Aim: How does the nervous system function? Do Now
... Aim: How does the nervous system function? Do Now: What is a stimulus? How do your senses work? Homework: 594-602 #1-5 ...
... Aim: How does the nervous system function? Do Now: What is a stimulus? How do your senses work? Homework: 594-602 #1-5 ...
Nervous System
... Influx of Ca2+ causes synaptic vesicles with neurotransmitter to fuse with presynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter is released by exocytosis into synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter binds to receptors in postsynaptic membrane Permeability of postsynaptic membrane is altered initiating on impulse on the se ...
... Influx of Ca2+ causes synaptic vesicles with neurotransmitter to fuse with presynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter is released by exocytosis into synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter binds to receptors in postsynaptic membrane Permeability of postsynaptic membrane is altered initiating on impulse on the se ...
Autonomic nervous system
... Synapse These neurotransmitters open chemical locks or excite the receptors. The neurotransmitters can excite the next neuron or stop it from transmitting (inhibition). The neurotransmitters are like the valves in a water system that allow flow in only one direction. There are many different ...
... Synapse These neurotransmitters open chemical locks or excite the receptors. The neurotransmitters can excite the next neuron or stop it from transmitting (inhibition). The neurotransmitters are like the valves in a water system that allow flow in only one direction. There are many different ...
Afferent (Sensory) Division Part 1
... • PNS – all neural structures outside the brain and spinal cord • Includes sensory receptors, peripheral nerves, associated ganglia, and motor ...
... • PNS – all neural structures outside the brain and spinal cord • Includes sensory receptors, peripheral nerves, associated ganglia, and motor ...
AP Psychology – Unit 3 – Biological Bases of Behavior
... a. verbally report that a key was seen. b. only be able to write the word key using her left hand. c. only be able to draw a picture of a key using her left hand. d. do none of the above. 31. The branching extensions of nerve cells that receive incoming signals from sensory receptors or from other n ...
... a. verbally report that a key was seen. b. only be able to write the word key using her left hand. c. only be able to draw a picture of a key using her left hand. d. do none of the above. 31. The branching extensions of nerve cells that receive incoming signals from sensory receptors or from other n ...
1 - My Blog
... a. verbally report that a key was seen. b. only be able to write the word key using her left hand. c. only be able to draw a picture of a key using her left hand. d. do none of the above. 31. The branching extensions of nerve cells that receive incoming signals from sensory receptors or from other n ...
... a. verbally report that a key was seen. b. only be able to write the word key using her left hand. c. only be able to draw a picture of a key using her left hand. d. do none of the above. 31. The branching extensions of nerve cells that receive incoming signals from sensory receptors or from other n ...
Unit 3- Biological Psychology Study Guide
... Know the similarities and differences between twins in terms of biological psychology and social-cultural psychology. Discuss chromosomal abnormalities (common), molecular genetics, and the gene-environment interaction in terms of their relations to biological psychology. Also, discuss the evolution ...
... Know the similarities and differences between twins in terms of biological psychology and social-cultural psychology. Discuss chromosomal abnormalities (common), molecular genetics, and the gene-environment interaction in terms of their relations to biological psychology. Also, discuss the evolution ...
neurons
... The cell body contains the nucleus, which provides energy for the neuron to carry out its functions. The cell body also contains genetic material and other structures that are found in virtually all the cells in the body. Extending out from the cell body are many short, branching fibers, called dend ...
... The cell body contains the nucleus, which provides energy for the neuron to carry out its functions. The cell body also contains genetic material and other structures that are found in virtually all the cells in the body. Extending out from the cell body are many short, branching fibers, called dend ...
Clinical Day
... • Progressive neurodegenerative disease that attacks nerve cells in brain and spinal cord • As neurons die, body functions lost ...
... • Progressive neurodegenerative disease that attacks nerve cells in brain and spinal cord • As neurons die, body functions lost ...
