrical negativity that travels along the surface of the neuron membrane is called a/an _______________________. 11. Indentations between the Schwann cells/myelin sheaths are called the _________ of ______________. 12. Nerve cells are also known as _________________ ...
Drug induced coma & Party drugs by Dr ML Tse
... • Brain activity = Interplay of neuron depolarization • Ion channel activities • Voltage-gated IC & Ligand-linked IC • Opening / Closing Production / Destruction control by receptor activites ...
... • Brain activity = Interplay of neuron depolarization • Ion channel activities • Voltage-gated IC & Ligand-linked IC • Opening / Closing Production / Destruction control by receptor activites ...
CHAPTER 4 STRUCTURE AND CELL BIOLOGY OF THE NEURON
... The cell body contains the nucleus and other organelles. It is the maintenance center of the neuron. It contains the cell's genetic material as well as the molecular machinery for synthesizing different chemical substances used for information transfer to other neurons, for maintenance and repair of ...
... The cell body contains the nucleus and other organelles. It is the maintenance center of the neuron. It contains the cell's genetic material as well as the molecular machinery for synthesizing different chemical substances used for information transfer to other neurons, for maintenance and repair of ...
Slide ()
... transcriptional modulators vorinostat (targeting histone deacetylase), azacytidine derivatives (targeting DNA methyltransferase), or retinoid receptor Source: PRINCIPLES OF CANCER TREATMENT, Harrison's Hematology and Oncology, 2e modulators all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) or bexarotene. Cytokine rece ...
... transcriptional modulators vorinostat (targeting histone deacetylase), azacytidine derivatives (targeting DNA methyltransferase), or retinoid receptor Source: PRINCIPLES OF CANCER TREATMENT, Harrison's Hematology and Oncology, 2e modulators all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) or bexarotene. Cytokine rece ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.