The Nervous System
... 3. As the stapes vibrates it causes the oval window to move back & forth. 4. Now at the inner ear, the cochlea, which is filled with fluid and lined with tiny hair cells, vibrates the fluid along the hair cells. 5. The hair cells respond by generating nerve impulses in the auditory nerve and t ...
... 3. As the stapes vibrates it causes the oval window to move back & forth. 4. Now at the inner ear, the cochlea, which is filled with fluid and lined with tiny hair cells, vibrates the fluid along the hair cells. 5. The hair cells respond by generating nerve impulses in the auditory nerve and t ...
Nerve activates contraction - Silver Falls School District
... stimulus depolarizes the neuron’s membrane allows Na+ to flow inside membrane exchange of ions initiates an action potential in neuron ...
... stimulus depolarizes the neuron’s membrane allows Na+ to flow inside membrane exchange of ions initiates an action potential in neuron ...
1. Receptor cells
... and medulla oblongata. • Medulla oblongata: contains vital centers for respiration and cardiovascular functions. (4) Limbic System: located above the brain stem that includes: - The hypothalamus is involved in temperature regulation, appetite control, endocrine function…etc. • Hippocampus is involve ...
... and medulla oblongata. • Medulla oblongata: contains vital centers for respiration and cardiovascular functions. (4) Limbic System: located above the brain stem that includes: - The hypothalamus is involved in temperature regulation, appetite control, endocrine function…etc. • Hippocampus is involve ...
Human Biology Human Body Systems Nervous System
... Travels via electrical current. RESTING POTENTIAL no impulse being conducted ...
... Travels via electrical current. RESTING POTENTIAL no impulse being conducted ...
My Reaction Test Score = Neural Transmission
... flows down the axon until it reaches the terminal button. At the end (terminal button) of the axon the signal causes small sacks (vesicles) of chemicals to be released into the space between the end of the axon and the dendrite of the next neuron. These chemicals (neurotransmitters) travel across th ...
... flows down the axon until it reaches the terminal button. At the end (terminal button) of the axon the signal causes small sacks (vesicles) of chemicals to be released into the space between the end of the axon and the dendrite of the next neuron. These chemicals (neurotransmitters) travel across th ...
Ch. 10 Outline
... E. Brief period of hyperpolarization (-90) All-or-None Response A. If a neuron responds at all, it responds completely B. A nerve impulse is conducted whenever a stimulus of threshold intensity or above is applied to an axon C. All impulses carried on an axon are the same strength Refractory Period ...
... E. Brief period of hyperpolarization (-90) All-or-None Response A. If a neuron responds at all, it responds completely B. A nerve impulse is conducted whenever a stimulus of threshold intensity or above is applied to an axon C. All impulses carried on an axon are the same strength Refractory Period ...
Nervous System - Downey Unified School District
... • THEY TRAVEL DOWN THE AXON TO THE NERVE TERMINAL • OTHER NEUROTRANSMITTERS ARE SYNTHESIZED IN THE CYTOPLASM OF THE NERVE TERMINALS AND ARE STORED IN VESICLES • WHEN AN ACTION POTENTIAL PASSES ALONG THE MEMBRANE OF A SYNAPTIC KNOB IT INCREASES PERMEABILITY ALLOWING CALCIUM IONS IN BY OPENING CHANNEL ...
... • THEY TRAVEL DOWN THE AXON TO THE NERVE TERMINAL • OTHER NEUROTRANSMITTERS ARE SYNTHESIZED IN THE CYTOPLASM OF THE NERVE TERMINALS AND ARE STORED IN VESICLES • WHEN AN ACTION POTENTIAL PASSES ALONG THE MEMBRANE OF A SYNAPTIC KNOB IT INCREASES PERMEABILITY ALLOWING CALCIUM IONS IN BY OPENING CHANNEL ...
Chem*3560 Lecture 31: Ion selective channels
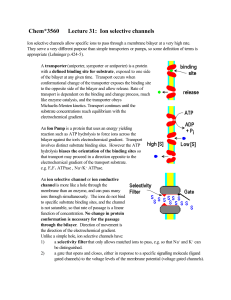
... of the bilayer at any given time. Transport occurs when conformational change of the transporter exposes the binding site to the opposite side of the bilayer and allow release. Rate of transport is dependent on the binding and change process, much like enzyme catalysis, and the transporter obeys Mic ...
... of the bilayer at any given time. Transport occurs when conformational change of the transporter exposes the binding site to the opposite side of the bilayer and allow release. Rate of transport is dependent on the binding and change process, much like enzyme catalysis, and the transporter obeys Mic ...
Chapter 28
... (2) why do they only flow in one direction? (a)Na+ channels are inactivated while K+ is diffusing out (b) If they can’t open, there can’t be an action potential iv) action potentials are all-or-none (1) they are always the same (2) there is no such thing as a strong or weak one (3) so how do we tell ...
... (2) why do they only flow in one direction? (a)Na+ channels are inactivated while K+ is diffusing out (b) If they can’t open, there can’t be an action potential iv) action potentials are all-or-none (1) they are always the same (2) there is no such thing as a strong or weak one (3) so how do we tell ...
Nervous System
... Transmission is carried out by molecules called neurotransmitters. These are stored in vesicles in the axon terminals. Impulse reaches terminal opens calcium channels Calcium enters the terminal vesicles move toward membrane for exocytosis neurotransmitters are released and diffuse through sy ...
... Transmission is carried out by molecules called neurotransmitters. These are stored in vesicles in the axon terminals. Impulse reaches terminal opens calcium channels Calcium enters the terminal vesicles move toward membrane for exocytosis neurotransmitters are released and diffuse through sy ...
No Slide Title
... After the Action Potential. • Neurons may have different thresholds of excitation but all obey the rule that once the threshold is reached, an action potential is triggered – this is called the ‘all-or-none rule’. • Following the action potential, the sodium gates remain closed for around 1ms and s ...
... After the Action Potential. • Neurons may have different thresholds of excitation but all obey the rule that once the threshold is reached, an action potential is triggered – this is called the ‘all-or-none rule’. • Following the action potential, the sodium gates remain closed for around 1ms and s ...
Chapter 17 Part A
... - mechanism of action potential passing between neurons - nerve impulse causes axomembrane sudden permeability to Ca++ ions that flood into the axon bulb - Ca++ ions cause microfilaments to pull synaptic vesicles to presynaptic (axon bulb) membrane - vesicles secrete neurotransmitter (exocytosis) in ...
... - mechanism of action potential passing between neurons - nerve impulse causes axomembrane sudden permeability to Ca++ ions that flood into the axon bulb - Ca++ ions cause microfilaments to pull synaptic vesicles to presynaptic (axon bulb) membrane - vesicles secrete neurotransmitter (exocytosis) in ...
too low levels
... A chemical message telling the next cell to fire or not to fire its own action potential More than 200 in our body all with different ...
... A chemical message telling the next cell to fire or not to fire its own action potential More than 200 in our body all with different ...
Chapter 12 Functional Organization of the Nervous System
... a. Epinerpherine is taken up repackaged in vessicles and reused or inactivated within the presynaptic terminal by monoamine oxidase (MAO). 3. The neurotransmitter diffuses out of the synaptic cleft. D. Receptor molecules in synapses 1. Receptors for neurotransmitters are specific. 2. A neurotransmi ...
... a. Epinerpherine is taken up repackaged in vessicles and reused or inactivated within the presynaptic terminal by monoamine oxidase (MAO). 3. The neurotransmitter diffuses out of the synaptic cleft. D. Receptor molecules in synapses 1. Receptors for neurotransmitters are specific. 2. A neurotransmi ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.